Investor Education
A Visual Guide to Stock Splits

A Visual Guide to Stock Splits
Imagine a shop window containing large pieces of cheese.
If the value of that cheese rises over time, the price may move beyond what the majority of people are willing to pay. This presents a problem as the store wants to continue selling cheese, and people still want to eat it.
The obvious solution is to divide the cheese into smaller pieces. That way, more people can once again afford to buy portions of it, and those who want more can simply buy more of the smaller pieces.
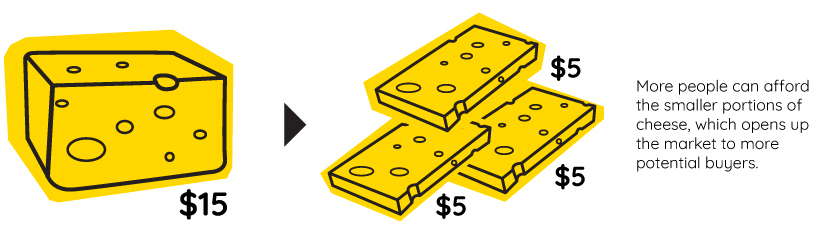
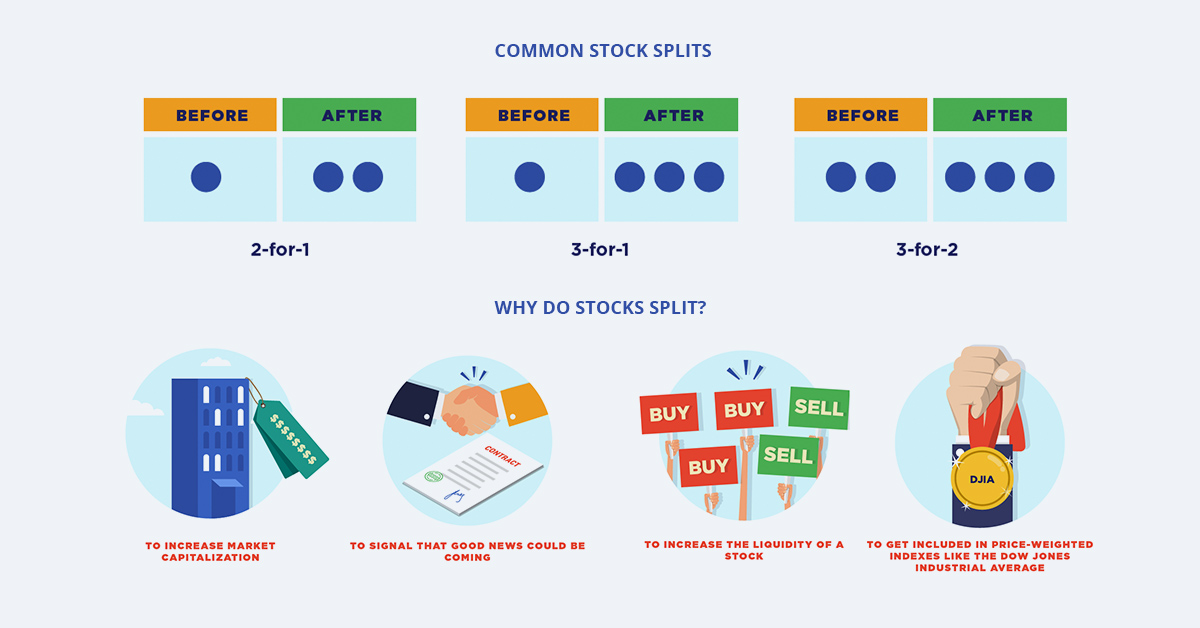
The total volume of the cheese is still worth the same amount, it’s only the portion size that changed. As the infographic above by StocksToTrade demonstrates, the same concept applies to stock splits.
Like wheels of cheese, stocks can be split a number of different ways. Some of the more common splits are 2-for-1, 3-for-1, and 3-for-2. Less common splits can take place as well, such as when Apple increased its outstanding shares by a 7-to-1 ratio in 2014.
Why Companies Do Stock Splits
Of course, stocks aren’t cheese.
The real world of the financial markets, driven by macro trends and animal spirits, is more complex than items in a shop window.
If companies want their stock price to continue rising, why would they want to split it, effectively lowering the price? Here are a some specific reasons why:
1. Liquidity
As our cheese example illustrated, stocks can sometimes see price appreciation to the point where they are no longer accessible to a wide range of investors. Splitting the stock (i.e. making an individual share cheaper) is an effective way of increasing the total number of investors who can purchase shares.
2. Sending a Message
In many cases, announcing a stock split is a harbinger of prosperity for a company. Nasdaq found that companies that split their stock outperformed the market. This is likely due to investor excitement and the fact that companies often split their stock as they approach periods of growth.
3. Reducing Capital Costs
Stocks with prices that are too high have spreads that are wider than similar stocks. When spreads—the difference between the bid and offer—are too large, they eats into investor returns.
4. Meeting Index Criteria
There are specific instances when a company may want to adjust its share price to meet certain index requirements.
One example is the Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA), the well-known 30-stock benchmark. The Dow is considered a price-weighted index, which means that the higher a company’s stock price, the more weight and influence it has within the index. Shortly after Apple conducted its 7-to-1 stock split in 2014, dropping the share price from about $650 to $90, the company was added to the DJIA.
On the flip side, a company might decide to pursue a reverse stock split. This takes the existing amount of shares held by investors and replaces them with fewer shares at a higher price. Aside from the general stigma associated with a lower share price, companies need to keep the price above a certain threshold or face the possibility of being delisted from an exchange.
Stock Splits Happen, but are not Inevitable
Alphabet will become the most recent high profile company to split their stock in early 2022. The company’s 20-for-1 stock split aims to make the share price more accessible to retail investors dropping the price from approximately $2,750 to $140 per share.
Conversely, Berkshire Hathaway has famously never split its stock. As a result, a single share of BRK.A is worth over $470,000. Berkshire Hathaway’s legendary founder, Warren Buffett, reasons that splitting the stock would run counter to his buy-and-hold investment philosophy.
Investor Education
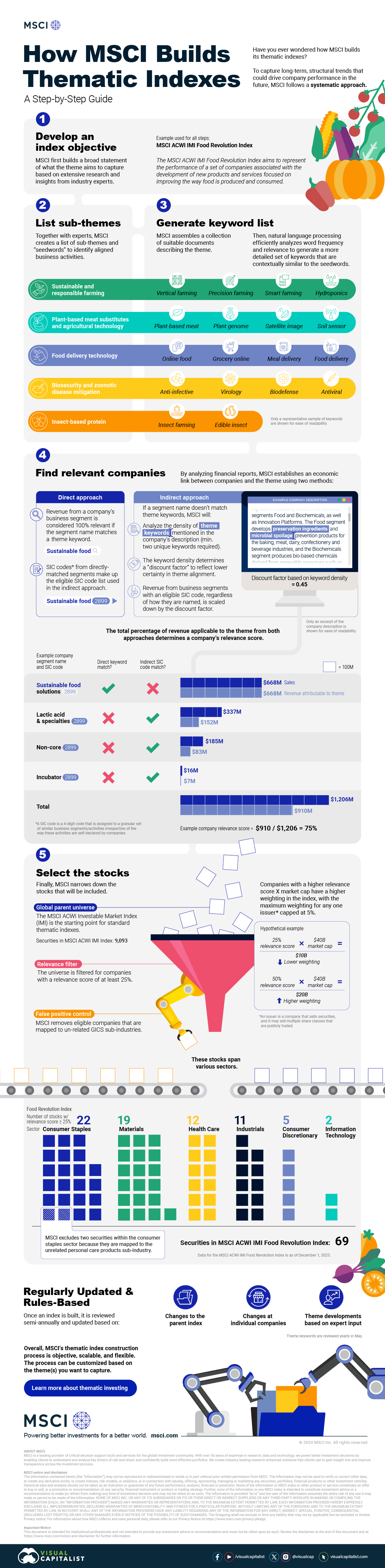
How MSCI Builds Thematic Indexes: A Step-by-Step Guide
From developing an index objective to choosing relevant stocks, this graphic breaks down how MSCI builds thematic indexes using examples.
How MSCI Builds Thematic Indexes: A Step-by-Step Guide
Have you ever wondered how MSCI builds its thematic indexes?
To capture long-term, structural trends that could drive business performance in the future, the company follows a systematic approach. This graphic from MSCI breaks down each step in the process used to create its thematic indexes.
Step 1: Develop an Index Objective
MSCI first builds a broad statement of what the theme aims to capture based on extensive research and insights from industry experts.
Steps 2 and 3: List Sub-Themes, Generate Keyword List
Together with experts, MSCI creates a list of sub-themes or “seedwords” to identify aligned business activities.
The team then assembles a collection of suitable documents describing the theme. Natural language processing efficiently analyzes word frequency and relevance to generate a more detailed set of keywords contextually similar to the seedwords.
Step 4: Find Relevant Companies
By analyzing financial reports, MSCI picks companies relevant to the theme using two methods:
- Direct approach: Revenue from a company’s business segment is considered 100% relevant if the segment name matches a theme keyword. Standard Industrial Classification (SIC) codes from these directly-matched segments make up the eligible SIC code list used in the indirect approach.
- Indirect approach: If a segment name doesn’t match theme keywords, MSCI will:
- Analyze the density of theme keywords mentioned in the company’s description. A minimum of two unique keywords is required.
- The keyword density determines a “discount factor” to reflect lower certainty in theme alignment.
- Revenue from business segments with an eligible SIC code, regardless of how they are named, is scaled down by the discount factor.
The total percentage of revenue applicable to the theme from both approaches determines a company’s relevance score.
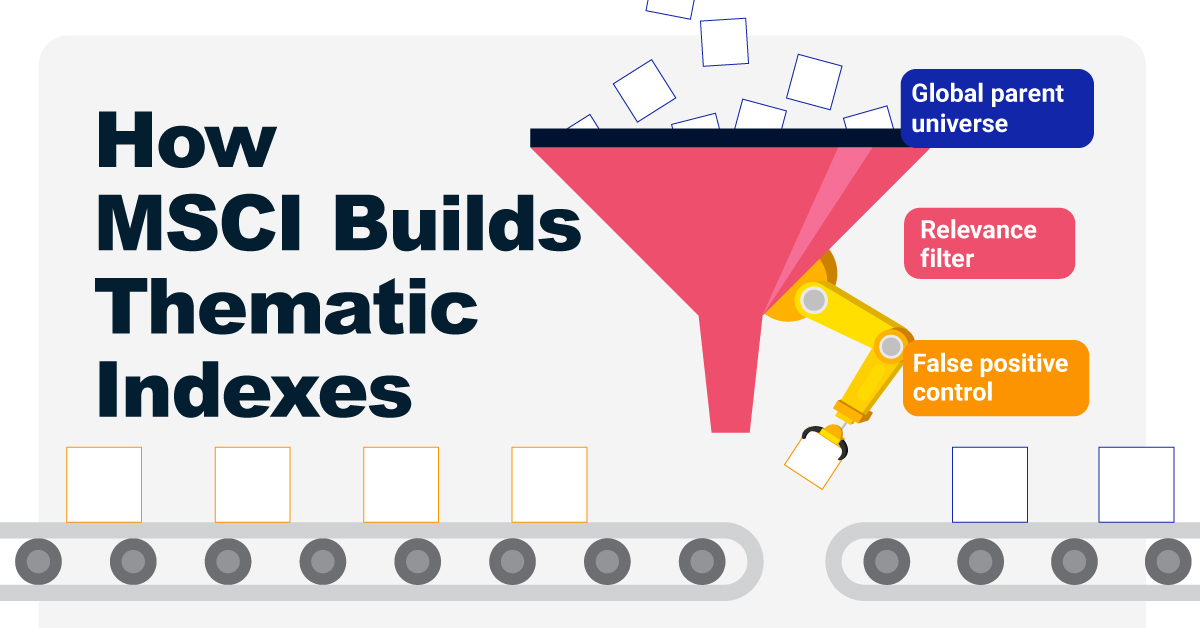
Step 5: Select the Stocks
Finally, MSCI narrows down the stocks that will be included:
- Global parent universe: The ACWI Investable Market Index (IMI) is the starting point for standard thematic indexes.
- Relevance filter: The universe is filtered for companies with a relevance score of at least 25%.
- False positive control: Eligible companies that are mapped to un-related GICS sub-industries are removed.
Companies with higher relevance scores and market caps have a higher weighting in the index, with the maximum weighting for any one issuer capped at 5%. The final selected stocks span various sectors.
MSCI Thematic Indexes: Regularly Updated and Rules-Based
Once an index is built, it is reviewed semi-annually and updated based on:
- Changes to the parent index
- Changes at individual companies
- Theme developments based on expert input
Theme keywords are reviewed yearly in May. Overall, MSCI’s thematic index construction process is objective, scalable, and flexible. The process can be customized based on the theme(s) you want to capture.

Learn more about MSCI’s thematic indexes.

-

 Investor Education6 months ago
Investor Education6 months agoThe 20 Most Common Investing Mistakes, in One Chart
Here are the most common investing mistakes to avoid, from emotionally-driven investing to paying too much in fees.
-
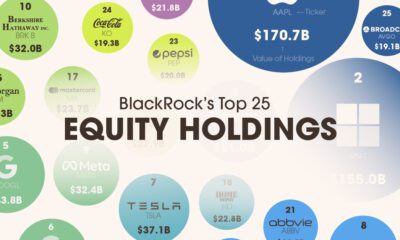
 Stocks10 months ago
Stocks10 months agoVisualizing BlackRock’s Top Equity Holdings
BlackRock is the world’s largest asset manager, with over $9 trillion in holdings. Here are the company’s top equity holdings.
-
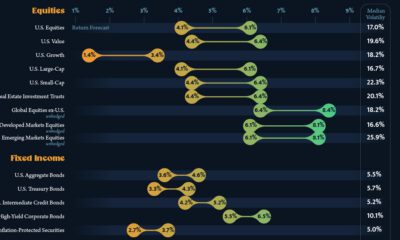
 Investor Education10 months ago
Investor Education10 months ago10-Year Annualized Forecasts for Major Asset Classes
This infographic visualizes 10-year annualized forecasts for both equities and fixed income using data from Vanguard.
-

 Investor Education1 year ago
Investor Education1 year agoVisualizing 90 Years of Stock and Bond Portfolio Performance
How have investment returns for different portfolio allocations of stocks and bonds compared over the last 90 years?
-
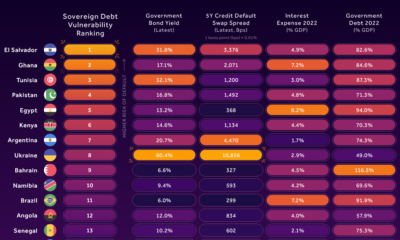
 Debt2 years ago
Debt2 years agoCountries with the Highest Default Risk in 2022
In this infographic, we examine new data that ranks the top 25 countries by their default risk.
-
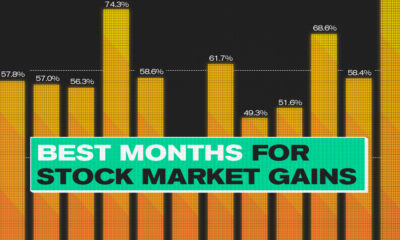
 Markets2 years ago
Markets2 years agoThe Best Months for Stock Market Gains
This infographic analyzes over 30 years of stock market performance to identify the best and worst months for gains.
-

 Maps1 week ago
Maps1 week agoThe Largest Earthquakes in the New York Area (1970-2024)
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoWhere Does One U.S. Tax Dollar Go?
-

 Automotive2 weeks ago
Automotive2 weeks agoAlmost Every EV Stock is Down After Q1 2024
-

 AI2 weeks ago
AI2 weeks agoThe Stock Performance of U.S. Chipmakers So Far in 2024
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoCharted: Big Four Market Share by S&P 500 Audits
-

 Real Estate2 weeks ago
Real Estate2 weeks agoRanked: The Most Valuable Housing Markets in America
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoWhich States Have the Highest Minimum Wage in America?
-

 AI2 weeks ago
AI2 weeks agoRanked: Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share