Technology
Africa’s Exploding Tech Startup Ecosystem
Africa’s Exploding Tech Startup Ecosystem
In terms of economic potential and growth, Africa has never been more important on the world stage.
Africa is home to the fastest growing cities, and more than half of the world’s population growth will take place on the continent over the coming decades. By 2050, cities like Lagos and Kinshasa will be global megacities, each holding well over 30 million inhabitants.
Africa is also at the start of a technological renaissance. It was recently reported by WeAreSocial that 7 of 10 of the world’s fastest growing internet populations are in Africa – the beginning of a trend that will likely re-shape entire economies as new companies leapfrog established technology, ideas, and infrastructure.
That said, much of that opportunity lies in the future. As of today, internet penetration is just 29% throughout Africa, meaning that the majority of growth and network effects are still to come.

A New Startup Ecosystem Emerges
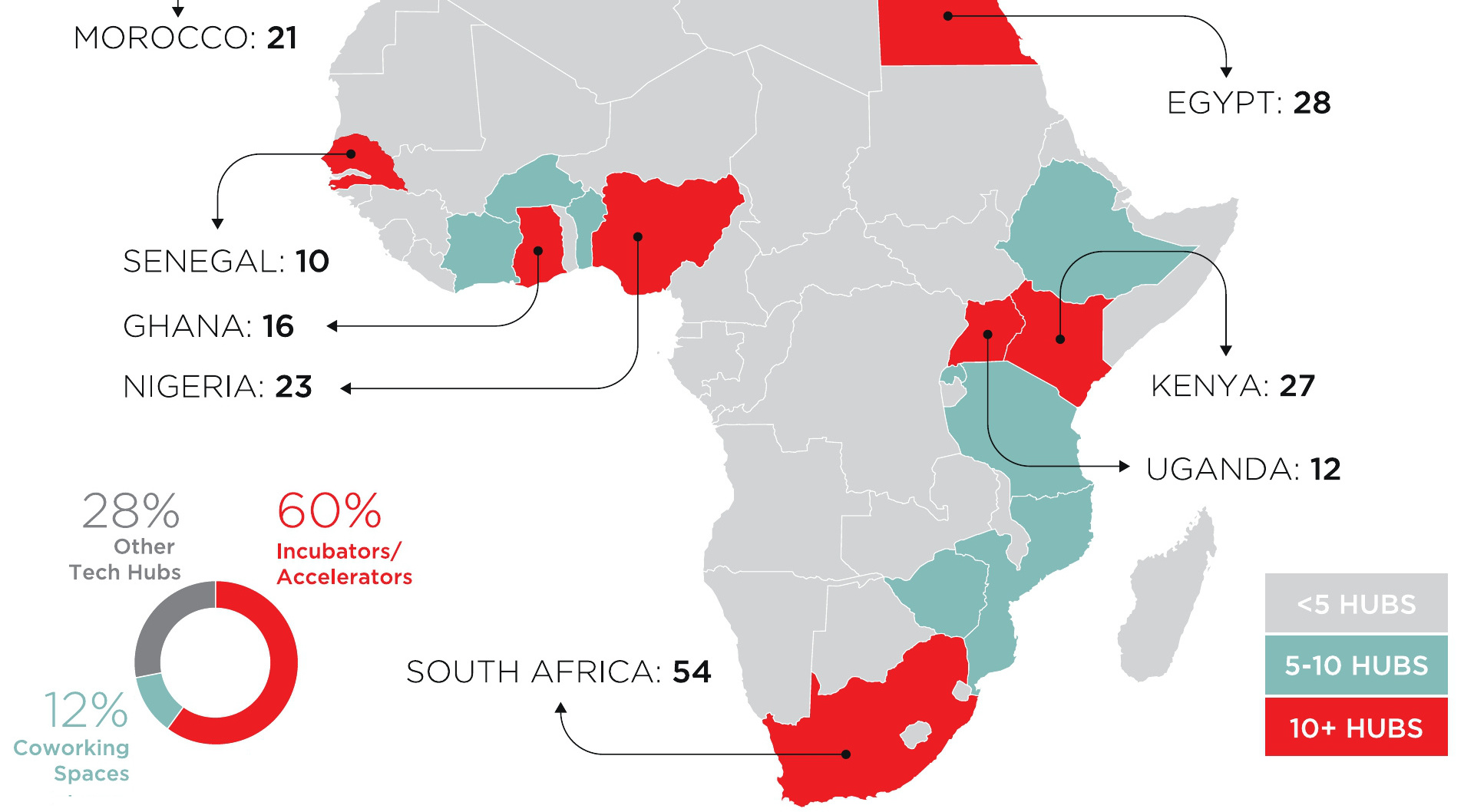
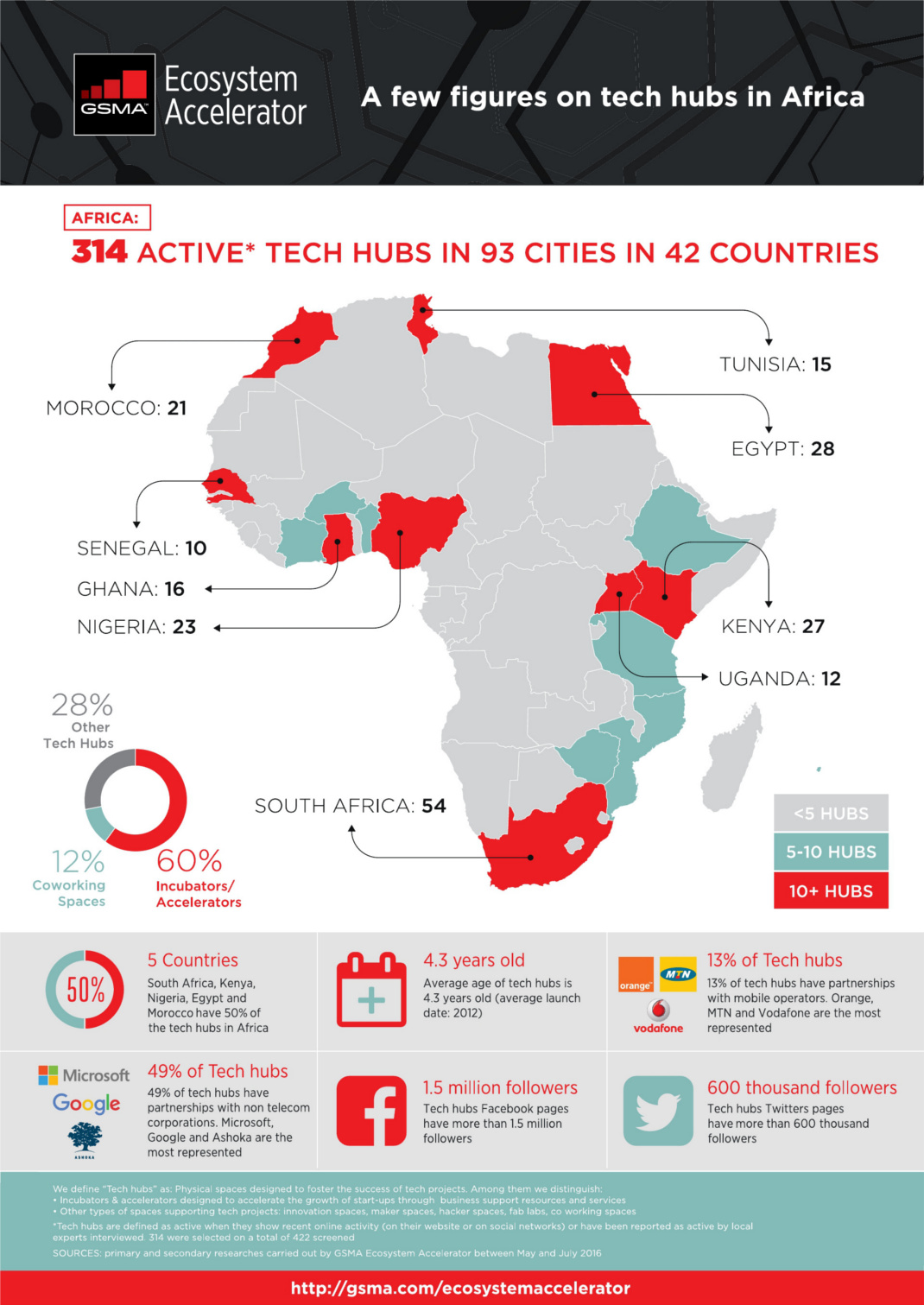
Today’s infographic from GSMA shows the 300+ hubs that have emerged in the African tech startup ecosystem. Many of these plan to take advantage of the aforementioned growth potential, including the 360 million smartphone owners expected on the continent by 2025.
Investors are recognizing the potential as well. Last year, it was estimated that African startups raised a record-breaking total of $366.8 million in investment.
Here’s that distribution sorted by country:
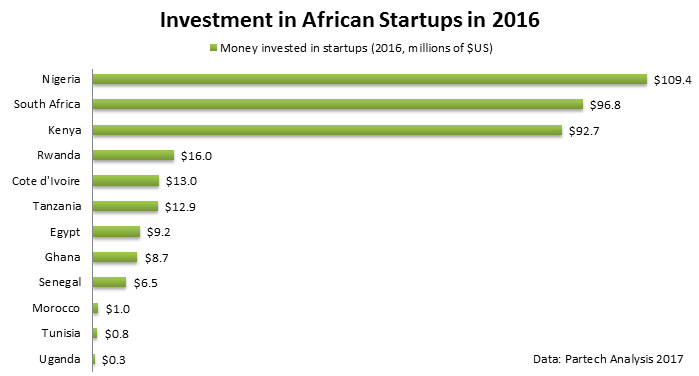
In what sectors did most of the action happen? According to a separate report by Disrupt Africa, the fintech sector received the most funding in 2016, but the agri-tech sector saw the biggest percentage growth as compared to the previous year.
Other sectors that got substantial amounts of attention include solar, health, e-commerce, entertainment, and e-learning.
Unique Opportunities
Every startup ecosystem is different, and hubs in Africa are no exception.
In particular, the continent has a unique wrinkle that also presents a huge opportunity: according to the African Development Bank, about 55% of sub-Saharan Africa’s economic activity is informal.
The [informal economy] is a massive commercial space without such services as business enterprise software, small business banking, affordable third-party logistics or internet access. Expect VC-backed startups to attempt scalable applications for nearly every corner of Africa’s informal economy.
– Jake Bright, World Economic Forum
Last year, Africa Internet Group became the first unicorn on the continent after receiving investments from Goldman Sachs, Rocket Internet, AXA Group, Orange, and others.
It’s also certain to be just one of many born on the African Savannah.
Technology
Visualizing AI Patents by Country
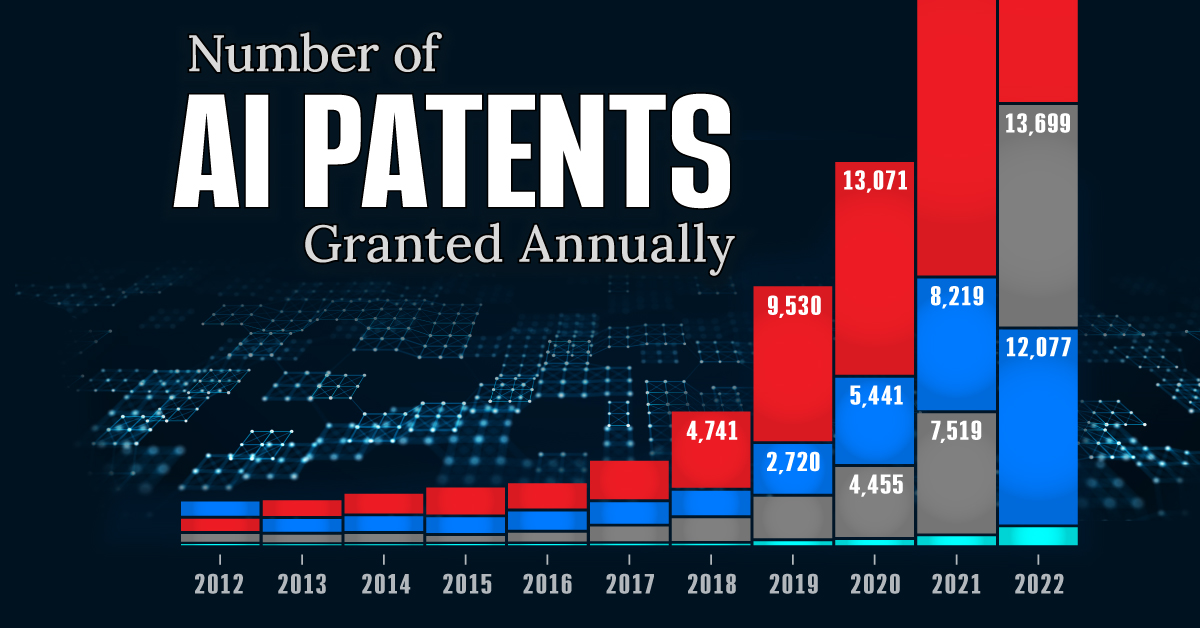
See which countries have been granted the most AI patents each year, from 2012 to 2022.
Visualizing AI Patents by Country
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on iOS or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
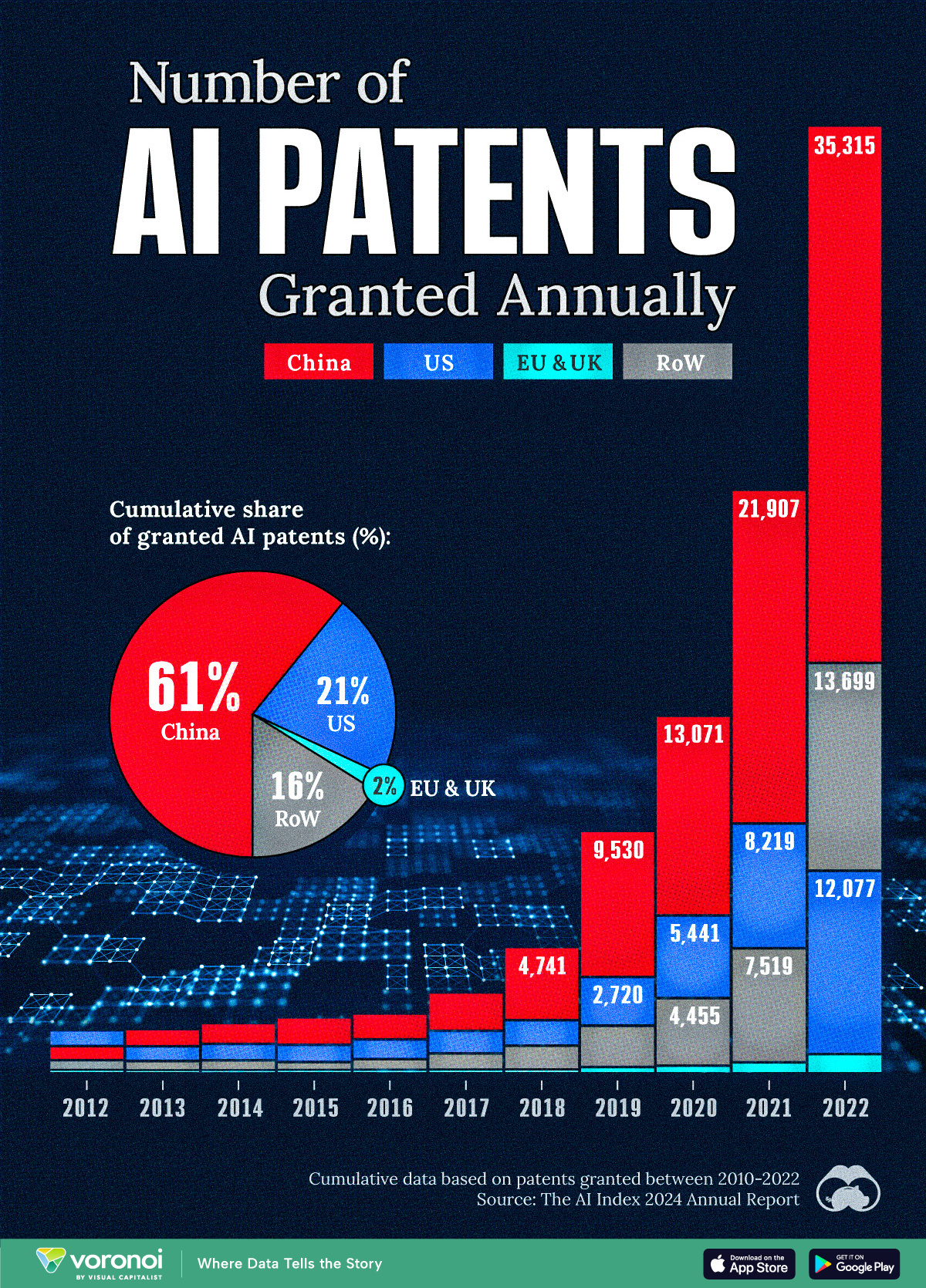
This infographic shows the number of AI-related patents granted each year from 2010 to 2022 (latest data available). These figures come from the Center for Security and Emerging Technology (CSET), accessed via Stanford University’s 2024 AI Index Report.
From this data, we can see that China first overtook the U.S. in 2013. Since then, the country has seen enormous growth in the number of AI patents granted each year.
| Year | China | EU and UK | U.S. | RoW | Global Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2010 | 307 | 137 | 984 | 571 | 1,999 |
| 2011 | 516 | 129 | 980 | 581 | 2,206 |
| 2012 | 926 | 112 | 950 | 660 | 2,648 |
| 2013 | 1,035 | 91 | 970 | 627 | 2,723 |
| 2014 | 1,278 | 97 | 1,078 | 667 | 3,120 |
| 2015 | 1,721 | 110 | 1,135 | 539 | 3,505 |
| 2016 | 1,621 | 128 | 1,298 | 714 | 3,761 |
| 2017 | 2,428 | 144 | 1,489 | 1,075 | 5,136 |
| 2018 | 4,741 | 155 | 1,674 | 1,574 | 8,144 |
| 2019 | 9,530 | 322 | 3,211 | 2,720 | 15,783 |
| 2020 | 13,071 | 406 | 5,441 | 4,455 | 23,373 |
| 2021 | 21,907 | 623 | 8,219 | 7,519 | 38,268 |
| 2022 | 35,315 | 1,173 | 12,077 | 13,699 | 62,264 |
In 2022, China was granted more patents than every other country combined.
While this suggests that the country is very active in researching the field of artificial intelligence, it doesn’t necessarily mean that China is the farthest in terms of capability.
Key Facts About AI Patents
According to CSET, AI patents relate to mathematical relationships and algorithms, which are considered abstract ideas under patent law. They can also have different meaning, depending on where they are filed.
In the U.S., AI patenting is concentrated amongst large companies including IBM, Microsoft, and Google. On the other hand, AI patenting in China is more distributed across government organizations, universities, and tech firms (e.g. Tencent).
In terms of focus area, China’s patents are typically related to computer vision, a field of AI that enables computers and systems to interpret visual data and inputs. Meanwhile America’s efforts are more evenly distributed across research fields.
Learn More About AI From Visual Capitalist
If you want to see more data visualizations on artificial intelligence, check out this graphic that shows which job departments will be impacted by AI the most.
-

 Markets1 week ago
Markets1 week agoU.S. Debt Interest Payments Reach $1 Trillion
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoRanked: The Most Valuable Housing Markets in America
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoWhich States Have the Highest Minimum Wage in America?
-

 AI2 weeks ago
AI2 weeks agoRanked: Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoRanked: The World’s Top Flight Routes, by Revenue
-

 Countries2 weeks ago
Countries2 weeks agoPopulation Projections: The World’s 6 Largest Countries in 2075
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoThe Top 10 States by Real GDP Growth in 2023
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoThe Smallest Gender Wage Gaps in OECD Countries