Markets
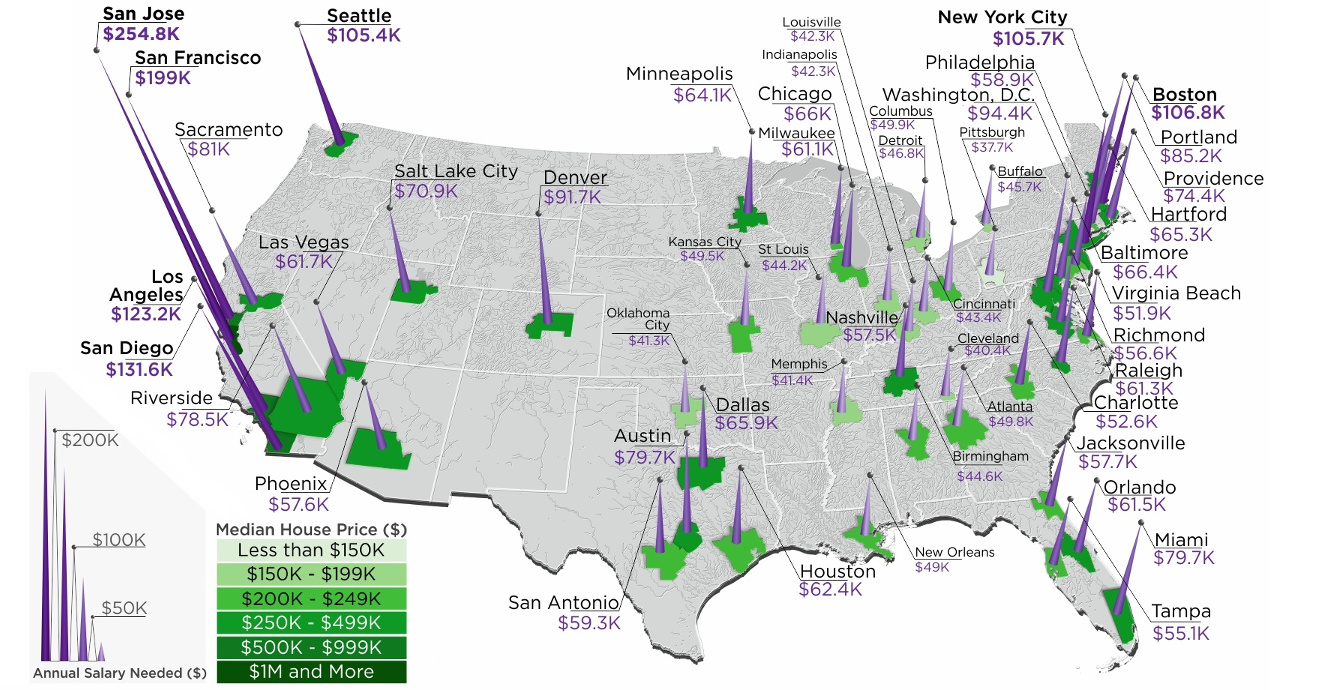
Mapped: The Salary Needed to Buy a Home in 50 U.S. Metro Areas
Check out the latest 2023 update of the salary needed to buy a home in the U.S.
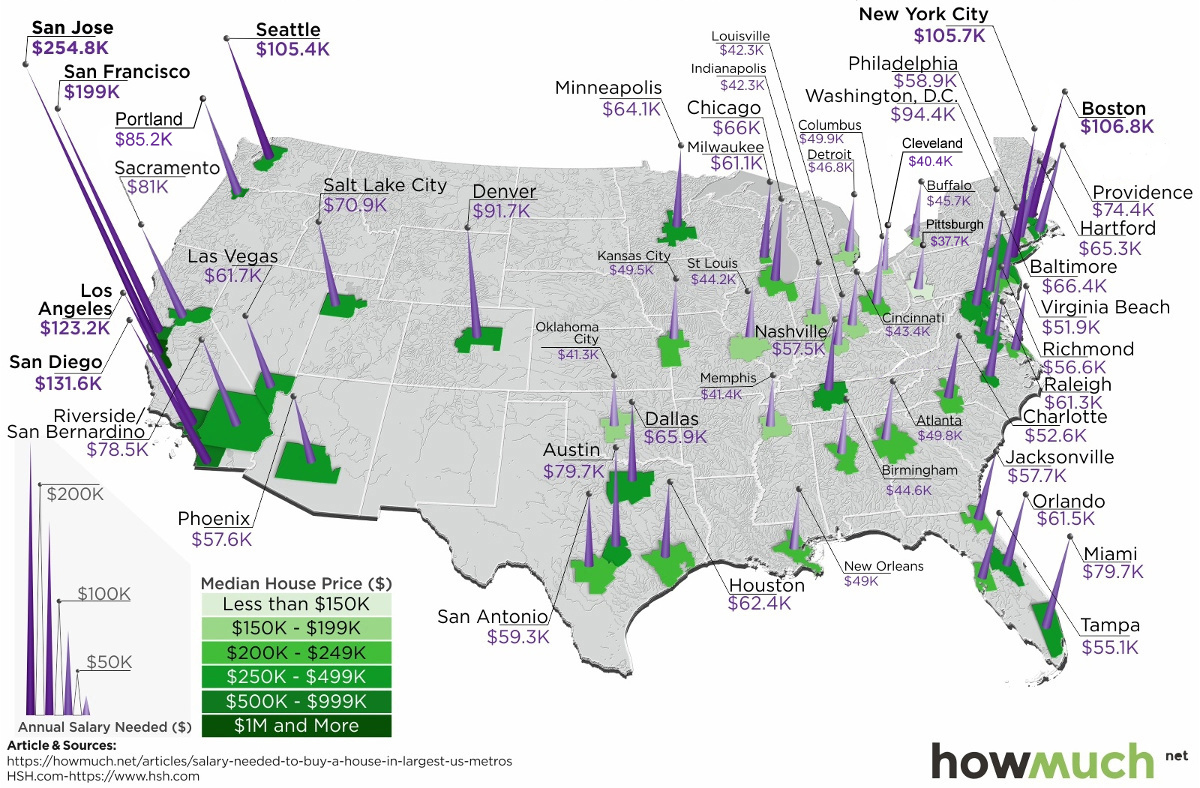
The Salary Needed to Buy a Home in 50 U.S. Metro Areas
Check out the latest 2023 update of the salary needed to buy a home in the U.S.
Over the last year, home prices have risen in 49 of the biggest 50 metro areas in the United States.
At the same time, mortgage rates have hit seven-year highs, making things more expensive for any prospective home buyer.
With this context in mind, today’s map comes from HowMuch.net, and it shows the salary needed to buy a home in the 50 largest U.S. metro areas.
The Least and Most Expensive Metro Areas
As a reference point, the median home in the United States costs about $257,600, according to the National Association of Realtors.
| Median Home Price | Montly Payment (PITI) | Salary Needed | |
|---|---|---|---|
| National | $257,600 | $1,433.91 | $61,453.51 |
With a 20% down payment and a 4.90% mortgage rate, and taking into account what’s needed to pay principal, interest, taxes, and insurance (PITI) on the home, it would mean a prospective buyer would need to have $61,453.51 in salary to afford such a purchase.
However, based on your frame of reference, this national estimate may seem extremely low or quite high. That’s because the salary required to buy in different major cities in the U.S. can fall anywhere between $37,659 to $254,835.
The 10 Cheapest Metro Areas
Here are the cheapest metro areas in the U.S., based on data and calculations from HSH.com:
| Rank | Metro Area | Median Home Price | Monthly Payment (PITI) | Salary Needed |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| #1 | Pittsburgh | $141,625 | $878.73 | $37,659.86 |
| #2 | Cleveland | $150,100 | $943.55 | $40,437.72 |
| #3 | Oklahoma City | $161,000 | $964.49 | $41,335.41 |
| #4 | Memphis | $174,000 | $966.02 | $41,400.93 |
| #5 | Indianapolis | $185,200 | $986.74 | $42,288.92 |
| #6 | Louisville | $180,100 | $987.54 | $42,323.15 |
| #7 | Cincinnati | $169,400 | $1,013.37 | $43,429.97 |
| #8 | St. Louis | $174,100 | $1,031.70 | $44,215.56 |
| #9 | Birmingham | $202,300 | $1,040.51 | $44,593.35 |
| #10 | Buffalo | $154,200 | $1,066.29 | $45,698.05 |
After the dust settles, Pittsburgh ranks as the cheapest metro area in the U.S. to buy a home. According to these calculations, buying a median home in Pittsburgh – which includes the surrounding metro area – requires an annual income of less than $40,000 to buy.
Just missing the list was Detroit, where a salary of $48,002.89 is needed.
The 10 Most Expensive Metro Areas
Now, here are the priciest markets in the country, also based on data from HSH.com:
| Rank | Metro Area | Median Home Price | Monthly Payment (PITI) | Salary Needed |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| #1 | San Jose | $1,250,000 | $5,946.17 | $254,835.73 |
| #2 | San Francisco | $952,200 | $4,642.82 | $198,978.01 |
| #3 | San Diego | $626,000 | $3,071.62 | $131,640.79 |
| #4 | Los Angeles | $576,100 | $2,873.64 | $123,156.01 |
| #5 | Boston | $460,300 | $2,491.76 | $106,789.93 |
| #6 | New York City | $403,900 | $2,465.97 | $105,684.33 |
| #7 | Seattle | $489,600 | $2,458.58 | $105,367.89 |
| #8 | Washington, D.C. | $417,400 | $2,202.87 | $94,408.70 |
| #9 | Denver | $438,300 | $2,139.02 | $91,672.45 |
| #10 | Portland | $389,000 | $1,987.37 | $85,173.08 |
Topping the list of the most expensive metro areas are San Jose and San Francisco, which are both cities fueled by the economic boom in Silicon Valley. Meanwhile, two other major metro areas in California, Los Angeles and San Diego, are not far behind.
New York City only ranks in sixth here, though it is worth noting that the NYC metro area extends well beyond the five boroughs. It includes Newark, Jersey City, and many nearby counties as well.
As a final point, it’s worth mentioning that all cities here (with the exception of Denver) are in coastal states.
Notes on Calculations
Data on median home prices comes from the National Association of Realtors and is based on 2018 Q4 information, while national mortgage rate data is derived from weekly surveys by Freddie Mac and the Mortgage Bankers Association of America for 30-year fixed rate mortgages.
Calculations include tax and homeowners insurance costs to determine the annual salary it takes to afford the base cost of owning a home (principal, interest, property tax and homeowner’s insurance, or PITI) in the nation’s 50 largest metropolitan areas.
Standard 28% “front-end” debt ratios and a 20% down payments subtracted from the median-home-price data are used to arrive at these figures.
Economy
Economic Growth Forecasts for G7 and BRICS Countries in 2024
The IMF has released its economic growth forecasts for 2024. How do the G7 and BRICS countries compare?

G7 & BRICS Real GDP Growth Forecasts for 2024
The International Monetary Fund’s (IMF) has released its real gross domestic product (GDP) growth forecasts for 2024, and while global growth is projected to stay steady at 3.2%, various major nations are seeing declining forecasts.
This chart visualizes the 2024 real GDP growth forecasts using data from the IMF’s 2024 World Economic Outlook for G7 and BRICS member nations along with Saudi Arabia, which is still considering an invitation to join the bloc.
Get the Key Insights of the IMF’s World Economic Outlook
Want a visual breakdown of the insights from the IMF’s 2024 World Economic Outlook report?
This visual is part of a special dispatch of the key takeaways exclusively for VC+ members.
Get the full dispatch of charts by signing up to VC+.
Mixed Economic Growth Prospects for Major Nations in 2024
Economic growth projections by the IMF for major nations are mixed, with the majority of G7 and BRICS countries forecasted to have slower growth in 2024 compared to 2023.
Only three BRICS-invited or member countries, Saudi Arabia, the UAE, and South Africa, have higher projected real GDP growth rates in 2024 than last year.
| Group | Country | Real GDP Growth (2023) | Real GDP Growth (2024P) |
|---|---|---|---|
| G7 | 🇺🇸 U.S. | 2.5% | 2.7% |
| G7 | 🇨🇦 Canada | 1.1% | 1.2% |
| G7 | 🇯🇵 Japan | 1.9% | 0.9% |
| G7 | 🇫🇷 France | 0.9% | 0.7% |
| G7 | 🇮🇹 Italy | 0.9% | 0.7% |
| G7 | 🇬🇧 UK | 0.1% | 0.5% |
| G7 | 🇩🇪 Germany | -0.3% | 0.2% |
| BRICS | 🇮🇳 India | 7.8% | 6.8% |
| BRICS | 🇨🇳 China | 5.2% | 4.6% |
| BRICS | 🇦🇪 UAE | 3.4% | 3.5% |
| BRICS | 🇮🇷 Iran | 4.7% | 3.3% |
| BRICS | 🇷🇺 Russia | 3.6% | 3.2% |
| BRICS | 🇪🇬 Egypt | 3.8% | 3.0% |
| BRICS-invited | 🇸🇦 Saudi Arabia | -0.8% | 2.6% |
| BRICS | 🇧🇷 Brazil | 2.9% | 2.2% |
| BRICS | 🇿🇦 South Africa | 0.6% | 0.9% |
| BRICS | 🇪🇹 Ethiopia | 7.2% | 6.2% |
| 🌍 World | 3.2% | 3.2% |
China and India are forecasted to maintain relatively high growth rates in 2024 at 4.6% and 6.8% respectively, but compared to the previous year, China is growing 0.6 percentage points slower while India is an entire percentage point slower.
On the other hand, four G7 nations are set to grow faster than last year, which includes Germany making its comeback from its negative real GDP growth of -0.3% in 2023.
Faster Growth for BRICS than G7 Nations
Despite mostly lower growth forecasts in 2024 compared to 2023, BRICS nations still have a significantly higher average growth forecast at 3.6% compared to the G7 average of 1%.
While the G7 countries’ combined GDP is around $15 trillion greater than the BRICS nations, with continued higher growth rates and the potential to add more members, BRICS looks likely to overtake the G7 in economic size within two decades.
BRICS Expansion Stutters Before October 2024 Summit
BRICS’ recent expansion has stuttered slightly, as Argentina’s newly-elected president Javier Milei declined its invitation and Saudi Arabia clarified that the country is still considering its invitation and has not joined BRICS yet.
Even with these initial growing pains, South Africa’s Foreign Minister Naledi Pandor told reporters in February that 34 different countries have submitted applications to join the growing BRICS bloc.
Any changes to the group are likely to be announced leading up to or at the 2024 BRICS summit which takes place October 22-24 in Kazan, Russia.
Get the Full Analysis of the IMF’s Outlook on VC+
This visual is part of an exclusive special dispatch for VC+ members which breaks down the key takeaways from the IMF’s 2024 World Economic Outlook.
For the full set of charts and analysis, sign up for VC+.
-

 Markets1 week ago
Markets1 week agoU.S. Debt Interest Payments Reach $1 Trillion
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoRanked: The Most Valuable Housing Markets in America
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoWhich States Have the Highest Minimum Wage in America?
-

 AI2 weeks ago
AI2 weeks agoRanked: Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoRanked: The World’s Top Flight Routes, by Revenue
-

 Countries2 weeks ago
Countries2 weeks agoPopulation Projections: The World’s 6 Largest Countries in 2075
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoThe Top 10 States by Real GDP Growth in 2023
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoThe Smallest Gender Wage Gaps in OECD Countries