Markets
Every U.S. Valuation Milestone Since 1781, Including Apple’s Ascent to $1 Trillion
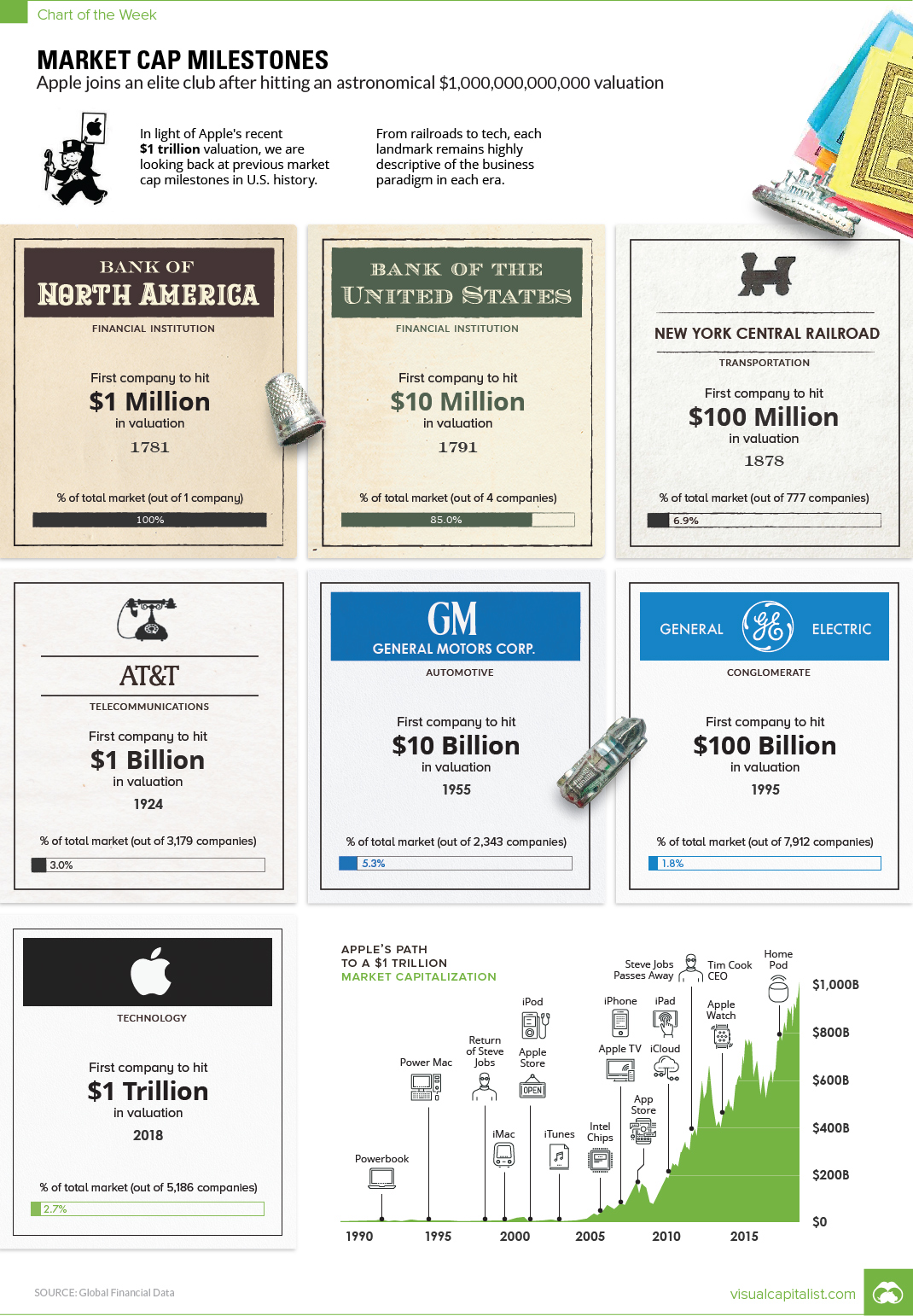
Apple’s Ascent to $1 Trillion, and Other Market Cap Milestones
The market has been buzzing about Apple’s $1 trillion market valuation.
It’s an incredible amount of wealth creation in any context – but getting to 12 zeros is especially impressive when you consider that Apple was just 90 days from declaring bankruptcy in 1997.
Today’s chart shows this milestone – as well as many of the ones before it – through a period of over 200 years of U.S. market history. It was inspired by this interesting post by Global Financial Data, which is worth reading in its own right.
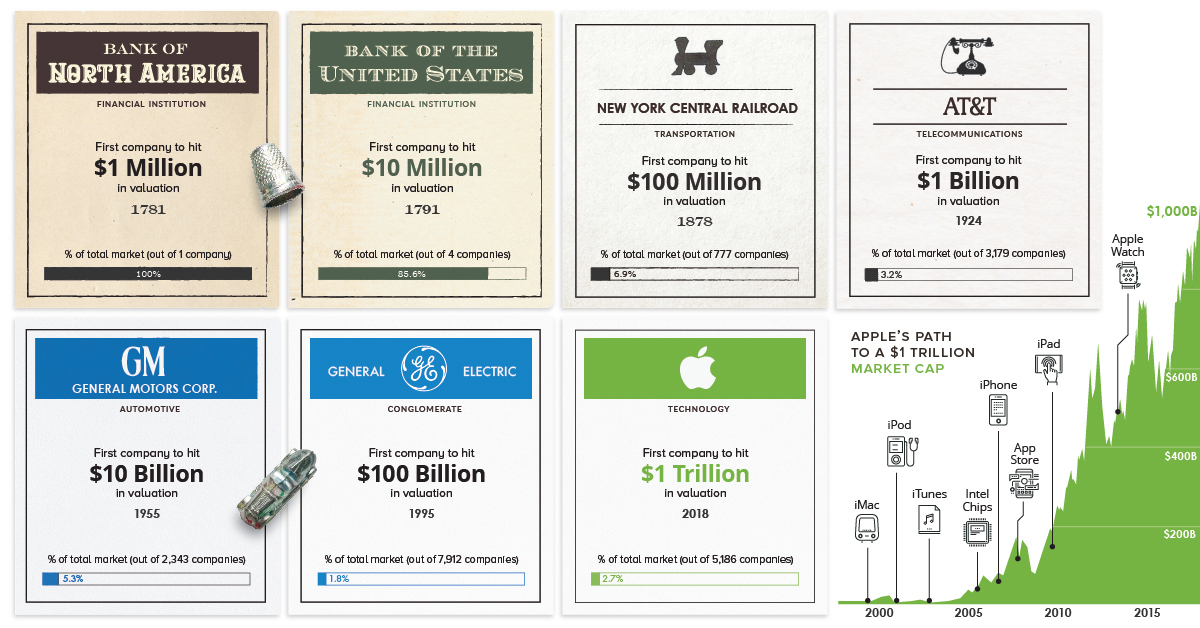
Market Cap Milestones
Over the last couple of centuries, and with the exception of brief moments in time such as the Japanese stock bubble of 1989, the largest company in the world has almost always been based in the United States.
Here are the major market cap milestones in the U.S. that preceded Apple’s recent $1 trillion valuation, achieved August 2nd, 2018:
Bank of North America (1781)
The first company to hit $1 million in market capitalization. It was the first ever IPO in the United States.
Bank of the United States (1791)
The first company to hit $10 million in market capitalization had a 20 year charter to start, and was championed by Alexander Hamilton.
New York Central Railroad (1878)
The first company to hit $100 million in market capitalization was a crucial railroad that connected New York City, Chicago, Boston, and St. Louis.
AT&T (1924)
The first company to hit $1 billion in market capitalization – this was far before the breakup of AT&T into the “Baby Bells”, which occurred in 1982.
General Motors (1955)
The first company to hit $10 billion in market capitalization. The 1950s were the golden years of growth for U.S. auto companies like GM and Ford, taking place well before the mass entry of foreign companies like Toyota into the domestic automobile market.
General Electric (1995)
The first company to hit $100 billion in market capitalization was only able to do so 23 years ago.
The Other Trillion Dollar Company
Interestingly, Apple is not the first company globally to ever hit $1 trillion in market capitalization.
The feat was achieved momentarily by PetroChina in 2007, after a successful debut on the Shanghai Stock Exchange that same year.
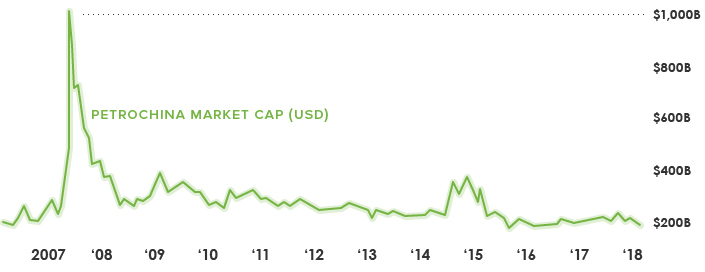
The stock price tripled that day to hit the mark, but then the company eventually lost more than $800 billion in valuation as oil prices collapsed and the Financial Crisis set in.
Markets
U.S. Debt Interest Payments Reach $1 Trillion
U.S. debt interest payments have surged past the $1 trillion dollar mark, amid high interest rates and an ever-expanding debt burden.

U.S. Debt Interest Payments Reach $1 Trillion
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on iOS or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
The cost of paying for America’s national debt crossed the $1 trillion dollar mark in 2023, driven by high interest rates and a record $34 trillion mountain of debt.
Over the last decade, U.S. debt interest payments have more than doubled amid vast government spending during the pandemic crisis. As debt payments continue to soar, the Congressional Budget Office (CBO) reported that debt servicing costs surpassed defense spending for the first time ever this year.
This graphic shows the sharp rise in U.S. debt payments, based on data from the Federal Reserve.
A $1 Trillion Interest Bill, and Growing
Below, we show how U.S. debt interest payments have risen at a faster pace than at another time in modern history:
| Date | Interest Payments | U.S. National Debt |
|---|---|---|
| 2023 | $1.0T | $34.0T |
| 2022 | $830B | $31.4T |
| 2021 | $612B | $29.6T |
| 2020 | $518B | $27.7T |
| 2019 | $564B | $23.2T |
| 2018 | $571B | $22.0T |
| 2017 | $493B | $20.5T |
| 2016 | $460B | $20.0T |
| 2015 | $435B | $18.9T |
| 2014 | $442B | $18.1T |
| 2013 | $425B | $17.2T |
| 2012 | $417B | $16.4T |
| 2011 | $433B | $15.2T |
| 2010 | $400B | $14.0T |
| 2009 | $354B | $12.3T |
| 2008 | $380B | $10.7T |
| 2007 | $414B | $9.2T |
| 2006 | $387B | $8.7T |
| 2005 | $355B | $8.2T |
| 2004 | $318B | $7.6T |
| 2003 | $294B | $7.0T |
| 2002 | $298B | $6.4T |
| 2001 | $318B | $5.9T |
| 2000 | $353B | $5.7T |
| 1999 | $353B | $5.8T |
| 1998 | $360B | $5.6T |
| 1997 | $368B | $5.5T |
| 1996 | $362B | $5.3T |
| 1995 | $357B | $5.0T |
| 1994 | $334B | $4.8T |
| 1993 | $311B | $4.5T |
| 1992 | $306B | $4.2T |
| 1991 | $308B | $3.8T |
| 1990 | $298B | $3.4T |
| 1989 | $275B | $3.0T |
| 1988 | $254B | $2.7T |
| 1987 | $240B | $2.4T |
| 1986 | $225B | $2.2T |
| 1985 | $219B | $1.9T |
| 1984 | $205B | $1.7T |
| 1983 | $176B | $1.4T |
| 1982 | $157B | $1.2T |
| 1981 | $142B | $1.0T |
| 1980 | $113B | $930.2B |
| 1979 | $96B | $845.1B |
| 1978 | $84B | $789.2B |
| 1977 | $69B | $718.9B |
| 1976 | $61B | $653.5B |
| 1975 | $55B | $576.6B |
| 1974 | $50B | $492.7B |
| 1973 | $45B | $469.1B |
| 1972 | $39B | $448.5B |
| 1971 | $36B | $424.1B |
| 1970 | $35B | $389.2B |
| 1969 | $30B | $368.2B |
| 1968 | $25B | $358.0B |
| 1967 | $23B | $344.7B |
| 1966 | $21B | $329.3B |
Interest payments represent seasonally adjusted annual rate at the end of Q4.
At current rates, the U.S. national debt is growing by a remarkable $1 trillion about every 100 days, equal to roughly $3.6 trillion per year.
As the national debt has ballooned, debt payments even exceeded Medicaid outlays in 2023—one of the government’s largest expenditures. On average, the U.S. spent more than $2 billion per day on interest costs last year. Going further, the U.S. government is projected to spend a historic $12.4 trillion on interest payments over the next decade, averaging about $37,100 per American.
Exacerbating matters is that the U.S. is running a steep deficit, which stood at $1.1 trillion for the first six months of fiscal 2024. This has accelerated due to the 43% increase in debt servicing costs along with a $31 billion dollar increase in defense spending from a year earlier. Additionally, a $30 billion increase in funding for the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation in light of the regional banking crisis last year was a major contributor to the deficit increase.
Overall, the CBO forecasts that roughly 75% of the federal deficit’s increase will be due to interest costs by 2034.
-

 Real Estate2 weeks ago
Real Estate2 weeks agoVisualizing America’s Shortage of Affordable Homes
-

 Technology1 week ago
Technology1 week agoRanked: Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share
-

 Money1 week ago
Money1 week agoWhich States Have the Highest Minimum Wage in America?
-

 Real Estate1 week ago
Real Estate1 week agoRanked: The Most Valuable Housing Markets in America
-

 Business2 weeks ago
Business2 weeks agoCharted: Big Four Market Share by S&P 500 Audits
-

 AI2 weeks ago
AI2 weeks agoThe Stock Performance of U.S. Chipmakers So Far in 2024
-

 Misc2 weeks ago
Misc2 weeks agoAlmost Every EV Stock is Down After Q1 2024
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoWhere Does One U.S. Tax Dollar Go?