Misc
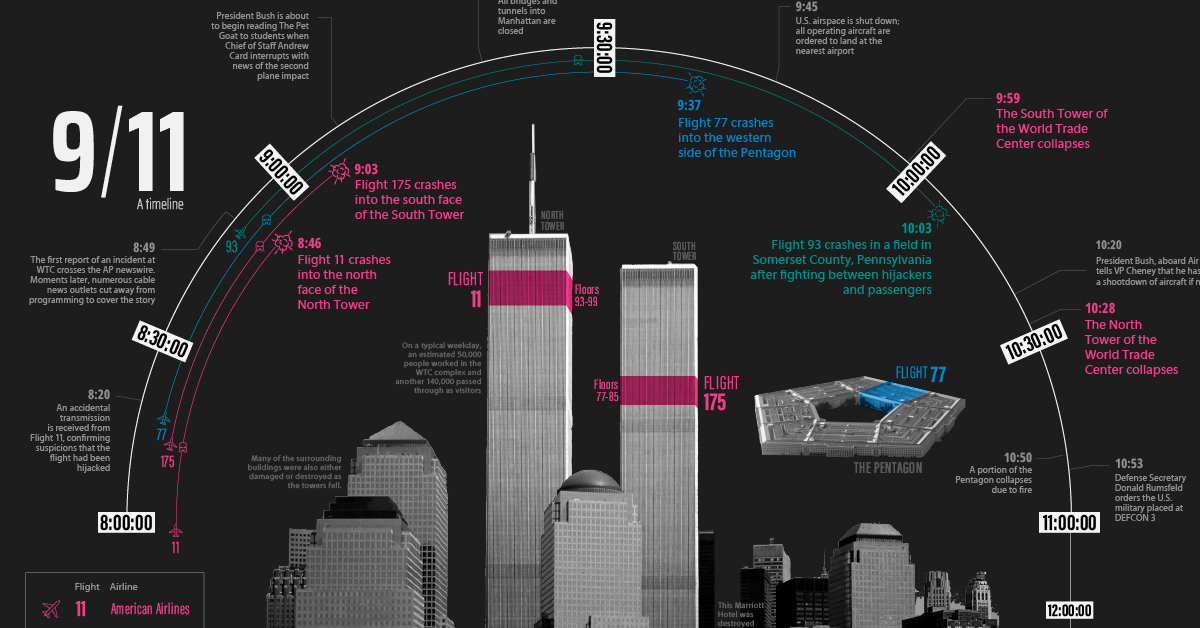
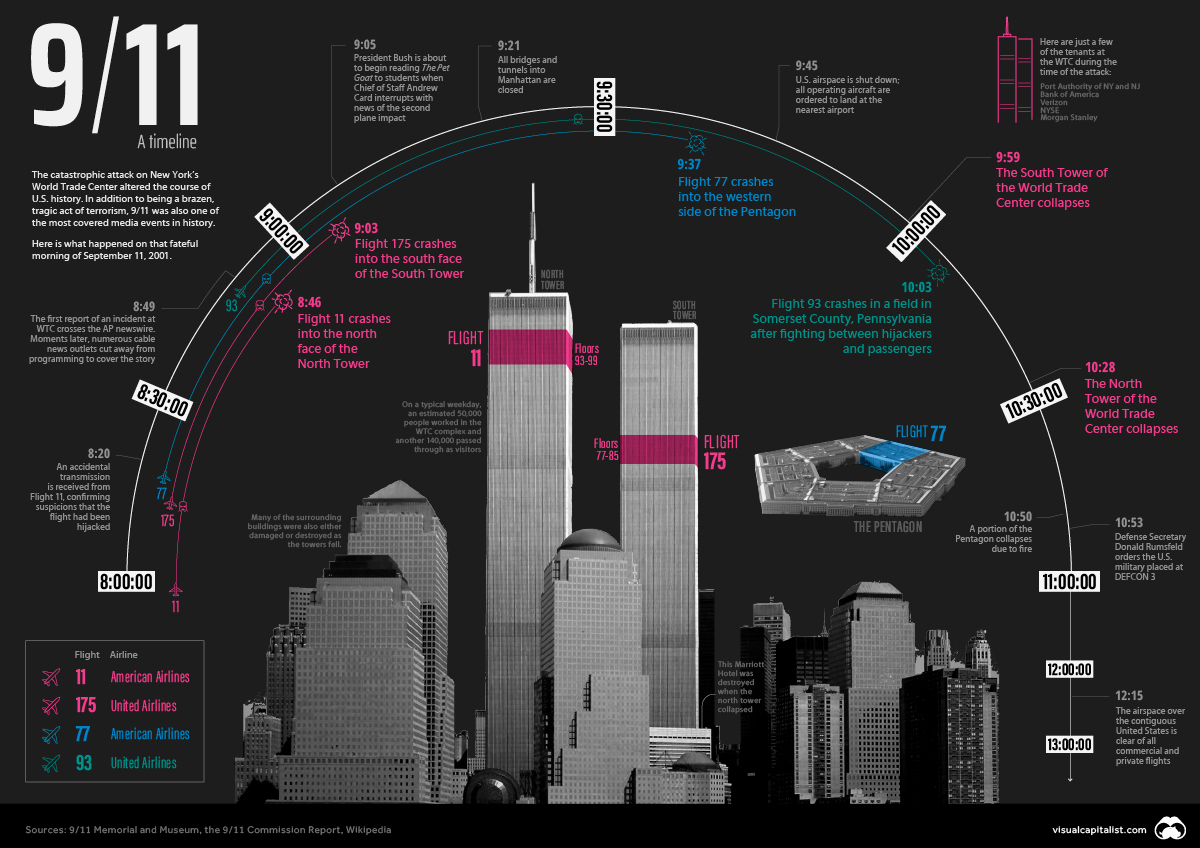
9/11 Timeline: Three Hours That Changed Everything
View the full-size version of this infographic
9/11 Timeline: Three Hours That Changed Everything
For Americans and people watching around the world, September 11, 2001, is a day that will never be forgotten.
Within three hours, New York’s tallest buildings were reduced to rubble, and the Pentagon—the nerve center of the American armed forces—was burning and partially collapsed. Thousands of civilians had lost their lives and were seriously injured, and the entire country was in collective shock, still trying to make sense of how a coordinated act of terrorism of that magnitude was allowed to take place on American soil.
In the 20 years since 9/11, the events that occurred that morning have been analyzed in-depth from a thousand different angles. Even though the attacks took place in the era just before mobile phones had viable cameras, there are countless images and videos of the event. As well, we now have the 9/11 Commission Report, which compiles interviews from over 1,200 people in 10 countries, and draws upon two and a half million pages of documents to present its findings.
For many people younger than Generation X, 9/11 is a feeling—a grim milestone from their youth—but the details are likely more fuzzy. The timeline visualization above is a high-level record of what happened that morning during the three hours when everything changed.
A Chronology of Terror
In its most simple form, the 9/11 attacks can be described as a coordinated hijacking of four commercial airplanes, which were then used to fly into high profile targets in New York City and Washington, DC. Here is a summary of the planes involved in the incident:
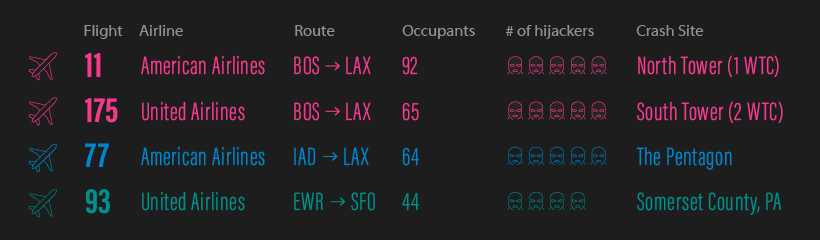
These four flights play a central role in what unfolded that morning. In the early hours of September 11, 2001, a collection of 19 would-be hijackers made their way through security at airports in Boston, Newark, and Washington, DC.
Our three-hour timeline begins just before 8am, as the first plane involved in the attack leaves the tarmac just outside of Boston. (In situations where the exact time isn’t known, a range is given.)
Sept 11, 2001, 7:59am – American Airlines Flight 11, a Boeing 767 carrying 81 passengers and 11 crew members, departs from Logan International Airport in Boston, bound for Los Angeles International Airport.
8:14 – United Airlines Flight 175, a Boeing 767, carrying 56 passengers and 9 crew members, departs from Logan International Airport in Boston, bound for Los Angeles International Airport.
8:14 – Flight 11 is hijacked over central Massachusetts. There are five hijackers on board.
8:20 – American Airlines Flight 77, a Boeing 757 with 58 passengers and 6 crew members, departs from Washington Dulles International Airport, for Los Angeles International Airport.
8:42 – United Airlines Flight 93, a Boeing 757 with 37 passengers and 7 crew members, departs from Newark International Airport, bound for San Francisco International Airport.
8:42–8:46 – Flight 175 is hijacked above northwest New Jersey. There are five hijackers on board.
8:46 – Flight 11 crashes into the north face of the North Tower (1 WTC) of the World Trade Center, between floors 93 and 99. All 92 people on board are killed.
8:50–8:54 – Flight 77 is hijacked above southern Ohio. There are five hijackers on board.
9:03 – Flight 175 crashes into the south face of the South Tower (2 WTC) of the World Trade Center, between floors 77 and 85. All 65 people on board are killed.
9:28 – Flight 93 is hijacked above northern Ohio. There are four hijackers on board.
9:37 – Flight 77 crashes into the western side of The Pentagon. All 64 people on board are killed.
9:45 – United States airspace is shut down; all operating aircraft are ordered to land at the nearest airport.
9:59 – The South Tower of the World Trade Center collapses, 56 minutes after the impact of Flight 175.
10:03 – Flight 93 is crashed by its hijackers in a field in Somerset County, Pennsylvania. Later reports indicate that passengers had learned about the World Trade Center and Pentagon crashes and were resisting the hijackers. All 44 people on board are killed in the crash.
10:28 – The North Tower of the World Trade Center collapses, 1 hour and 42 minutes after the impact of Flight 11. The Marriott Hotel at the base of the two towers is also destroyed.
10:50 – Five stories of the western side of the Pentagon collapse due to the fire.
Two and a half hours after the first plane left Boston, the iconic “Twin Towers” lay in ruins in Lower Manhattan, and brave first responders and military personnel were scrambling to save lives and secure the country.
Life in America was set on a new trajectory.
Information Shockwave
Two decades is a long time in the world of technology and media. Though the communication channels of that era may seem slow by today’s standards, the September 11 terrorist attacks still took place in the age of 24-hour cable news coverage and nascent online reporting.
Add in the fact that New York was (and still is) a linchpin of global media, and it’s easy to see why media coverage of the attack spread so quickly.
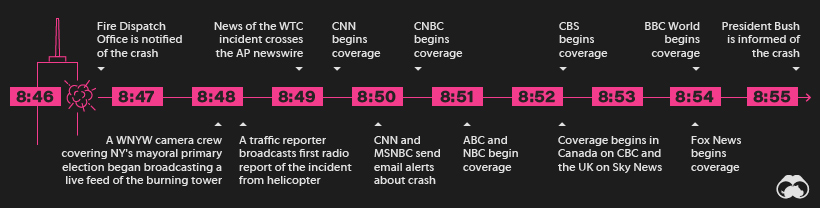
Within two minutes of the first impact on the World Trade Center, a nearby camera crew covering New York’s mayoral primary election was already broadcasting a live feed of the burning building to a TV audience. Within three minutes, news of the attack hit the Associated Press newswire, and moments after that, most major networks cut away from scheduled programming to cover the story.
Less than 10 minutes after the impact, President Bush–who was attending an event at a Florida elementary school–was informed of the crash (which at that point was characterized as an accident).
Because media outlets were able to cover the incident so quickly, millions of people witnessed the second plane striking the South Tower in real-time a mere 17 minutes after the first impact. This was a defining moment as millions of people around the world experience the events precisely as they unfolded.
The still-young internet was strained that day. Moments after the impact of the North Tower, the CNN and MSNBC websites experienced a crushing load of traffic that overwhelmed servers. The FBI’s website also experienced issues after posting the images of the 9/11 hijackers later that day.
Lasting Impact
The Pentagon has been repaired, and a shiny, 94-story World Trade Center now punctuates the skyline of Lower Manhattan, but not all wounds have healed.
For one, many 9/11 survivors are living with lingering health issues believed to be linked to the toxic smoke from the attack and building collapse. Many others are living with the absence of the nearly 3,000 loved-ones who died during the attacks.
The Department of Homeland Security (DHS) is still a lasting legacy of the 9/11 attacks. When DHS began operations in 2003, it was the largest U.S. government reorganization in the 50 years since the Department of Defense was created. In addition to this largely “hidden” layer of security, people now encounter more vigorous security protocol at airports around the world.
As well, the recent withdrawal from Afghanistan was a reminder that long shadow of the attack is still influencing events today, even two decades later.
Misc
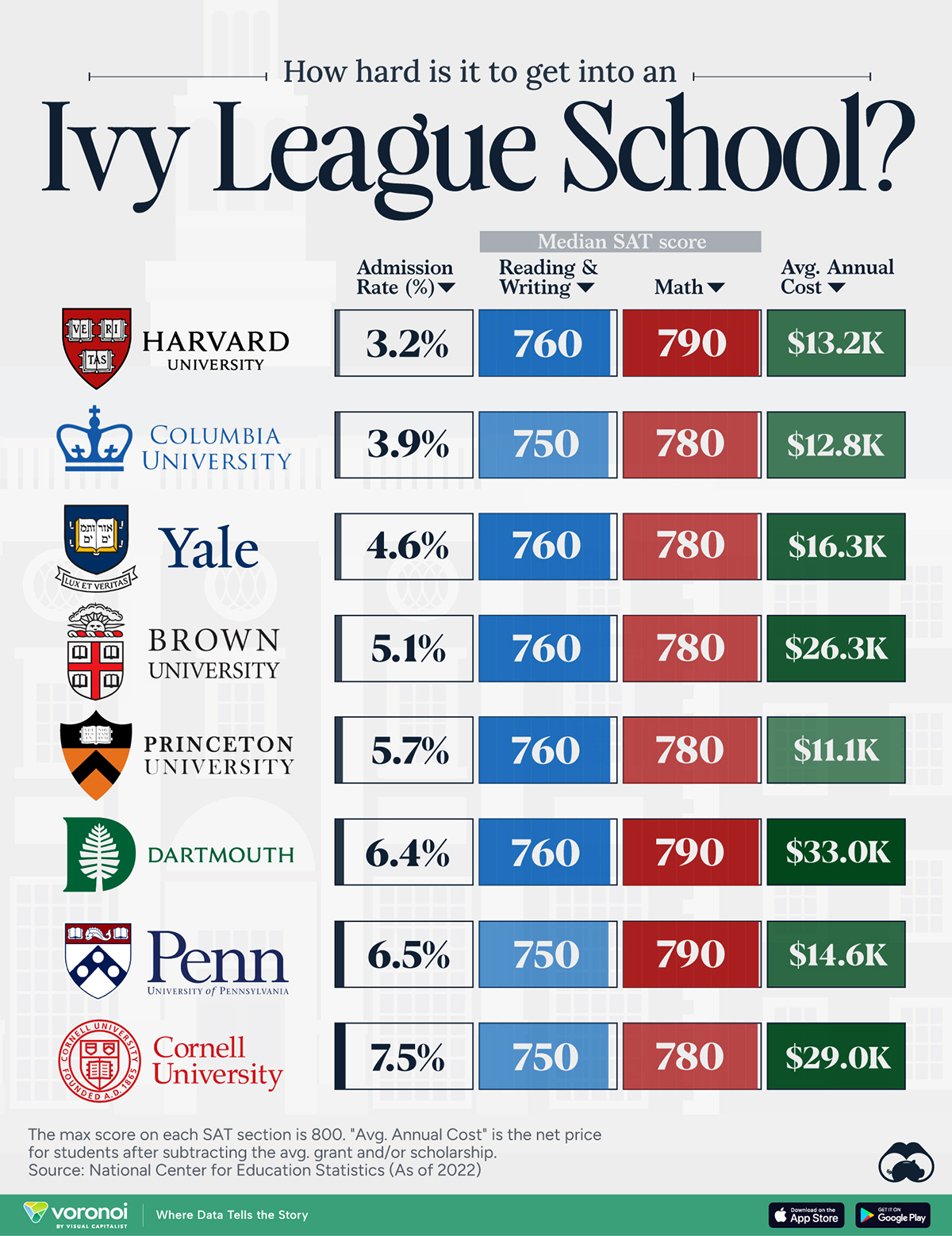
How Hard Is It to Get Into an Ivy League School?
We detail the admission rates and average annual cost for Ivy League schools, as well as the median SAT scores required to be accepted.
How Hard Is It to Get Into an Ivy League School?
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on iOS or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
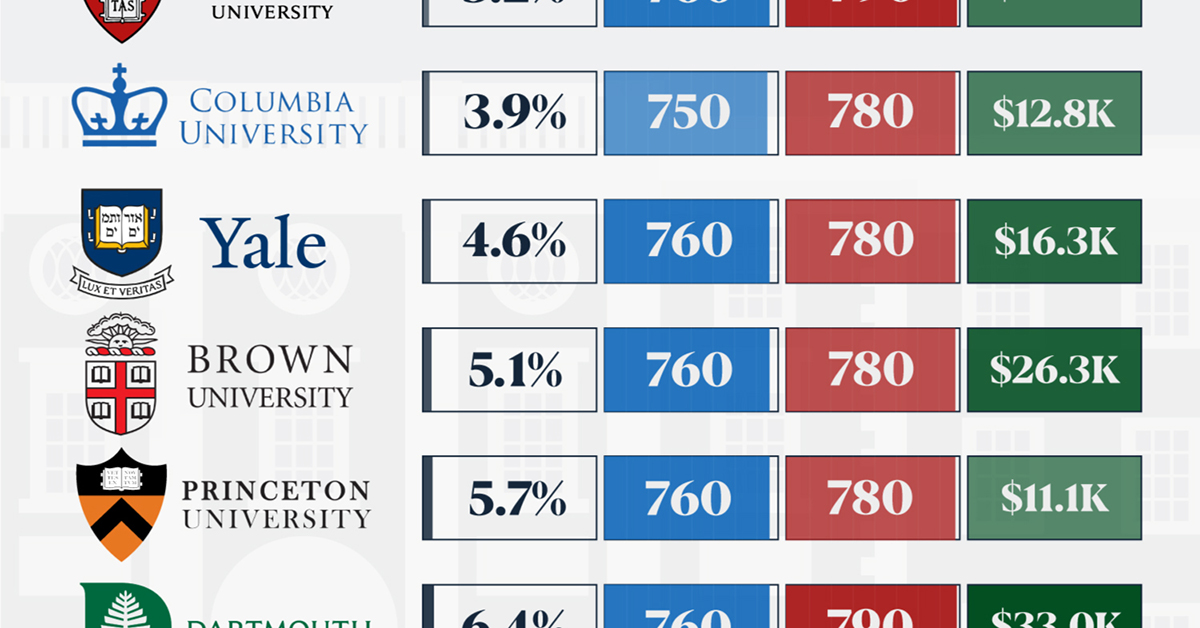
Ivy League institutions are renowned worldwide for their academic excellence and long-standing traditions. But how hard is it to get into one of the top universities in the U.S.?
In this graphic, we detail the admission rates and average annual cost for Ivy League schools, as well as the median SAT scores required to be accepted. The data comes from the National Center for Education Statistics and was compiled by 24/7 Wall St.
Note that “average annual cost” represents the net price a student pays after subtracting the average value of grants and/or scholarships received.
Harvard is the Most Selective
The SAT is a standardized test commonly used for college admissions in the United States. It’s taken by high school juniors and seniors to assess their readiness for college-level academic work.
When comparing SAT scores, Harvard and Dartmouth are among the most challenging universities to gain admission to. The median SAT scores for their students are 760 for reading and writing and 790 for math. Still, Harvard has half the admission rate (3.2%) compared to Dartmouth (6.4%).
| School | Admission rate (%) | SAT Score: Reading & Writing | SAT Score: Math | Avg Annual Cost* |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Harvard University | 3.2 | 760 | 790 | $13,259 |
| Columbia University | 3.9 | 750 | 780 | $12,836 |
| Yale University | 4.6 | 760 | 780 | $16,341 |
| Brown University | 5.1 | 760 | 780 | $26,308 |
| Princeton University | 5.7 | 760 | 780 | $11,080 |
| Dartmouth College | 6.4 | 760 | 790 | $33,023 |
| University of Pennsylvania | 6.5 | 750 | 790 | $14,851 |
| Cornell University | 7.5 | 750 | 780 | $29,011 |
*Costs after receiving federal financial aid.
Additionally, Dartmouth has the highest average annual cost at $33,000. Princeton has the lowest at $11,100.
While student debt has surged in the United States in recent years, hitting $1.73 trillion in 2023, the worth of obtaining a degree from any of the schools listed surpasses mere academics. This is evidenced by the substantial incomes earned by former students.
Harvard grads, for example, have the highest average starting salary in the country, at $91,700.
-

 Maps2 weeks ago
Maps2 weeks agoMapped: Average Wages Across Europe
-

 Money1 week ago
Money1 week agoWhich States Have the Highest Minimum Wage in America?
-

 Real Estate1 week ago
Real Estate1 week agoRanked: The Most Valuable Housing Markets in America
-

 Markets1 week ago
Markets1 week agoCharted: Big Four Market Share by S&P 500 Audits
-

 AI1 week ago
AI1 week agoThe Stock Performance of U.S. Chipmakers So Far in 2024
-

 Automotive2 weeks ago
Automotive2 weeks agoAlmost Every EV Stock is Down After Q1 2024
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoWhere Does One U.S. Tax Dollar Go?
-

 Green2 weeks ago
Green2 weeks agoRanked: Top Countries by Total Forest Loss Since 2001