Technology
3D Printing is Finally Changing the Manufacturing Landscape
3D Printing is Finally Changing the Manufacturing Landscape
The right software can change industries quickly.
For fast-moving companies like Airbnb, Stripe, Uber, Facebook, or Slack, the piping – such as the internet and smartphones – is already well-established, allowing these startups to scale at unprecedented speeds.
For 3D printing and other such “hard” technologies? Things end up being a lot more complicated.
A Long Time Coming
The rise of 3D printing reached peak hype years ago – and as far back as 2014, we were illustrating how 3D printing could ultimately shape the future of business. However, since those days, the technology has arguably fallen into the dreaded “trough of disillusionment” category on the famous Gartner Hype Cycle.
The harsh reality is that it’s just really hard to move things like 3D printing forward at the same type of speed as software. For the technology to scale at a commercial level, products would need to be flawless and intuitive from the get-go (they weren’t), and all engineering, technological, and design problems would need to be solved at lightning-quick speeds. Instead, it takes huge amounts of research, investment, patience, and iterations to get to the next level.
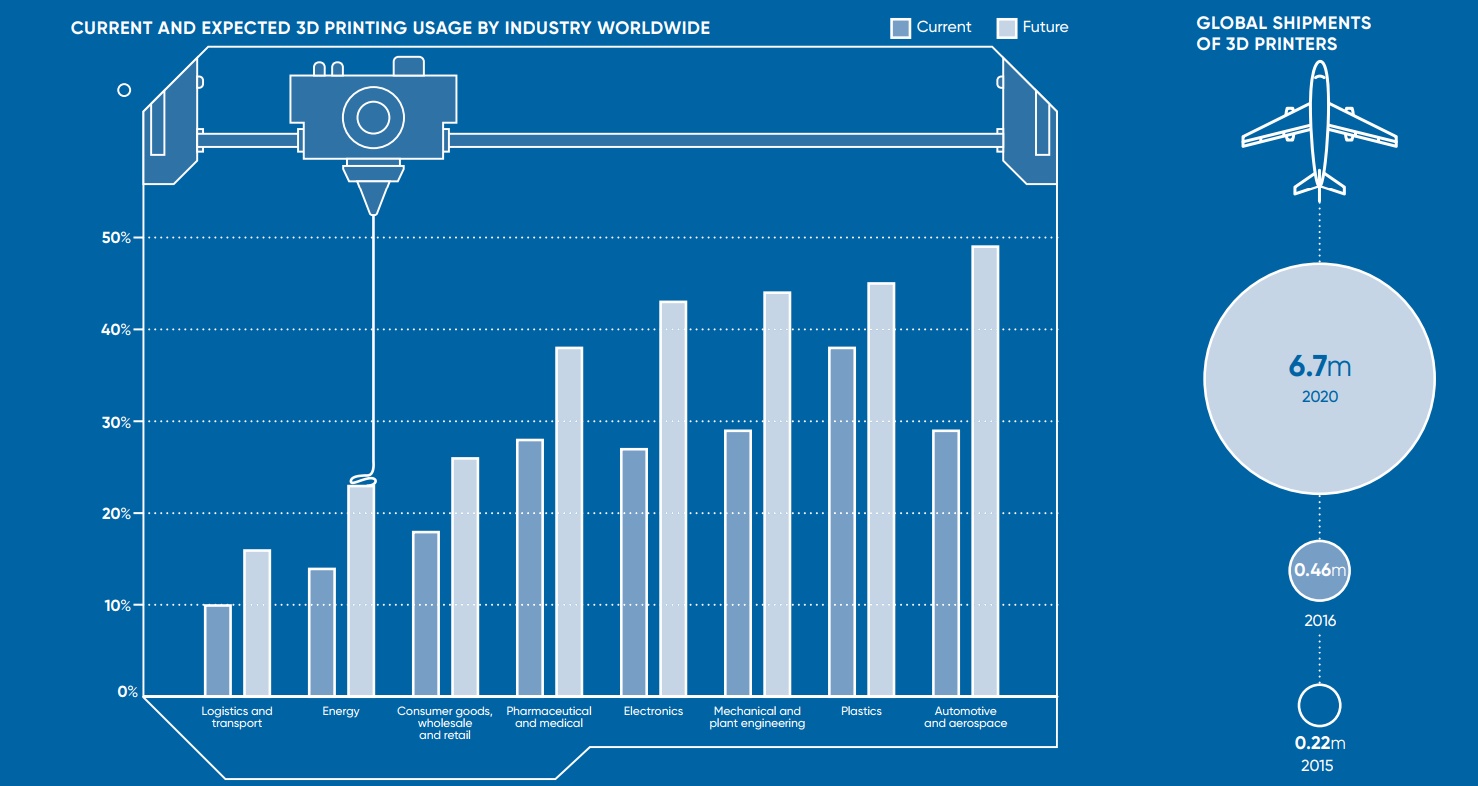
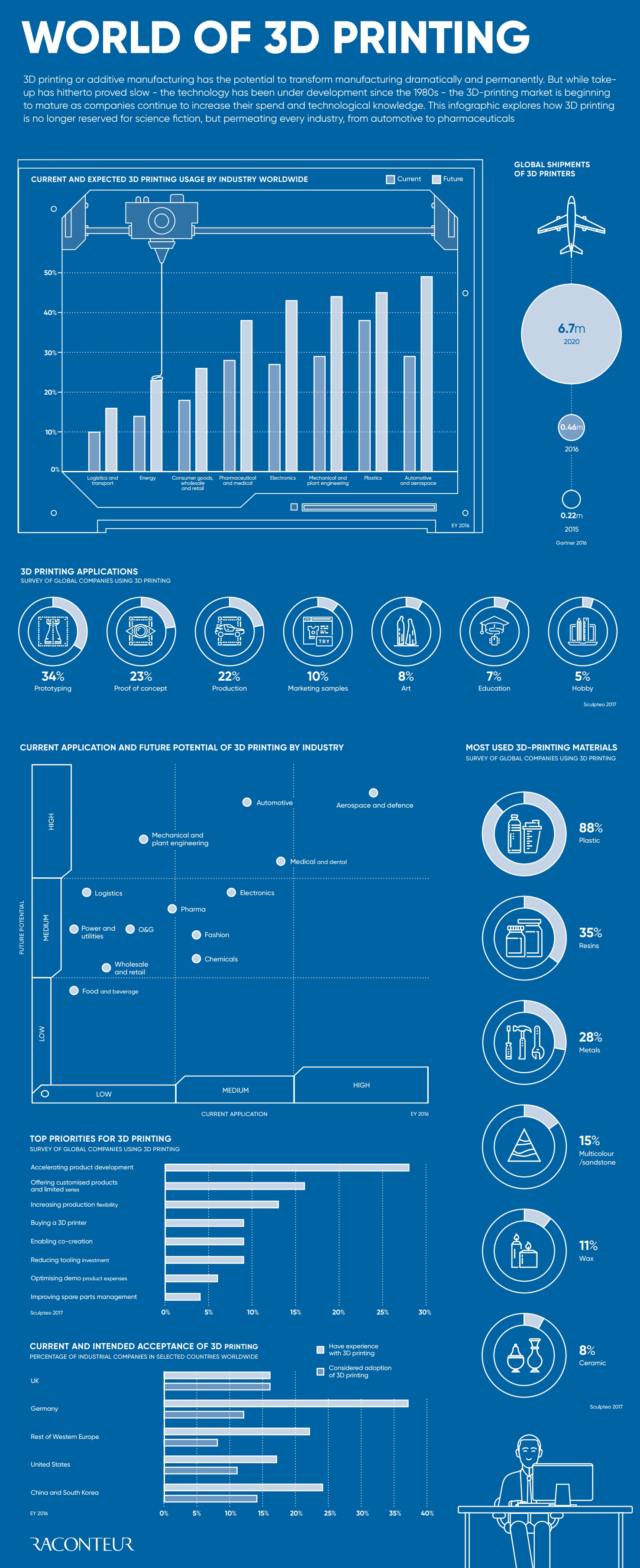
Today’s infographic comes to us from Raconteur, and it highlights a most recent snapshot of the 3D printing industry. Importantly, it shows that the technology is still chugging along in a way that is changing how things are made – just at a less hype-worthy pace.
Building From Ground Up
3D printing has now permeated practically every industry in at least some capacity, being used in a wide range of sectors from consumer goods to pharmaceuticals.
According to a report by EY, the potential for additive manufacturing is highest in the automotive and aerospace industries. For example, it’s expected that about half (49%) of automotive companies will use 3D printing to directly manufacture car parts in order to achieve operational efficiencies. These companies believe that 3D printing will help them address challenges such as demand for increased customization, continued improvement, and lightweight components.
As a result of increased demand and more familiarity with the technology, Gartner said shipments of 3D printers increased 108% between 2015 and 2016, resulting in 456,000 units shipped globally. More importantly, by 2020 this number will be at 6.7 million units, which would represent phenomenal growth for the technology.
As of today, most companies are still using 3D printers for accelerating product development, such as prototyping (34% of applications) and for proof of concept (23%). However, as 3D printing gets more use in additional areas – such as mass customization and collaboration on products – it’s possible the ship will really begin to sail, even if it was slightly delayed in getting out of the gate.
Technology
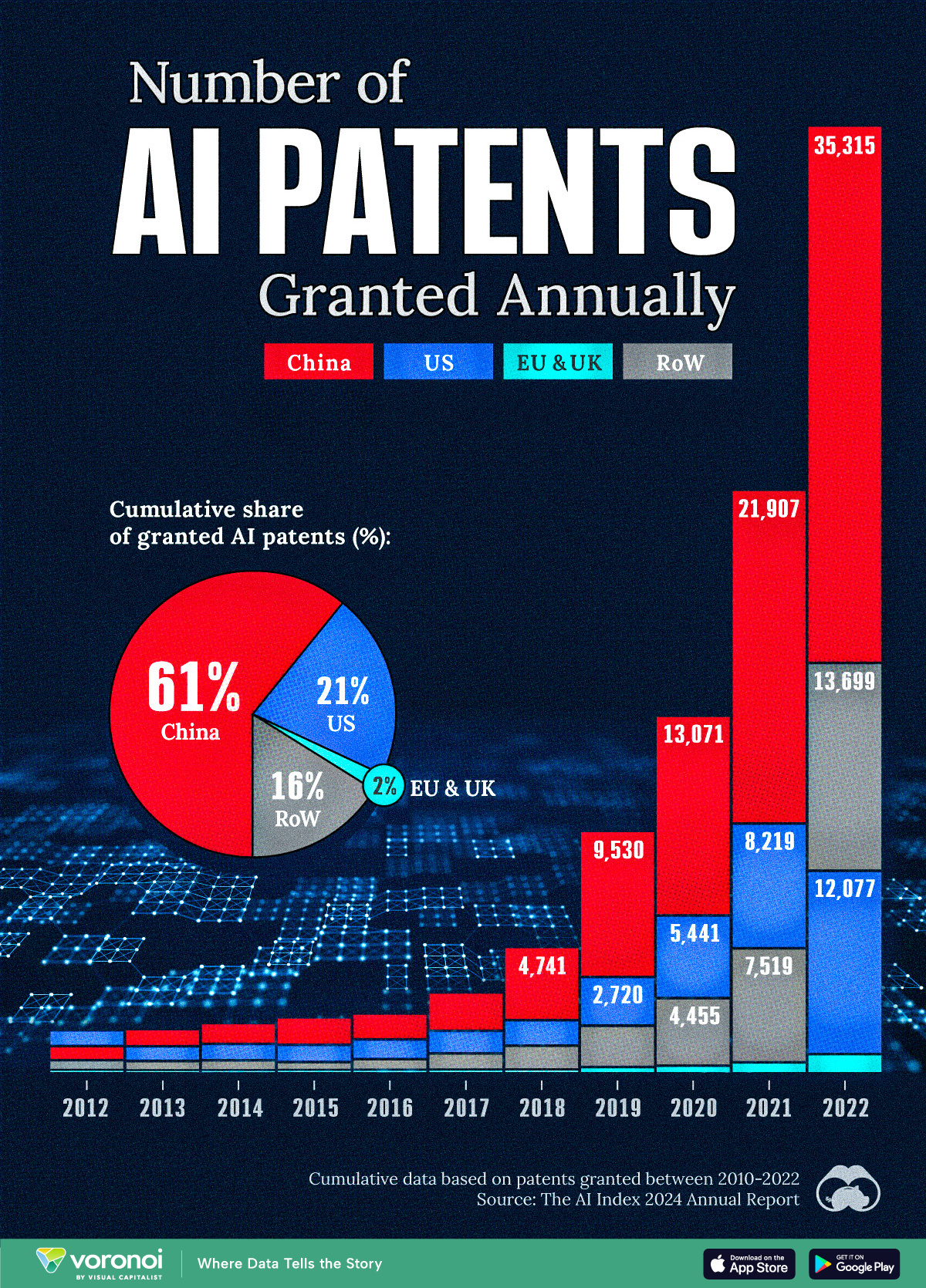
Visualizing AI Patents by Country
See which countries have been granted the most AI patents each year, from 2012 to 2022.
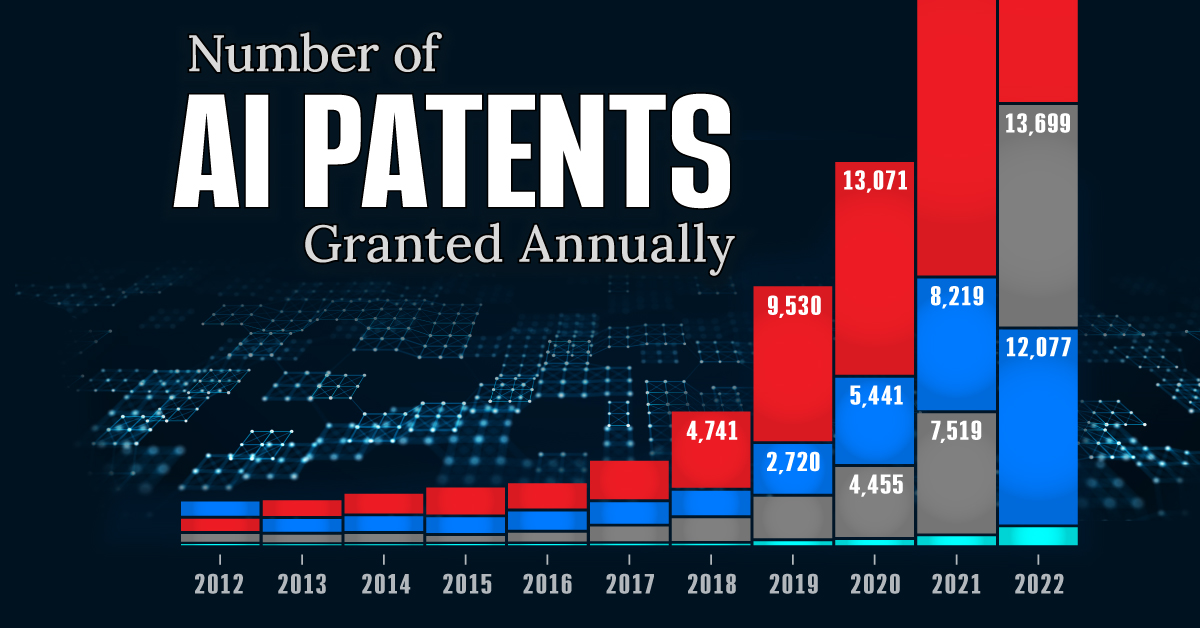
Visualizing AI Patents by Country
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on iOS or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
This infographic shows the number of AI-related patents granted each year from 2010 to 2022 (latest data available). These figures come from the Center for Security and Emerging Technology (CSET), accessed via Stanford University’s 2024 AI Index Report.
From this data, we can see that China first overtook the U.S. in 2013. Since then, the country has seen enormous growth in the number of AI patents granted each year.
| Year | China | EU and UK | U.S. | RoW | Global Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2010 | 307 | 137 | 984 | 571 | 1,999 |
| 2011 | 516 | 129 | 980 | 581 | 2,206 |
| 2012 | 926 | 112 | 950 | 660 | 2,648 |
| 2013 | 1,035 | 91 | 970 | 627 | 2,723 |
| 2014 | 1,278 | 97 | 1,078 | 667 | 3,120 |
| 2015 | 1,721 | 110 | 1,135 | 539 | 3,505 |
| 2016 | 1,621 | 128 | 1,298 | 714 | 3,761 |
| 2017 | 2,428 | 144 | 1,489 | 1,075 | 5,136 |
| 2018 | 4,741 | 155 | 1,674 | 1,574 | 8,144 |
| 2019 | 9,530 | 322 | 3,211 | 2,720 | 15,783 |
| 2020 | 13,071 | 406 | 5,441 | 4,455 | 23,373 |
| 2021 | 21,907 | 623 | 8,219 | 7,519 | 38,268 |
| 2022 | 35,315 | 1,173 | 12,077 | 13,699 | 62,264 |
In 2022, China was granted more patents than every other country combined.
While this suggests that the country is very active in researching the field of artificial intelligence, it doesn’t necessarily mean that China is the farthest in terms of capability.
Key Facts About AI Patents
According to CSET, AI patents relate to mathematical relationships and algorithms, which are considered abstract ideas under patent law. They can also have different meaning, depending on where they are filed.
In the U.S., AI patenting is concentrated amongst large companies including IBM, Microsoft, and Google. On the other hand, AI patenting in China is more distributed across government organizations, universities, and tech firms (e.g. Tencent).
In terms of focus area, China’s patents are typically related to computer vision, a field of AI that enables computers and systems to interpret visual data and inputs. Meanwhile America’s efforts are more evenly distributed across research fields.
Learn More About AI From Visual Capitalist
If you want to see more data visualizations on artificial intelligence, check out this graphic that shows which job departments will be impacted by AI the most.
-

 Markets1 week ago
Markets1 week agoU.S. Debt Interest Payments Reach $1 Trillion
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoRanked: The Most Valuable Housing Markets in America
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoWhich States Have the Highest Minimum Wage in America?
-

 AI2 weeks ago
AI2 weeks agoRanked: Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoRanked: The World’s Top Flight Routes, by Revenue
-

 Countries2 weeks ago
Countries2 weeks agoPopulation Projections: The World’s 6 Largest Countries in 2075
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoThe Top 10 States by Real GDP Growth in 2023
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoThe Smallest Gender Wage Gaps in OECD Countries