Technology
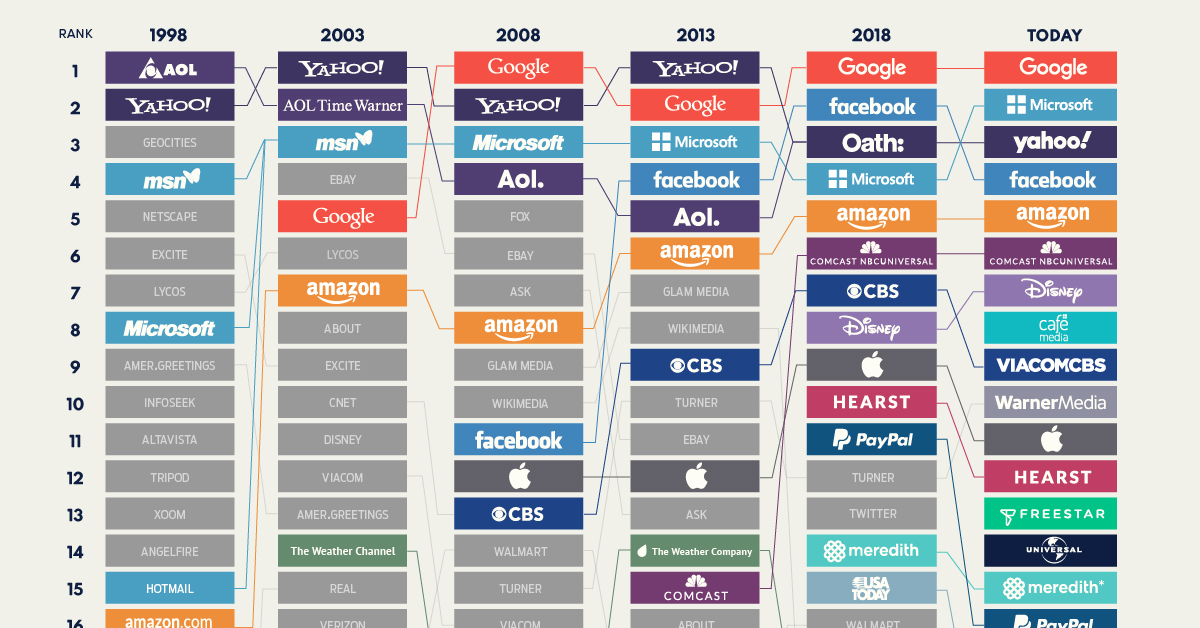
The 20 Internet Giants That Rule the Web

The 20 Internet Giants That Rule the Web (1998-Today)
With each passing year, an increasingly large segment of the population no longer remembers images loading a single pixel row at a time, the earsplitting sound of a 56k modem, or the early domination of web portals.
Many of the top websites in 1998 were news aggregators or search portals, which are easy concepts to understand. Today, brand touch-points are often spread out between devices (e.g. mobile apps vs. desktop) and a myriad of services and sub-brands (e.g. Facebook’s constellation of apps). As a result, the world’s biggest websites are complex, interconnected web properties.
The visualization above, which primarily uses data from ComScore’s U.S. Multi-Platform Properties ranking, looks at which of the internet giants have evolved to stay on top, and which have faded into internet lore.
America Moves Online
For millions of curious people the late ’90s, the iconic AOL compact disc was the key that opened the door to the World Wide Web. At its peak, an estimated 35 million people accessed the internet using AOL, and the company rode the Dotcom bubble to dizzying heights, reaching a valuation of $222 billion dollars in 1999.
AOL’s brand may not carry the caché it once did, but the brand never completely faded into obscurity. The company continually evolved, finally merging with Yahoo after Verizon acquired both of the legendary online brands. Verizon had high hopes for the company—called Oath—to evolve into a “third option” for advertisers and users who were fed up with Google and Facebook.
Sadly, those ambitions did not materialize as planned. In 2019, Oath was renamed Verizon Media, and was eventually sold once again in 2021.
A City of Gifs and Web Logs
As internet usage began to reach critical mass, web hosts such as AngelFire and GeoCities made it easy for people to create a new home on the Web.
GeoCities, in particular, made a huge impact on the early internet, hosting millions of websites and giving people a way to actually participate in creating online content. If it were a physical community of “home” pages, it would’ve been the third largest city in America, after Los Angeles.
This early online community was at risk of being erased permanently when GeoCities was finally shuttered by Yahoo in 2009, but luckily, the nonprofit Internet Archive took special efforts to create a thorough record of GeoCities-hosted pages.
From A to Z
In December of 1998, long before Amazon became the well-oiled retail machine we know today, the company was in the midst of a massive holiday season crunch.
In the real world, employees were pulling long hours and even sleeping in cars to keep the goods flowing, while online, Amazon.com had become one of the biggest sites on the internet as people began to get comfortable with the idea of purchasing goods online. Demand surged as the company began to expand their offering beyond books.
Amazon.com has grown to be the most successful merchant on the Internet.
– New York Times (1998)
Digital Magazine Rack
Meredith will be an unfamiliar brand to many people looking at today’s top 20 list. While Meredith may not be a household name, the company controlled many of the country’s most popular magazine brands (People, AllRecipes, Martha Stewart, Health, etc.) including their sizable digital footprints. The company also owned a slew of local television networks around the United States.
After its acquisition of Time Inc. in 2017, Meredith became the largest magazine publisher in the world. Since then, however, Meredith has divested many of its most valuable assets (Time, Sports Illustrated, Fortune). In December 2021, Meredith merged with IAC’s Dotdash.
“Hey, Google”
When people have burning questions, they increasingly turn to the internet for answers, but the diversity of sources for those answers is shrinking.
Even as recently as 2013, we can see that About.com, Ask.com, and Answers.com were still among the biggest websites in America. Today though, Google appears to have cemented its status as a universal wellspring of answers.
As smart speakers and voice assistants continue penetrate the market and influence search behavior, Google is unlikely to face any near-term competition from any company not already in the top 20 list.
New Kids on the Block
Social media has long since outgrown its fad stage and is now a common digital thread connecting people across the world. While Facebook rapidly jumped into the top 20 by 2007, other social media infused brands took longer to grow into internet giants.
By 2018, Twitter, Snapchat, and Facebook’s umbrella of platforms were all in the top 20, and you can see a more detailed and up-to-date breakdown of the social media universe here.
A Tangled Web
Today’s internet giants have evolved far beyond their ancestors from two decades ago. Many of the companies in the top 20 run numerous platforms and content streams, and more often than not, they are not household names.
A few, such as Mediavine and CafeMedia, are services that manage ads. Others manage content distribution, such as music, or manage a constellation of smaller media properties, as is the case with Hearst.
Lastly, there are still the tech giants. Remarkably, three of the top five web properties were in the top 20 list in 1998. In the fast-paced digital ecosystem, that’s some remarkable staying power.
This article was inspired by an earlier work by Philip Bump, published in the Washington Post.
Technology
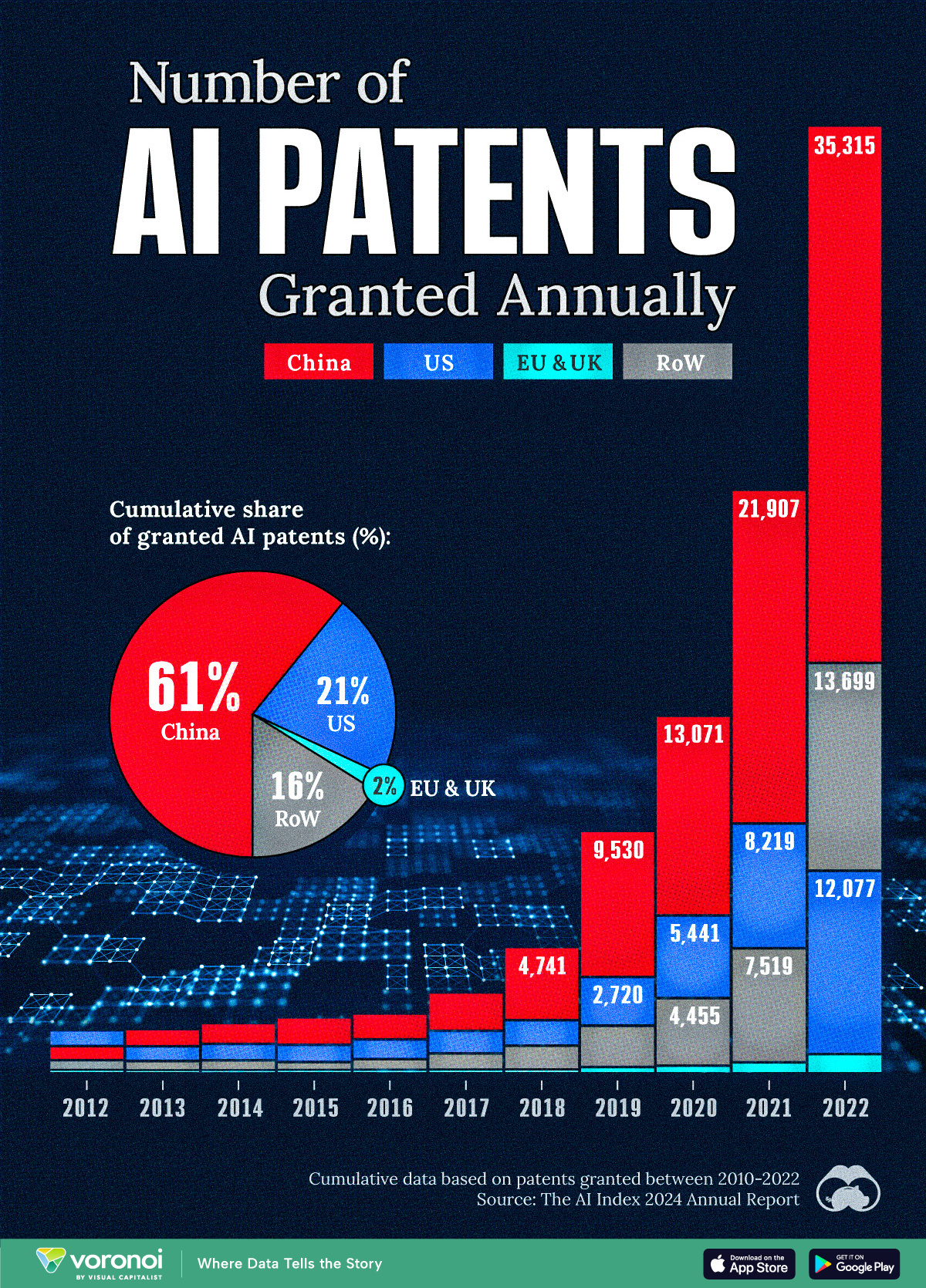
Visualizing AI Patents by Country
See which countries have been granted the most AI patents each year, from 2012 to 2022.
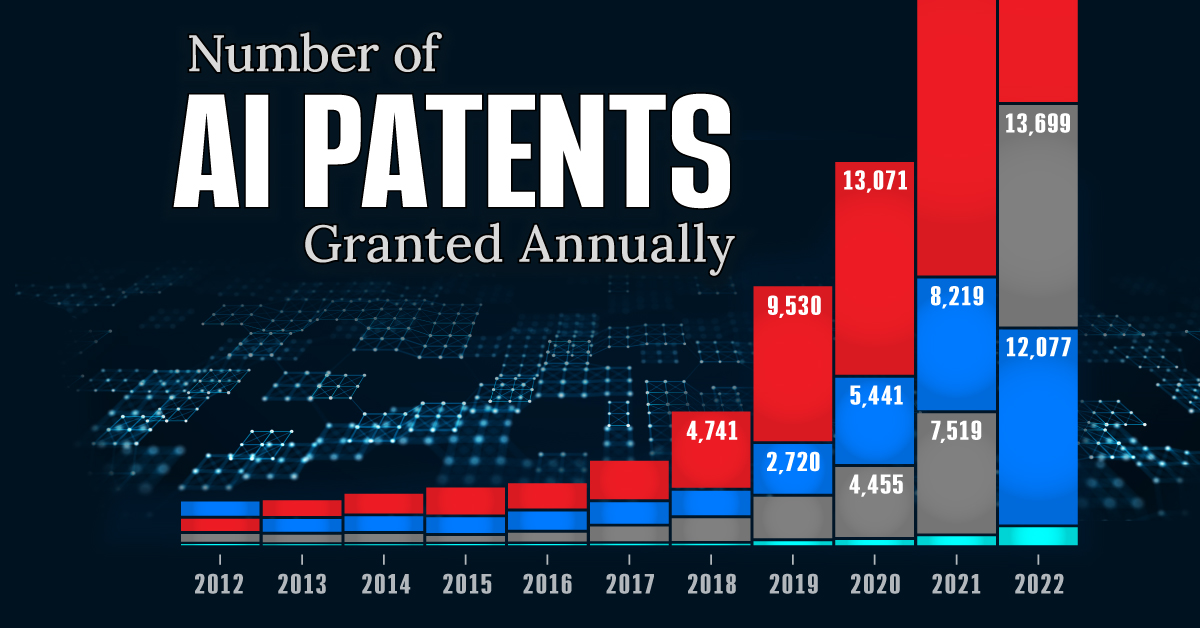
Visualizing AI Patents by Country
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on iOS or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
This infographic shows the number of AI-related patents granted each year from 2010 to 2022 (latest data available). These figures come from the Center for Security and Emerging Technology (CSET), accessed via Stanford University’s 2024 AI Index Report.
From this data, we can see that China first overtook the U.S. in 2013. Since then, the country has seen enormous growth in the number of AI patents granted each year.
| Year | China | EU and UK | U.S. | RoW | Global Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2010 | 307 | 137 | 984 | 571 | 1,999 |
| 2011 | 516 | 129 | 980 | 581 | 2,206 |
| 2012 | 926 | 112 | 950 | 660 | 2,648 |
| 2013 | 1,035 | 91 | 970 | 627 | 2,723 |
| 2014 | 1,278 | 97 | 1,078 | 667 | 3,120 |
| 2015 | 1,721 | 110 | 1,135 | 539 | 3,505 |
| 2016 | 1,621 | 128 | 1,298 | 714 | 3,761 |
| 2017 | 2,428 | 144 | 1,489 | 1,075 | 5,136 |
| 2018 | 4,741 | 155 | 1,674 | 1,574 | 8,144 |
| 2019 | 9,530 | 322 | 3,211 | 2,720 | 15,783 |
| 2020 | 13,071 | 406 | 5,441 | 4,455 | 23,373 |
| 2021 | 21,907 | 623 | 8,219 | 7,519 | 38,268 |
| 2022 | 35,315 | 1,173 | 12,077 | 13,699 | 62,264 |
In 2022, China was granted more patents than every other country combined.
While this suggests that the country is very active in researching the field of artificial intelligence, it doesn’t necessarily mean that China is the farthest in terms of capability.
Key Facts About AI Patents
According to CSET, AI patents relate to mathematical relationships and algorithms, which are considered abstract ideas under patent law. They can also have different meaning, depending on where they are filed.
In the U.S., AI patenting is concentrated amongst large companies including IBM, Microsoft, and Google. On the other hand, AI patenting in China is more distributed across government organizations, universities, and tech firms (e.g. Tencent).
In terms of focus area, China’s patents are typically related to computer vision, a field of AI that enables computers and systems to interpret visual data and inputs. Meanwhile America’s efforts are more evenly distributed across research fields.
Learn More About AI From Visual Capitalist
If you want to see more data visualizations on artificial intelligence, check out this graphic that shows which job departments will be impacted by AI the most.
-

 Markets1 week ago
Markets1 week agoU.S. Debt Interest Payments Reach $1 Trillion
-

 Business2 weeks ago
Business2 weeks agoCharted: Big Four Market Share by S&P 500 Audits
-

 Real Estate2 weeks ago
Real Estate2 weeks agoRanked: The Most Valuable Housing Markets in America
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoWhich States Have the Highest Minimum Wage in America?
-

 AI2 weeks ago
AI2 weeks agoRanked: Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoRanked: The World’s Top Flight Routes, by Revenue
-

 Demographics2 weeks ago
Demographics2 weeks agoPopulation Projections: The World’s 6 Largest Countries in 2075
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoThe Top 10 States by Real GDP Growth in 2023