Politics
Who Came to America, and When?
The United States has a long-standing history of being a “nation of immigrants”, and today the country is home to roughly 46.6 million residents that were born outside of the country.
Here are three maps and data visualizations that give us some history of who came to America, and when it all happened.
200 Years of Immigration
To begin, this video from Metrocosm shows immigration to the U.S. starting from 1820. Each dot represents 10,000 people.
At first, immigration is coming almost exclusively from Europe.
But by around 1900, immigration from Russia, China, Canada, Turkey and Japan picks up – but then WWII devastates global mobility, and immigration to the U.S. grinds to a halt.
After WWII, it is the Cold War era, but the rate of arrivals slowly picks up again. Immigration eventually peaks between 1990-2000 after the fall of the Iron Curtain. Asian and Mexican immigration is also particularly strong around this time.
Another Perspective
Here’s another look – this time, it’s a data visualization from Insightful Interaction using data from the Yearbook of Immigration Statistics from 1820 to 2015.
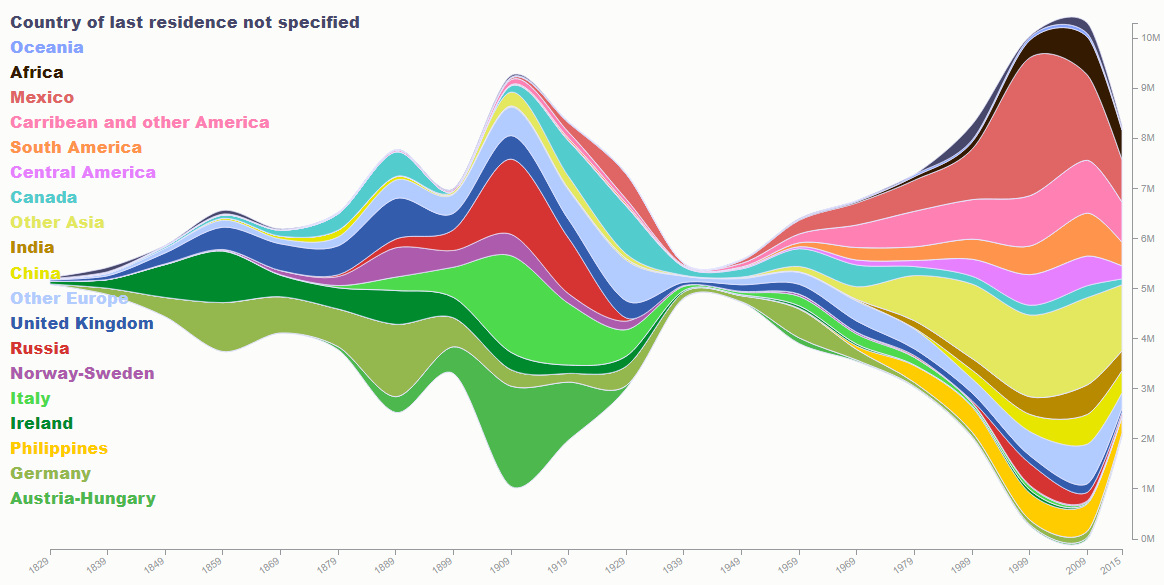
Similar peaks in immigration near 1900 and 2000 can be seen. The dip from WWII is even more pronounced when visualizing the data this way.
The boom in newcomers from Mexico is also evident in the 1990s, though it has tapered off significantly in recent years.
Made in America
Over time, more people start feeling like their roots are tied to America, rather than having ancestry from somewhere else.
This final visualization from Overflow Data that shows the percentage of people in each state that claim to have American ancestry:
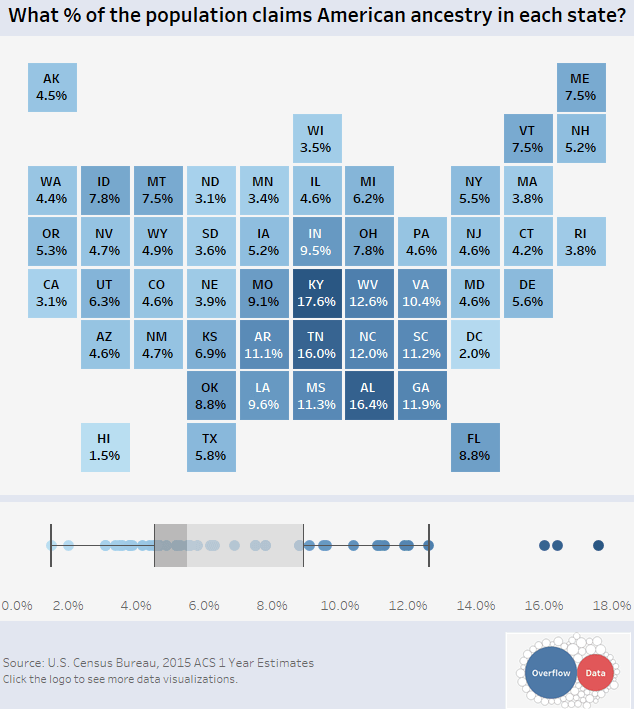
People in the country’s heartland and southern states are more likely to identify as having American ancestry, while folks along the coasts and northern states tend to see themselves as having ancestry from other parts of the world.
The highest rates of self-identification happen in Kentucky (17.6%), Tennessee (16.0%), and Alabama (16.4%). The lowest can be found in Hawaii (1.5%), D.C. (2.0%), and California (3.1%).
Economy
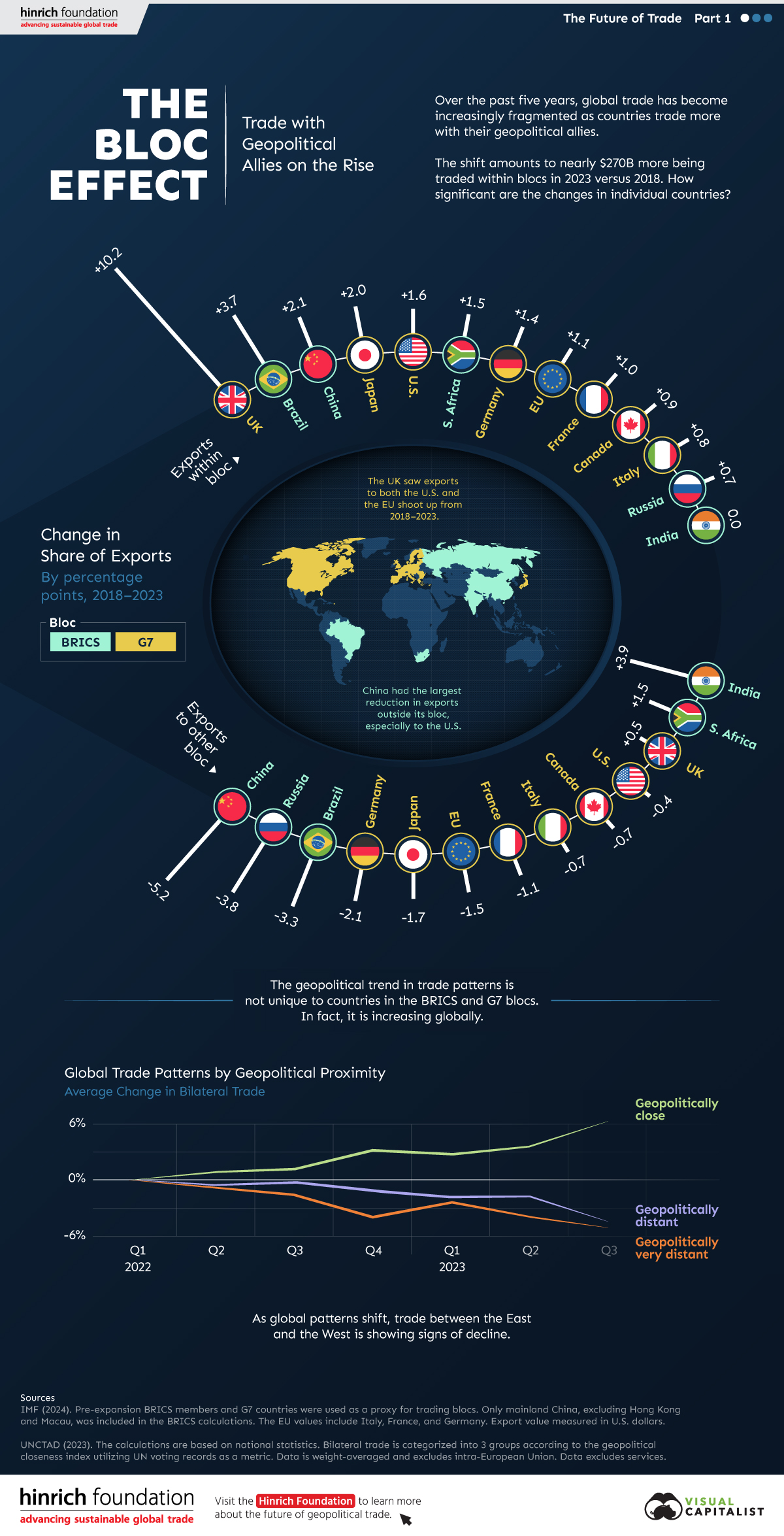
The Bloc Effect: International Trade with Geopolitical Allies on the Rise
Rising geopolitical tensions are shaping the future of international trade, but what is the effect on trading among G7 and BRICS countries?

The Bloc Effect: International Trade with Allies on the Rise
International trade has become increasingly fragmented over the last five years as countries have shifted to trading more with their geopolitical allies.
This graphic from The Hinrich Foundation, the first in a three-part series covering the future of trade, provides visual context to the growing divide in trade in G7 and pre-expansion BRICS countries, which are used as proxies for geopolitical blocs.
Trade Shifts in G7 and BRICS Countries
This analysis uses IMF data to examine differences in shares of exports within and between trading blocs from 2018 to 2023. For example, we looked at the percentage of China’s exports with other BRICS members as well as with G7 members to see how these proportions shifted in percentage points (pp) over time.
Countries traded nearly $270 billion more with allies in 2023 compared to 2018. This shift came at the expense of trade with rival blocs, which saw a decline of $314 billion.
Country Change in Exports Within Bloc (pp) Change in Exports With Other Bloc (pp)
🇮🇳 India 0.0 3.9
🇷🇺 Russia 0.7 -3.8
🇮🇹 Italy 0.8 -0.7
🇨🇦 Canada 0.9 -0.7
🇫🇷 France 1.0 -1.1
🇪🇺 EU 1.1 -1.5
🇩🇪 Germany 1.4 -2.1
🇿🇦 South Africa 1.5 1.5
🇺🇸 U.S. 1.6 -0.4
🇯🇵 Japan 2.0 -1.7
🇨🇳 China 2.1 -5.2
🇧🇷 Brazil 3.7 -3.3
🇬🇧 UK 10.2 0.5
All shifts reported are in percentage points. For example, the EU saw its share of exports to G7 countries rise from 74.3% in 2018 to 75.4% in 2023, which equates to a 1.1 percentage point increase.
The UK saw the largest uptick in trading with other countries within the G7 (+10.2 percentage points), namely the EU, as the post-Brexit trade slump to the region recovered.
Meanwhile, the U.S.-China trade dispute caused China’s share of exports to the G7 to fall by 5.2 percentage points from 2018 to 2023, the largest decline in our sample set. In fact, partly as a result of the conflict, the U.S. has by far the highest number of harmful tariffs in place.
The Russia-Ukraine War and ensuing sanctions by the West contributed to Russia’s share of exports to the G7 falling by 3.8 percentage points over the same timeframe.
India, South Africa, and the UK bucked the trend and continued to witness advances in exports with the opposing bloc.
Average Trade Shifts of G7 and BRICS Blocs
Though results varied significantly on a country-by-country basis, the broader trend towards favoring geopolitical allies in international trade is clear.
Bloc Change in Exports Within Bloc (pp) Change in Exports With Other Bloc (pp)
Average 2.1 -1.1
BRICS 1.6 -1.4
G7 incl. EU 2.4 -1.0
Overall, BRICS countries saw a larger shift away from exports with the other bloc, while for G7 countries the shift within their own bloc was more pronounced. This implies that though BRICS countries are trading less with the G7, they are relying more on trade partners outside their bloc to make up for the lost G7 share.
A Global Shift in International Trade and Geopolitical Proximity
The movement towards strengthening trade relations based on geopolitical proximity is a global trend.
The United Nations categorizes countries along a scale of geopolitical proximity based on UN voting records.
According to the organization’s analysis, international trade between geopolitically close countries rose from the first quarter of 2022 (when Russia first invaded Ukraine) to the third quarter of 2023 by over 6%. Conversely, trade with geopolitically distant countries declined.
The second piece in this series will explore China’s gradual move away from using the U.S. dollar in trade settlements.

Visit the Hinrich Foundation to learn more about the future of geopolitical trade

-

 Economy11 hours ago
Economy11 hours agoEconomic Growth Forecasts for G7 and BRICS Countries in 2024
The IMF has released its economic growth forecasts for 2024. How do the G7 and BRICS countries compare?
-

 United States1 week ago
United States1 week agoRanked: The Largest U.S. Corporations by Number of Employees
We visualized the top U.S. companies by employees, revealing the massive scale of retailers like Walmart, Target, and Home Depot.
-

 Economy2 weeks ago
Economy2 weeks agoWhere U.S. Inflation Hit the Hardest in March 2024
We visualized product categories that saw the highest % increase in price due to U.S. inflation as of March 2024.
-

 Economy4 weeks ago
Economy4 weeks agoG20 Inflation Rates: Feb 2024 vs COVID Peak
We visualize inflation rates across G20 countries as of Feb 2024, in the context of their COVID-19 pandemic peak.
-

 Economy1 month ago
Economy1 month agoMapped: Unemployment Claims by State
This visual heatmap of unemployment claims by state highlights New York, California, and Alaska leading the country by a wide margin.
-
 Economy2 months ago
Economy2 months agoConfidence in the Global Economy, by Country
Will the global economy be stronger in 2024 than in 2023?
-

 Markets1 week ago
Markets1 week agoU.S. Debt Interest Payments Reach $1 Trillion
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoRanked: The Most Valuable Housing Markets in America
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoWhich States Have the Highest Minimum Wage in America?
-

 AI2 weeks ago
AI2 weeks agoRanked: Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoRanked: The World’s Top Flight Routes, by Revenue
-

 Demographics2 weeks ago
Demographics2 weeks agoPopulation Projections: The World’s 6 Largest Countries in 2075
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoThe Top 10 States by Real GDP Growth in 2023
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoThe Smallest Gender Wage Gaps in OECD Countries