Environment
5 Things to Know About Europe’s Scorching Heatwave
5 Things to Know About Europe’s Scorching Heatwave
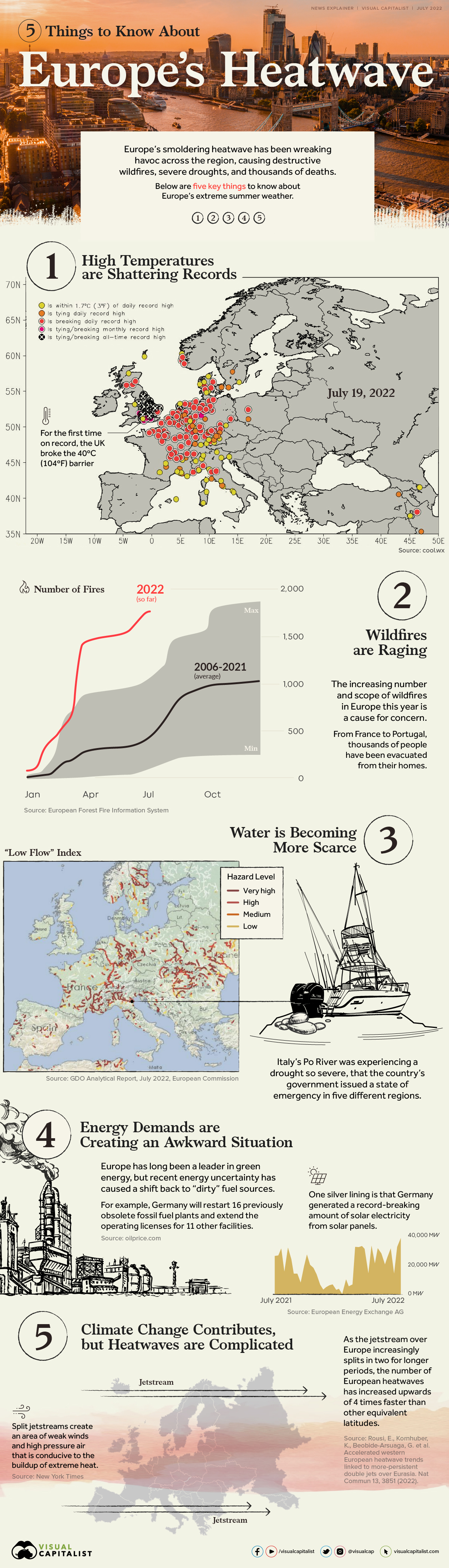
For the last few months, Europe’s smoldering heatwave has been wreaking havoc across the region, causing destructive wildfires, severe droughts, and thousands of deaths.
The EU’s record-breaking temperatures are making headlines around the world, as experts worry these extreme heatwaves could be the region’s new normal.
Given the volume of coverage on the topic, we sifted through dozens of articles and Twitter threads (so you don’t have to) and complied a list of the five major things to know about Europe’s smothering heatwave.
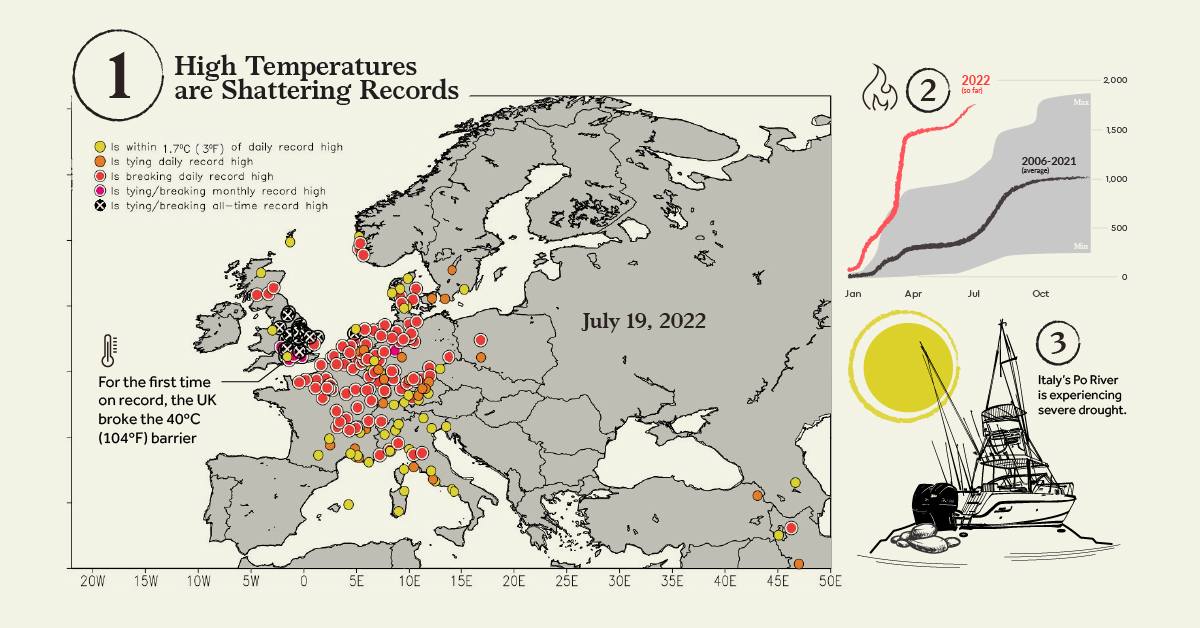
① High Temperatures are Shattering Records
Temperatures have been hitting all-time highs across the region.
On Monday, July 18, dozens of towns across France reported record-breaking temperatures of up to 42°C (107.6°F). In the same week, the UK experienced its hottest day on record at 40.3°C (104.5°F), breaking Britain’s previous record of (38.7°C) 101.7°F that was set back in 2019.
The heat in London was so unprecedented, the city’s national rail service issued a warning to the public, urging passengers to stay home and only travel if necessary. Some major rail lines were even closed for parts of the day on Tuesday, July 19.
② Europe is Feeling the Burn
The smoldering heat is fueling disastrous wildfires across the continent. As of July 20, an estimated 1,977 wildfires have blazed across the region in 2022—almost 3x the average amount, according to historical data from the European Forest Fire Information System.
Mediterranean countries have been hit particularly hard, with thousands of people in Portugal, Spain, and France evacuating their homes.
③ Going With the (Low) Flow
Along with the devastating wildfires, Europe’s heatwave is also causing a series of droughts across the region.
While most European cities have at least one river or lake crossing their urban landscape, these rivers and bodies of water are at risk of drying out. For instance in early July, Italy’s Po River was experiencing a drought so severe, that the country’s government issued a state of emergency in five different regions.
④ Energy Demands are Creating an Awkward Situation
Last year, Europe set ambitious goals to cut 55% of its greenhouse gas emissions by 2030.
But, in the wake of a global energy crisis, many European countries have put their green transition plans on hold as they turn to “dirtier” fuels like coal to keep their economies running business-as-usual. This timing is a tad awkward, considering the fact the region is currently ablaze with record-breaking temperatures that experts believe are human-induced.
The aforementioned “low flow” on many European rivers are also impacting hydroelectricity and even nuclear electricity generation, as too little water is available for cooling purposes.
On the bright side, at least Germany has made some progress in the realm of renewable energy—on July 17, the country generated a record-breaking amount of electricity from solar panels.
⑤ Climate Change is a Factor, but Heatwaves are Complicated
Experts claim that climate change is playing a part in these record-breaking heatwaves. Around the world, global surface temperatures have risen by about 1.0°C (1.8°F) since the 1850s, and scientists claim this temperature increase has been indisputably influenced by human activity.
However, there may be other factors that are influencing these extreme heatwaves. While the exact specifics are difficult to nail down due to the variable nature of the climate, a recent study published in Nature Communications found that Europe’s escalating heatwaves could be partly attributed to changing air currents, which are blowing hot air from North Africa to Europe.
The Bottom Line
At least 1,500 lives have been lost so far amidst this record-breaking heatwave. And since temperatures are expected to remain high across the region for at least another week, this figure will likely increase.
European homes are generally not well equipped for exceptionally high temperatures, and since the continent has the oldest median age of any region, its population is particularly susceptible to the negative effects of extreme weather.
Livelihoods are also being impacted by the extreme weather. Temperatures are drying out soil, which is creating poor growing conditions for corn farmers in France, Romania, and Spain, the region’s top corn producers.
Long story short—Europe’s heatwave is having disastrous effects on its economy and infrastructure, as well as the overall wellbeing of the region’s population.
Update: The map from cool.wx was revised to better reflect Europe’s present day borders.
Green
Ranked: Top Countries by Total Forest Loss Since 2001
The country with the most forest loss since 2001 lost as much forest cover as the next four countries combined.

Ranked: Top Countries By Total Forest Loss Since 2001
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on iOS or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
Forests are critical natural resources, often caught in the crosshairs of economic development. Thanks to expanding human settlement, agriculture, and industry, the world lost nearly 1 million square kilometers (km²) of forest cover since 2001.
But where has most of this deforestation occurred?
We rank the countries by the total decrease in their forest area between 2001 and 2021, measured in square kilometers along with their percentage decrease for context. All of this data was sourced from the World Bank.
A caveat to this data: countries are ranked by total forest loss, so countries with the largest forests feature predominantly on this list.
Which Country Has Lost the Most Forests (2001-2021)?
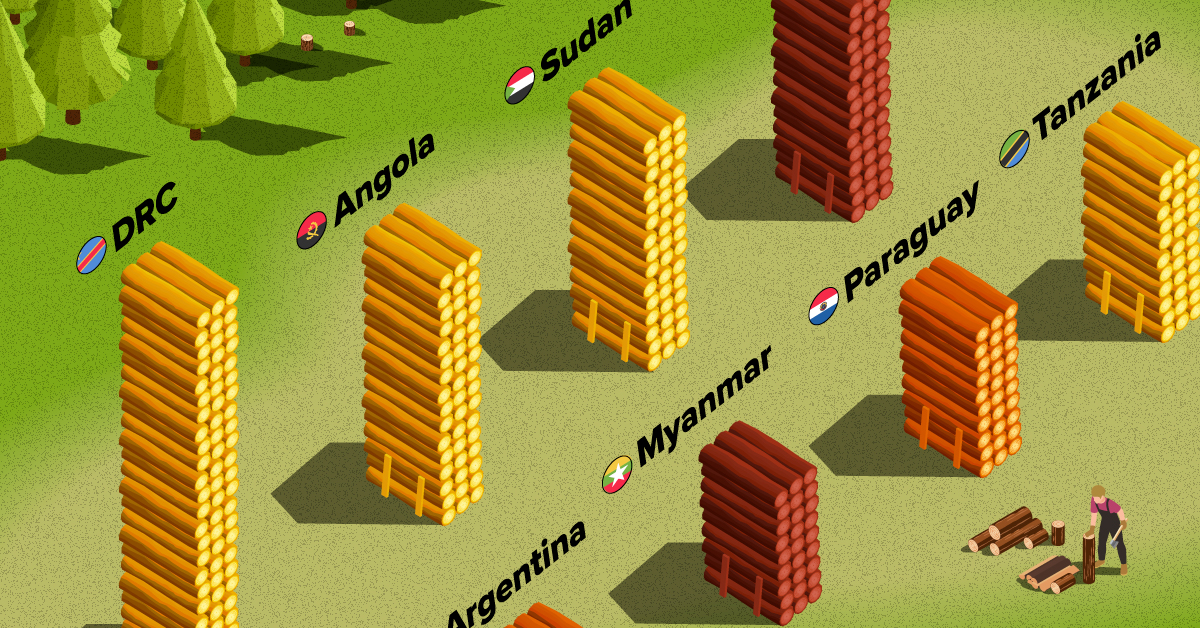
Brazil has lost more than half a million square kilometers of forest in the last two decades. Agricultural expansion for beef and soy production alongside mining and infrastructure growth are the primary drivers behind this large scale deforestation.
This has also caused periodic fires in the Amazon rainforest, drawing repeated alarm from around the world. In fact, Brazil has lost as much forest cover as the next four countries combined.
The table below lists the countries included in this graphic, as well as several others further down the ranking.
| Rank | Country | Region | 2001–21 Change (in km2) | % of Forest Loss |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 🇧🇷 Brazil | South America | -517,464 | -9% |
| 2 | 🇨🇩 DRC | Africa | -181,721 | -13% |
| 3 | 🇦🇴 Angola | Africa | -111,012 | -14% |
| 4 | 🇸🇩 Sudan | Africa | -106,213 | -37% |
| 5 | 🇮🇩 Indonesia | Asia | -95,903 | -9% |
| 6 | 🇹🇿 Tanzania | Africa | -80,220 | -15% |
| 7 | 🇵🇾 Paraguay | South America | -68,266 | -30% |
| 8 | 🇲🇲 Myanmar | Asia | -62,712 | -18% |
| 9 | 🇦🇷 Argentina | South America | -45,979 | -14% |
| 10 | 🇲🇿 Mozambique | Africa | -44,688 | -11% |
| 11 | 🇧🇴 Bolivia | South America | -42,791 | -8% |
| 12 | 🇨🇴 Colombia | South America | -36,001 | -6% |
| 13 | 🇳🇬 Nigeria | Africa | -32,661 | -13% |
| 14 | 🇵🇪 Peru | South America | -30,155 | -4% |
| 15 | 🇰🇭 Cambodia | Asia | -28,491 | -26% |
| 16 | 🇻🇪 Venezuela | South America | -28,130 | -6% |
| 17 | 🇲🇽 Mexico | North America | -26,732 | -4% |
| 18 | 🇿🇲 Zambia | Africa | -23,924 | -5% |
| 19 | 🇧🇼 Botswana | Africa | -23,660 | -14% |
| 20 | 🇨🇮 Cote d'Ivoire | Africa | -22,577 | -45% |
What is quickly apparent is how most of the countries on this list are from Africa and South America. A study found a correlation where developing economies tend to have higher deforestation rates than advanced economies. Former colonies have also experienced more forest loss than those that were not colonized.
In Asia, Indonesia’s burgeoning palm oil industry is a key driver to deforestation, though efforts are now being made to reverse its impact. Meanwhile, Cambodia experienced rapid clear-cutting for its growing rubber plantations and timber industry.
Finally, Myanmar has long contended with illegal logging, but the country’s ongoing civil war is styming conversation efforts.
-

 Green2 weeks ago
Green2 weeks agoRanked: Top Countries by Total Forest Loss Since 2001
-

 Travel1 week ago
Travel1 week agoRanked: The World’s Top Flight Routes, by Revenue
-

 Technology2 weeks ago
Technology2 weeks agoRanked: Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoWhich States Have the Highest Minimum Wage in America?
-

 Real Estate2 weeks ago
Real Estate2 weeks agoRanked: The Most Valuable Housing Markets in America
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoCharted: Big Four Market Share by S&P 500 Audits
-

 AI2 weeks ago
AI2 weeks agoThe Stock Performance of U.S. Chipmakers So Far in 2024
-

 Automotive2 weeks ago
Automotive2 weeks agoAlmost Every EV Stock is Down After Q1 2024