Politics
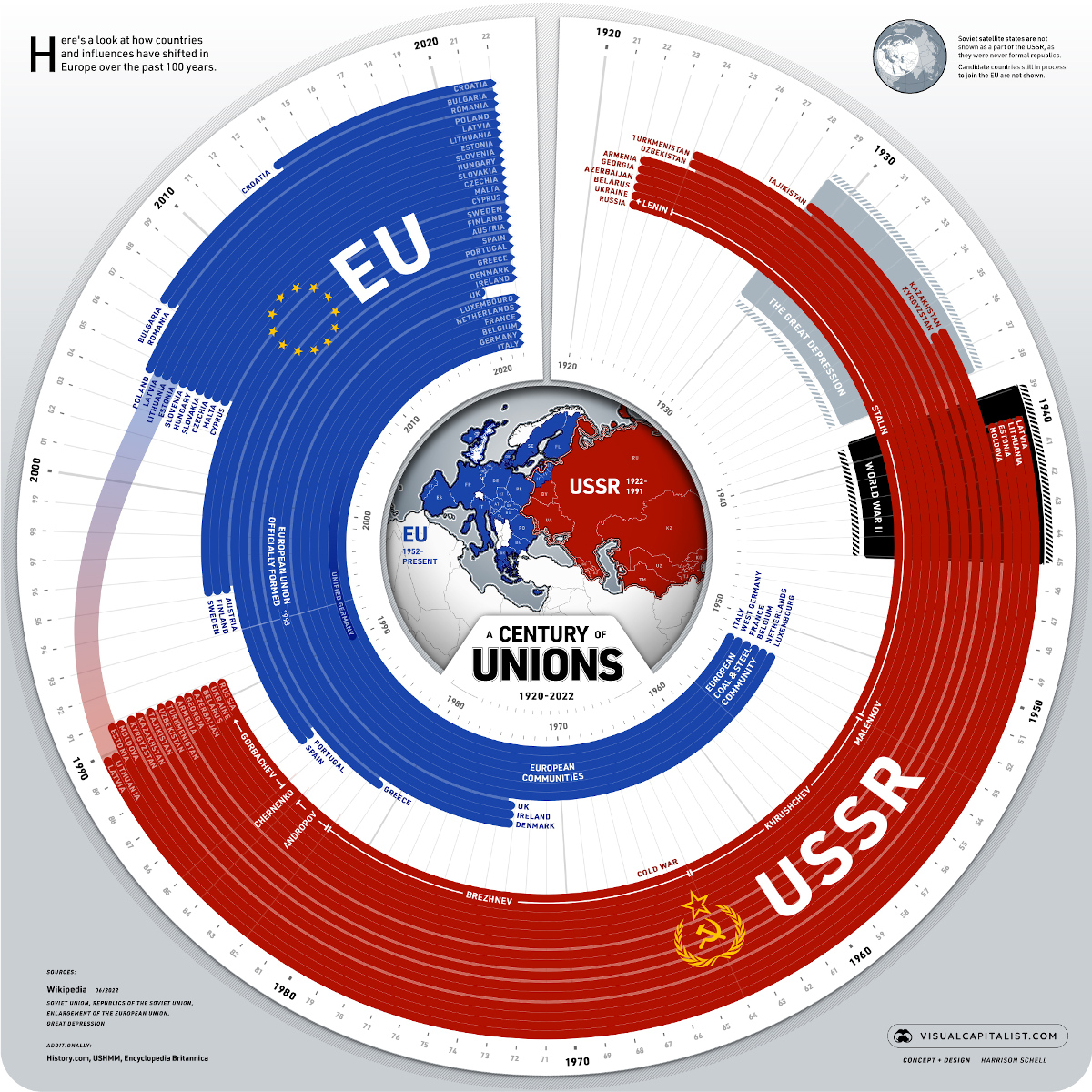
A Century of Unions in Europe (1920-2022)
View the full-size infographic
Timeline: A Century of Unions in Europe (1920-2022)
On February 24th, Russia invaded Ukraine launching one of the biggest wars on European soil since World War II. The invasion reflects a longstanding belief of Russia’s that Ukraine—and much of the Soviet Union’s former republics and satellite states—is still their territory to claim. But what is the “former glory” of Russia?
Of the USSR’s former republics and satellite states, many have moved on to join the European Union, and in Putin’s eyes have become more “Westernized” and further from Russian values. In fact, Ukraine recently had its candidacy status approved with the EU.
It’s now been a full century since the formation of the USSR. Much has changed since then, and this visual timeline breaks down how countries within and near Europe have aligned themselves over those 100 years.
The USSR / Soviet Union
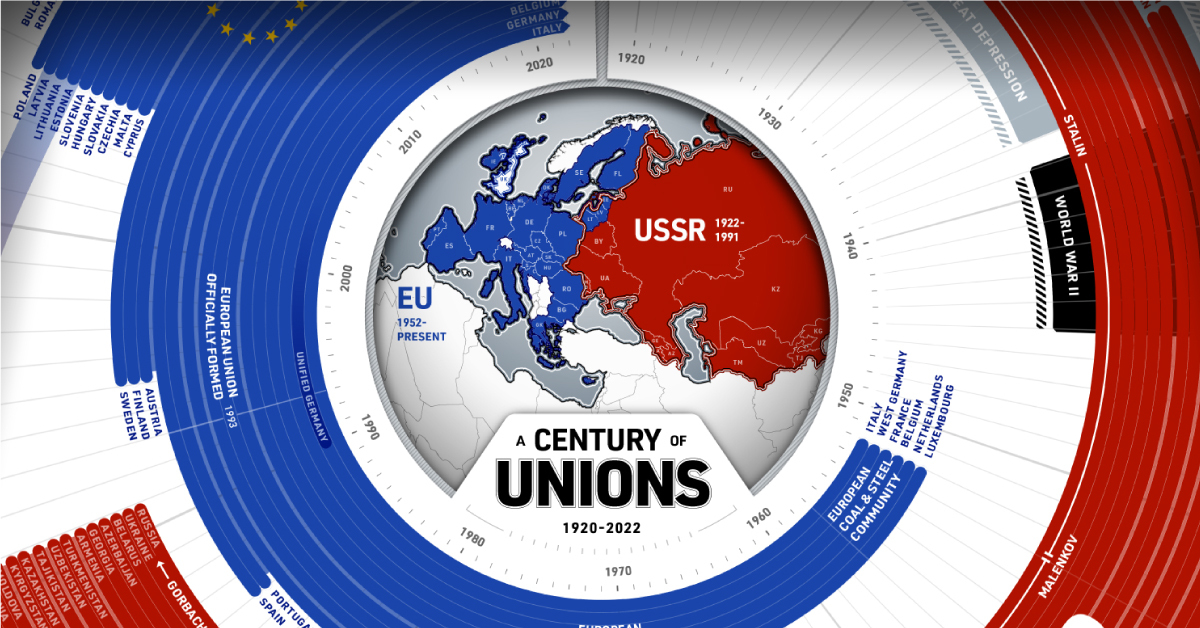
The Soviet Union—officially titled the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (USSR)—was formed 100 years ago in 1922 and was dissolved in 1991 almost 70 years later. At its height it was home to 15 republics, over 286 million people, and stretched from the Pacific Ocean to Ukraine, with virtual control and influence in countries as far west as East Germany.
Notable leaders characterized both the rise and fall of the USSR, starting with its establishment under Vladimir Lenin until the union’s dissolution under Mikhail Gorbachev. Latvia and Lithuania were among the first republics to make the move for sovereignty, beginning the demise of the Soviet Union.
Here’s a look at which modern day countries were a part of the USSR.
| Modern Day Country | Name Under USSR | Date Joined | Date Gained Independence |
|---|---|---|---|
| 🇬🇪 Georgia | Georgian Soviet Socialist Republic | 1922 | 1991 |
| 🇺🇦 Ukraine | Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic | 1922 | 1991 |
| 🇦🇲 Armenia | Armenian Soviet Socialist Republic | 1922 | 1991 |
| 🇦🇿 Azerbaijan | Azerbaijan Soviet Socialist Republic | 1922 | 1991 |
| 🇧🇾 Belarus | Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic | 1922 | 1991 |
| 🇷🇺 Russia | Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic | 1922 | 1991 |
| 🇺🇿 Uzbekistan | Uzbek Soviet Socialist Republic | 1924 | 1991 |
| 🇹🇲 Turkmenistan | Turkmen Soviet Socialist Republic | 1924 | 1991 |
| 🇹🇯 Tajikistan | Tajik Soviet Socialist Republic | 1929 | 1991 |
| 🇰🇬 Kyrgyzstan | Kirghiz Soviet Socialist Republic | 1936 | 1991 |
| 🇰🇿 Kazakhstan | Kazakh Soviet Socialist Republic | 1936 | 1991 |
| 🇱🇹 Lithuania | Lithuanian Soviet Socialist Republic | 1940 | 1990 |
| 🇪🇪 Estonia | Estonian Soviet Socialist Republic | 1940 | 1991 |
| 🇱🇻 Latvia | Latvian Soviet Socialist Republic | 1940 | 1990 |
| 🇲🇩 Moldova | Moldavian Soviet Socialist Republic | 1940 | 1991 |
Additionally, there were multiple satellite states, which were not formally joined with the USSR, but operated under intense Soviet influence.
| Modern Day Country | Country Name at the Time |
|---|---|
| 🇦🇱 Albania | People's Republic of Albania |
| 🇵🇱 Poland | Polish People's Republic |
| 🇧🇬 Bulgaria | People's Republic of Bulgaria |
| 🇷🇴 Romania | Romanian People's Republic |
| 🇨🇿 Czechia | Czechoslovak Socialist Republic |
| 🇸🇰 Slovakia | Czechoslovak Socialist Republic |
| 🇩🇪 Germany | East Germany (German Democratic Republic) |
| 🇭🇺 Hungary | Hungarian People's Republic |
| 🇸🇮 Slovenia | Federal People's Republic of Yugoslavia |
| 🇭🇷 Croatia | Federal People's Republic of Yugoslavia |
| 🇷🇸 Serbia | Federal People's Republic of Yugoslavia |
| 🇧🇦 Bosnia & Herzegovina | Federal People's Republic of Yugoslavia |
| 🇲🇪 Montenegro | Federal People's Republic of Yugoslavia |
| 🇲🇰 North Macedonia | Federal People's Republic of Yugoslavia |
| 🇲🇳 Mongolia | Mongolian People's Republic |
Today, there are still some countries that align themselves with Putin and Russia over the EU.
Belarus, sometimes called Europe’s “last dictatorship”, shares a border with both Ukraine and Russia and facilitated the entry of Russian soldiers into Ukraine. Furthermore, according to the Pentagon, Russian missiles have been launched from Belarus.
The European Union
The European Union was officially formed in 1993 and has 27 member states. Some former USSR republics are now a part of the union including Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania. The most recent member to join was Croatia in 2013.
The EU has its roots in the European Coal & Steel Community which was formed in 1952 with Italy, France, West Germany and a few other countries comprising its first members. There are currently six candidate countries on track to join the EU — all but one were either former Soviet satellite states or formal republics:
- 🇦🇱 Albania
- 🇲🇪 Montenegro
- 🇲🇰 North Macedonia
- 🇷🇸 Serbia
- 🇹🇷 Turkey
- 🇺🇦 Ukraine
- 🇲🇩 Moldova
There are many reasons countries opt to join the EU: a common currency, easier movement of goods and people between national borders, and, of course, military protection.
However, in 2020 the UK formally left the union, making it the first country in history to do so. Here’s a look at every EU member state.
| EU Member States | Year Joined | Former USSR Republic? | Former USSR Satellite State? |
|---|---|---|---|
| 🇦🇹 Austria | 1995 | No | No |
| 🇧🇪 Belgium | 1952 | No | No |
| 🇧🇬 Bulgaria | 2007 | No | Yes |
| 🇭🇷 Croatia | 2013 | No | Yes |
| 🇨🇾 Cyprus | 2004 | No | No |
| 🇨🇿 Czechia | 2004 | No | Yes |
| 🇩🇰 Denmark | 1973 | No | No |
| 🇪🇪 Estonia | 2004 | Yes | -- |
| 🇫🇮 Finland | 1995 | No | No |
| 🇫🇷 France | 1952 | No | No |
| 🇩🇪 Germany | 1952 | No | Yes (East Germany) |
| 🇬🇷 Greece | 1981 | No | No |
| 🇭🇺 Hungary | 2004 | No | Yes |
| 🇮🇪 Ireland | 1973 | No | No |
| 🇮🇹 Italy | 1952 | No | No |
| 🇱🇻 Latvia | 2004 | Yes | -- |
| 🇱🇹 Lithuania | 2004 | Yes | -- |
| 🇱🇺 Luxembourg | 1952 | No | No |
| 🇲🇹 Malta | 2004 | No | No |
| 🇳🇱 Netherlands | 1952 | No | No |
| 🇵🇱 Poland | 2004 | No | Yes |
| 🇵🇹 Portugal | 1986 | No | No |
| 🇷🇴 Romania | 2007 | No | Yes |
| 🇸🇰 Slovakia | 2004 | No | Yes |
| 🇸🇮 Slovenia | 2004 | No | Yes |
| 🇪🇸 Spain | 1986 | No | No |
| 🇸🇪 Sweden | 1995 | No | No |
Ukraine’s Outlook
The iron curtain that was draped across Europe, which used to divide the continent politically and ideologically, has since been drawn back. But the war in Ukraine is a threat to many in Europe, and countries such as Poland have voiced fears about the spillover of conflict.
In late June, the European Council approved Ukraine’s bid for expedited candidacy to the EU, but the process will still likely be lengthy—for example, it took Croatia 10 years to formally join at the normal pace.
Beyond other needs such as military support, joining the union would allow refugees from Ukraine the freedom to migrate and work in other EU countries with ease.
Economy
The Bloc Effect: International Trade with Geopolitical Allies on the Rise
Rising geopolitical tensions are shaping the future of international trade, but what is the effect on trading among G7 and BRICS countries?

The Bloc Effect: International Trade with Allies on the Rise
International trade has become increasingly fragmented over the last five years as countries have shifted to trading more with their geopolitical allies.
This graphic from The Hinrich Foundation, the first in a three-part series covering the future of trade, provides visual context to the growing divide in trade in G7 and pre-expansion BRICS countries, which are used as proxies for geopolitical blocs.
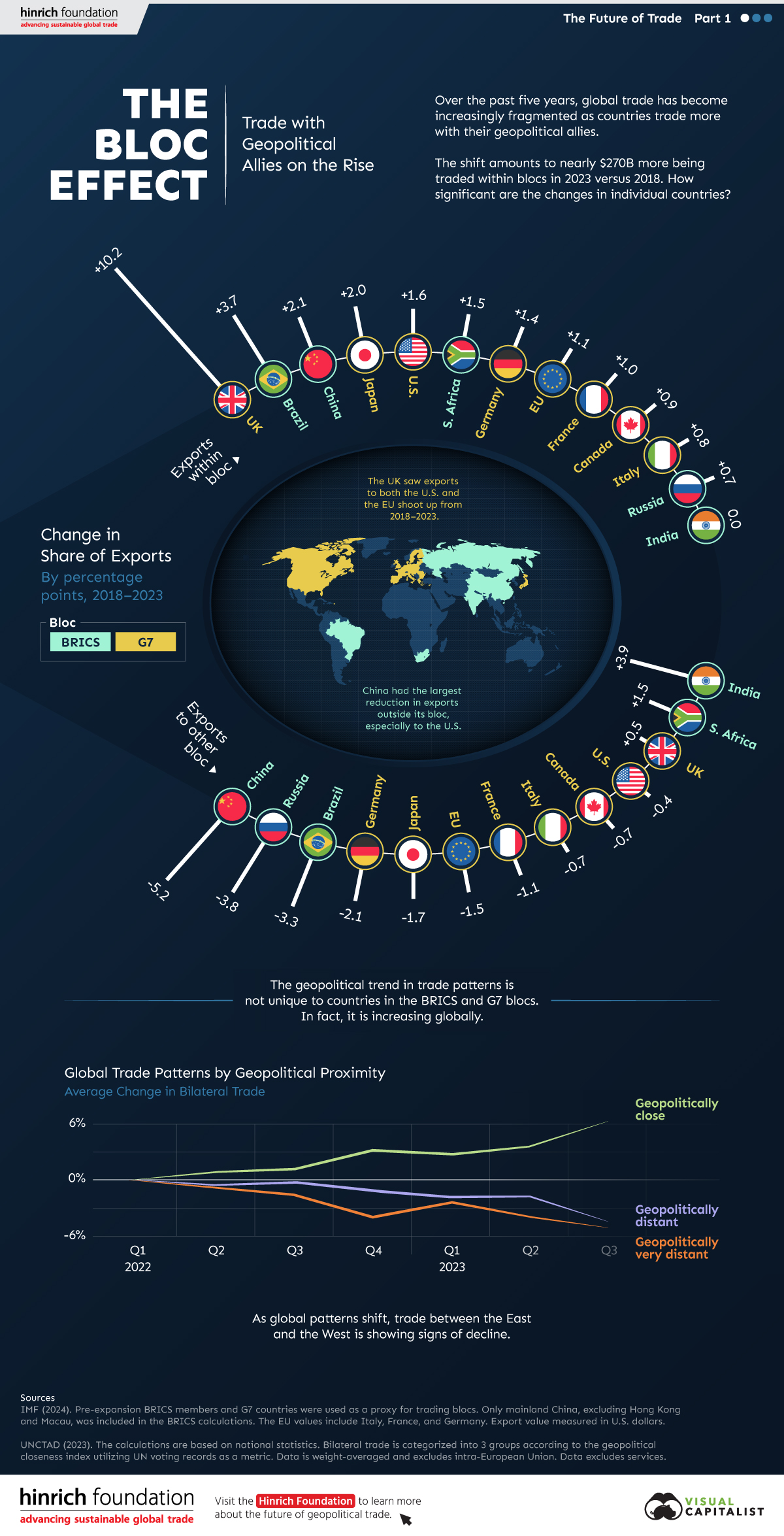
Trade Shifts in G7 and BRICS Countries
This analysis uses IMF data to examine differences in shares of exports within and between trading blocs from 2018 to 2023. For example, we looked at the percentage of China’s exports with other BRICS members as well as with G7 members to see how these proportions shifted in percentage points (pp) over time.
Countries traded nearly $270 billion more with allies in 2023 compared to 2018. This shift came at the expense of trade with rival blocs, which saw a decline of $314 billion.
Country Change in Exports Within Bloc (pp) Change in Exports With Other Bloc (pp)
🇮🇳 India 0.0 3.9
🇷🇺 Russia 0.7 -3.8
🇮🇹 Italy 0.8 -0.7
🇨🇦 Canada 0.9 -0.7
🇫🇷 France 1.0 -1.1
🇪🇺 EU 1.1 -1.5
🇩🇪 Germany 1.4 -2.1
🇿🇦 South Africa 1.5 1.5
🇺🇸 U.S. 1.6 -0.4
🇯🇵 Japan 2.0 -1.7
🇨🇳 China 2.1 -5.2
🇧🇷 Brazil 3.7 -3.3
🇬🇧 UK 10.2 0.5
All shifts reported are in percentage points. For example, the EU saw its share of exports to G7 countries rise from 74.3% in 2018 to 75.4% in 2023, which equates to a 1.1 percentage point increase.
The UK saw the largest uptick in trading with other countries within the G7 (+10.2 percentage points), namely the EU, as the post-Brexit trade slump to the region recovered.
Meanwhile, the U.S.-China trade dispute caused China’s share of exports to the G7 to fall by 5.2 percentage points from 2018 to 2023, the largest decline in our sample set. In fact, partly as a result of the conflict, the U.S. has by far the highest number of harmful tariffs in place.
The Russia-Ukraine War and ensuing sanctions by the West contributed to Russia’s share of exports to the G7 falling by 3.8 percentage points over the same timeframe.
India, South Africa, and the UK bucked the trend and continued to witness advances in exports with the opposing bloc.
Average Trade Shifts of G7 and BRICS Blocs
Though results varied significantly on a country-by-country basis, the broader trend towards favoring geopolitical allies in international trade is clear.
Bloc Change in Exports Within Bloc (pp) Change in Exports With Other Bloc (pp)
Average 2.1 -1.1
BRICS 1.6 -1.4
G7 incl. EU 2.4 -1.0
Overall, BRICS countries saw a larger shift away from exports with the other bloc, while for G7 countries the shift within their own bloc was more pronounced. This implies that though BRICS countries are trading less with the G7, they are relying more on trade partners outside their bloc to make up for the lost G7 share.
A Global Shift in International Trade and Geopolitical Proximity
The movement towards strengthening trade relations based on geopolitical proximity is a global trend.
The United Nations categorizes countries along a scale of geopolitical proximity based on UN voting records.
According to the organization’s analysis, international trade between geopolitically close countries rose from the first quarter of 2022 (when Russia first invaded Ukraine) to the third quarter of 2023 by over 6%. Conversely, trade with geopolitically distant countries declined.
The second piece in this series will explore China’s gradual move away from using the U.S. dollar in trade settlements.

Visit the Hinrich Foundation to learn more about the future of geopolitical trade

-

 Economy2 hours ago
Economy2 hours agoEconomic Growth Forecasts for G7 and BRICS Countries in 2024
The IMF has released its economic growth forecasts for 2024. How do the G7 and BRICS countries compare?
-

 United States1 week ago
United States1 week agoRanked: The Largest U.S. Corporations by Number of Employees
We visualized the top U.S. companies by employees, revealing the massive scale of retailers like Walmart, Target, and Home Depot.
-

 Economy2 weeks ago
Economy2 weeks agoWhere U.S. Inflation Hit the Hardest in March 2024
We visualized product categories that saw the highest % increase in price due to U.S. inflation as of March 2024.
-

 Economy4 weeks ago
Economy4 weeks agoG20 Inflation Rates: Feb 2024 vs COVID Peak
We visualize inflation rates across G20 countries as of Feb 2024, in the context of their COVID-19 pandemic peak.
-

 Economy1 month ago
Economy1 month agoMapped: Unemployment Claims by State
This visual heatmap of unemployment claims by state highlights New York, California, and Alaska leading the country by a wide margin.
-
 Economy2 months ago
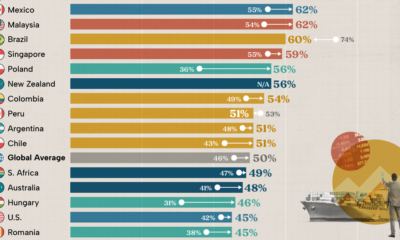
Economy2 months agoConfidence in the Global Economy, by Country
Will the global economy be stronger in 2024 than in 2023?
-

 Markets1 week ago
Markets1 week agoU.S. Debt Interest Payments Reach $1 Trillion
-

 Business2 weeks ago
Business2 weeks agoCharted: Big Four Market Share by S&P 500 Audits
-

 Real Estate2 weeks ago
Real Estate2 weeks agoRanked: The Most Valuable Housing Markets in America
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoWhich States Have the Highest Minimum Wage in America?
-

 AI2 weeks ago
AI2 weeks agoRanked: Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoRanked: The World’s Top Flight Routes, by Revenue
-

 Demographics2 weeks ago
Demographics2 weeks agoPopulation Projections: The World’s 6 Largest Countries in 2075
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoThe Top 10 States by Real GDP Growth in 2023