Technology
There’s Big Money to Be Made in Asteroid Mining
Click below to expand to the full version of the infographic
Image courtesy of: Wired
There’s Big Money to Be Made in Asteroid Mining
See the full version of the infographic.
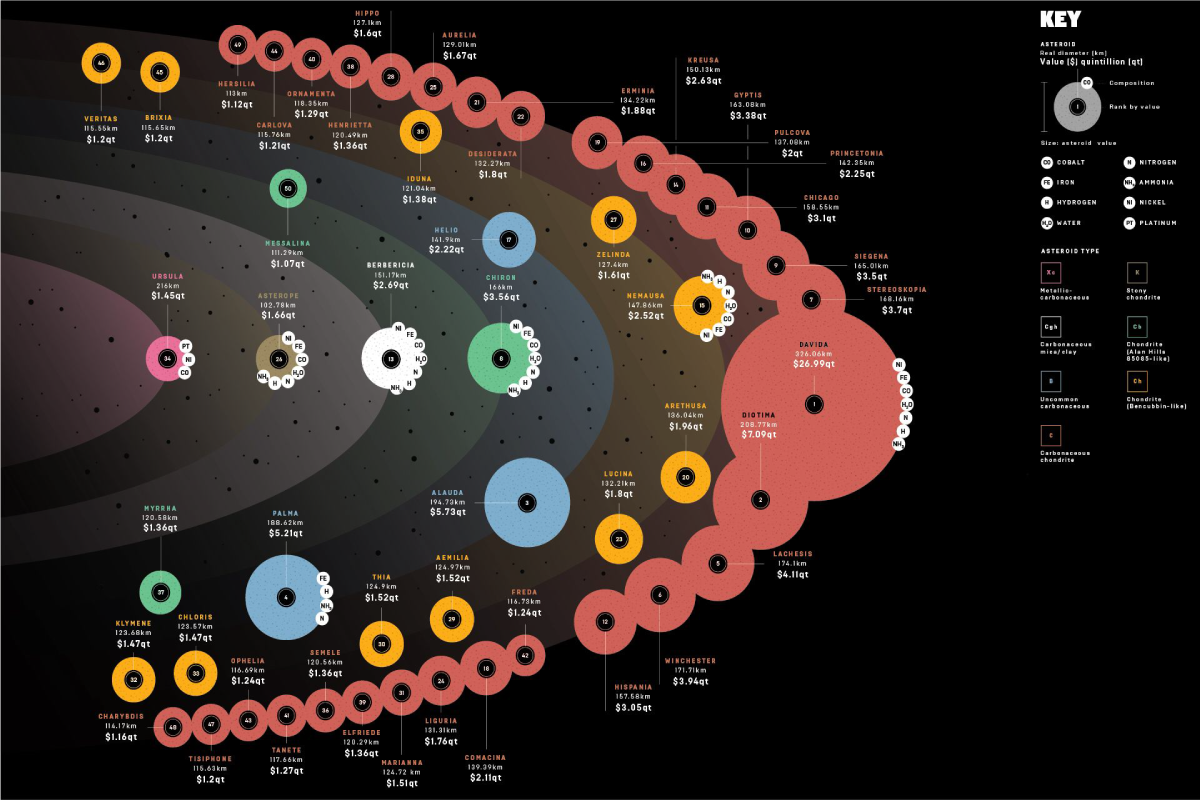
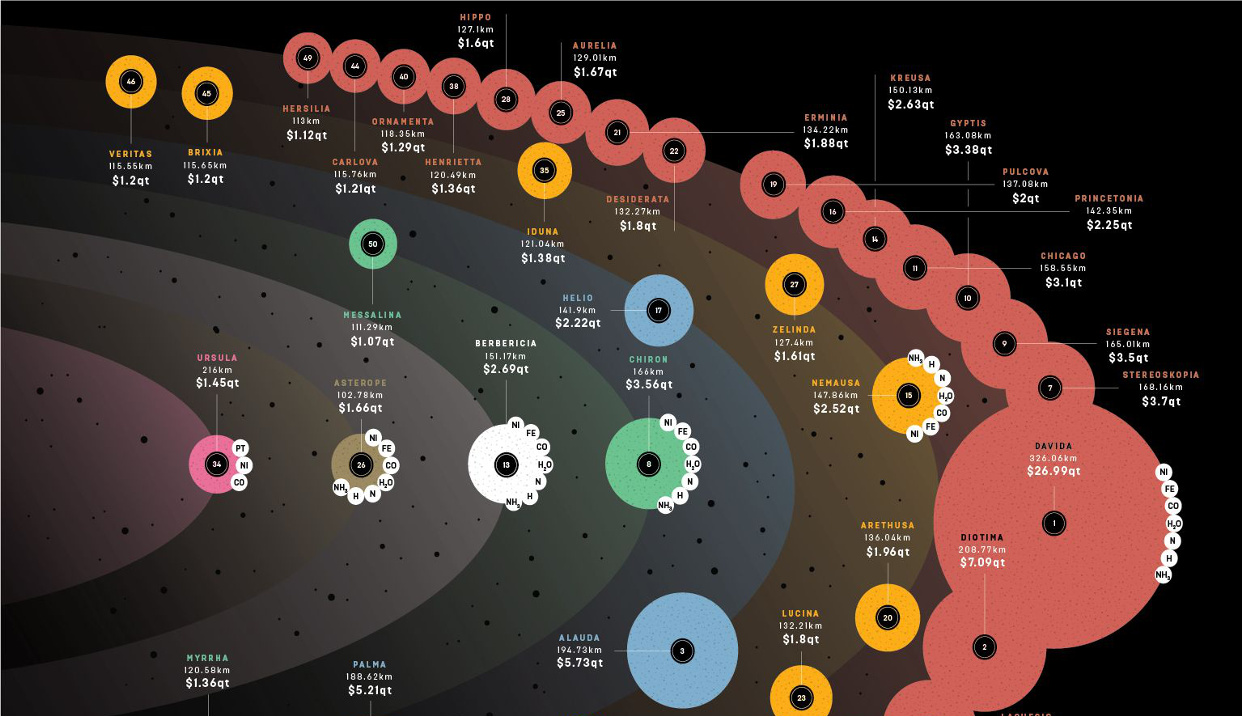
If humans were ever able to get their hands on just one asteroid, it would be a game-changer.
That’s because the value of many asteroids are measured in the quintillions of dollars, which makes the market for Earth’s annual production of raw metals – about $660 billion per year – look paltry in comparison.
The reality is that the Earth’s crust is saddled with uneconomic materials, while certain types of asteroids are almost pure metal. X-type asteroids, for example, are thought to be the remnants of large asteroids that were pulverized in collisions in which their dense, metallic cores got separated from the mantle.
There is one such X-type asteroid near earth that is believed to hold more platinum than ever mined in human history.
Near-Earth Mining Targets
Asteroid mining companies such as Planetary Resources and Deep Space Industries are the first-movers in the sector, and they’ve already started to identify prospective targets to boldly mine where no man has mined before.
Both companies are looking specifically at near-Earth asteroids in the near-term, which are the easiest ones to get to. So far, roughly 15,000 such objects have been discovered, and their orbits all come in close proximity to Earth.
Planetary Resources has identified eight of these as potential targets and has listed them publicly, while Deep Space Industries has claimed to have “half a dozen very, very attractive targets”.
While these will be important for verifying the feasibility of asteroid mining, the reality is that near-Earth asteroids are just tiny minnows in an ocean of big fish. Their main advantage is that they are relatively easy to access, but most targets identified so far are less than 1,000 ft (300 m) in diameter – meaning the potential economic payoff of a mission is still unclear.
Where the Money is Made
The exciting part of asteroid mining is the asteroid belt itself, which lies between Mars and Jupiter. It is there that over 1 million asteroids exist, including about 200 that are over 60 miles (100 km) in diameter.
NASA estimates this belt to hold $700 quintillion of bounty. That’s about $100 billion for each person on Earth.
There are obviously many technical challenges that must be overcome to make mining these possible. As it stands, NASA aims to bring back a grab sample from the surface of asteroid Bennu that is 2 and 70 ounces (about 60 to 2,000 grams) in size. The cost of the mission? Approximately $1 billion.
To do anything like that on a large scale will require robots, spacecraft, and other technologies that simply do not exist yet. Further, missions like this could cost trillions of dollars – a huge risk and burden in the case that a mission is unsuccessful.
Until then, the near-Earth asteroids are the fertile testing ground for aspirational asteroid miners – and we look forward to seeing what is possible in the future.
Brands
How Tech Logos Have Evolved Over Time
From complete overhauls to more subtle tweaks, these tech logos have had quite a journey. Featuring: Google, Apple, and more.

How Tech Logos Have Evolved Over Time
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on iOS or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
One would be hard-pressed to find a company that has never changed its logo. Granted, some brands—like Rolex, IBM, and Coca-Cola—tend to just have more minimalistic updates. But other companies undergo an entire identity change, thus necessitating a full overhaul.
In this graphic, we visualized the evolution of prominent tech companies’ logos over time. All of these brands ranked highly in a Q1 2024 YouGov study of America’s most famous tech brands. The logo changes are sourced from 1000logos.net.
How Many Times Has Google Changed Its Logo?
Google and Facebook share a 98% fame rating according to YouGov. But while Facebook’s rise was captured in The Social Network (2010), Google’s history tends to be a little less lionized in popular culture.
For example, Google was initially called “Backrub” because it analyzed “back links” to understand how important a website was. Since its founding, Google has undergone eight logo changes, finally settling on its current one in 2015.
| Company | Number of Logo Changes |
|---|---|
| 8 | |
| HP | 8 |
| Amazon | 6 |
| Microsoft | 6 |
| Samsung | 6 |
| Apple | 5* |
Note: *Includes color changes. Source: 1000Logos.net
Another fun origin story is Microsoft, which started off as Traf-O-Data, a traffic counter reading company that generated reports for traffic engineers. By 1975, the company was renamed. But it wasn’t until 2012 that Microsoft put the iconic Windows logo—still the most popular desktop operating system—alongside its name.
And then there’s Samsung, which started as a grocery trading store in 1938. Its pivot to electronics started in the 1970s with black and white television sets. For 55 years, the company kept some form of stars from its first logo, until 1993, when the iconic encircled blue Samsung logo debuted.
Finally, Apple’s first logo in 1976 featured Isaac Newton reading under a tree—moments before an apple fell on his head. Two years later, the iconic bitten apple logo would be designed at Steve Jobs’ behest, and it would take another two decades for it to go monochrome.
-

 Green1 week ago
Green1 week agoRanked: The Countries With the Most Air Pollution in 2023
-

 Automotive2 weeks ago
Automotive2 weeks agoAlmost Every EV Stock is Down After Q1 2024
-

 AI2 weeks ago
AI2 weeks agoThe Stock Performance of U.S. Chipmakers So Far in 2024
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoCharted: Big Four Market Share by S&P 500 Audits
-

 Real Estate2 weeks ago
Real Estate2 weeks agoRanked: The Most Valuable Housing Markets in America
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoWhich States Have the Highest Minimum Wage in America?
-

 AI2 weeks ago
AI2 weeks agoRanked: Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share
-

 Travel2 weeks ago
Travel2 weeks agoRanked: The World’s Top Flight Routes, by Revenue