Money
The History of Money Explained in One Infographic

The History of Money Explained in One Infographic
Today’s infographic from Mint.com highlights the history of money, including the many monetary experiments that have taken place since ancient times.
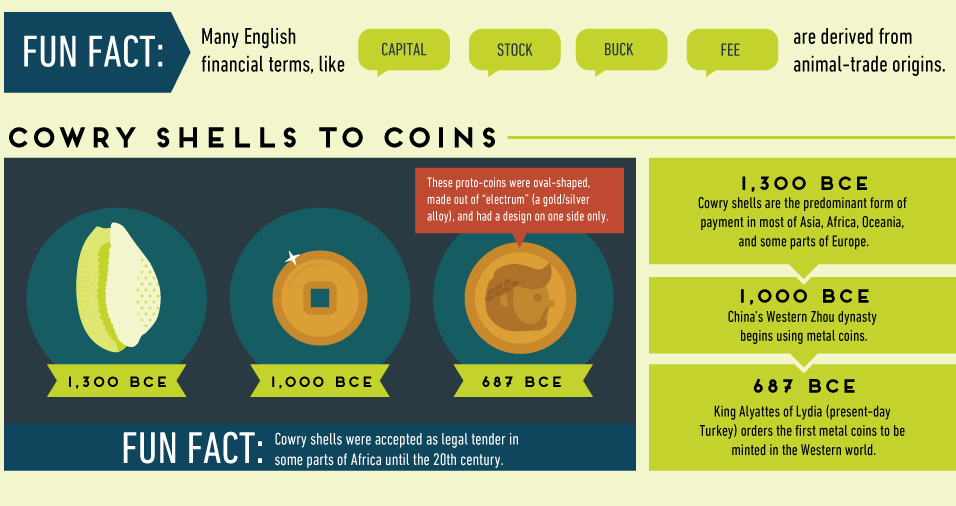
Some innovations have stood the test of time – precious metals, for example, have been used for thousands of years. Paper money and banknotes are also widespread in use, after first being turned to in China in 806 after a copper shortage prevented the minting of new coins.
Other experiments didn’t have much staying power. The adoption of strange currencies such as squirrel pelts, cowry shells, or parmesan cheese are only remembered for their peculiarity.
Further, other attempts to stabilize the monetary system were abandoned early as well. The original U.S. gold standard lasted just 54 years, after FDR ditched it during the Great Depression. The Bretton Woods version (gold-exchange standard) lasted even shorter, abandoned after being in place for 26 years when Nixon ended all convertibility between the U.S. dollar and gold in 1971.
The Newest Chapter in Our Monetary History
Although the infographic ends with the introduction of cryptocurrency in 2009, it should be noted that the newest chapter in the history of money is taking place right before our eyes.
The “War on Cash” has been accelerating in recent years, as governments and central banks have called for the elimination of high denomination banknotes. While these anti-cash motions have also been made in many Western countries, the most vivid example of the demonetization is currently happening in India.
In November 2016, Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi demonetized 500 and 1000 rupee notes, eliminating 86% of the country’s notes overnight. While Indians could theoretically exchange 500 and 1,000 rupee notes for higher denominations, it was only up to a limit of 4,000 rupees per person. Sums above that had to be routed through a bank account in a country where only 50% of Indians have such access.
There have been at least 112 reported deaths associated with this demonetization – including suicides and the passing of elderly people waiting in bank queues for days to exchange money. India’s largest organization of manufacturers, the All India Manufacturers Organization, also estimates in a report that micro-small scale industries suffered 35% jobs losses and a 50% dip in revenue in the first 34 days since demonetization.
While demonetization in India is off to a rough start, some believe it can still be ultimately successful in the long-term. Regardless, the “War on Cash” still has incredible global momentum – and the end result – however it turns out – will likely form another important chapter in the history of money.
Demographics
The Smallest Gender Wage Gaps in OECD Countries
Which OECD countries have the smallest gender wage gaps? We look at the 10 countries with gaps lower than the average.
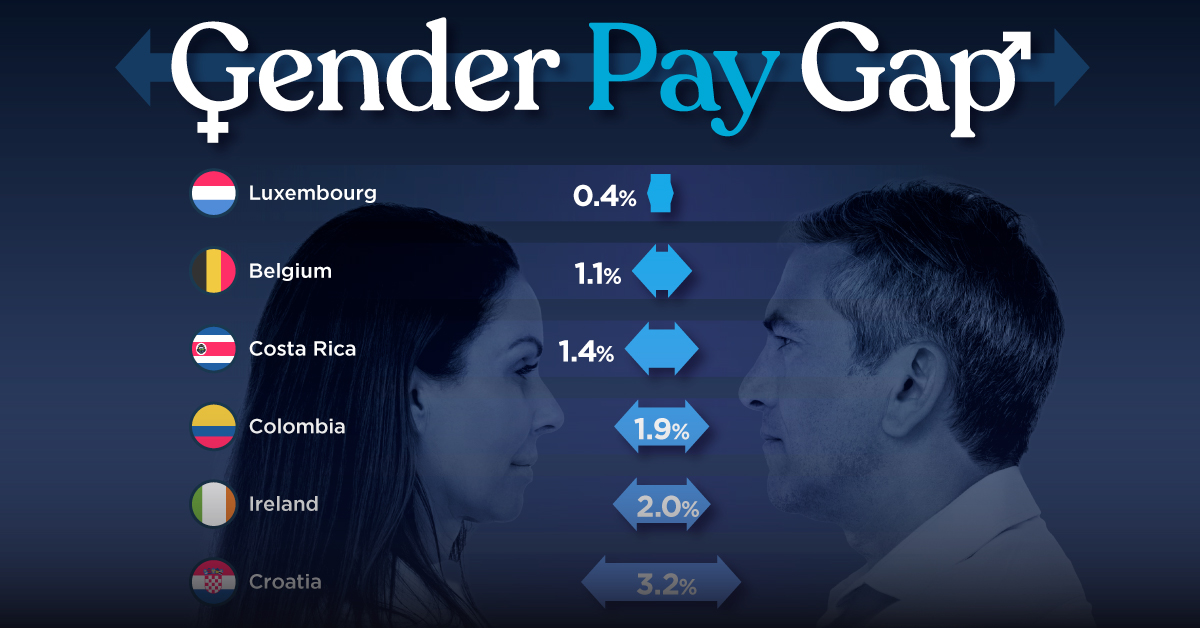
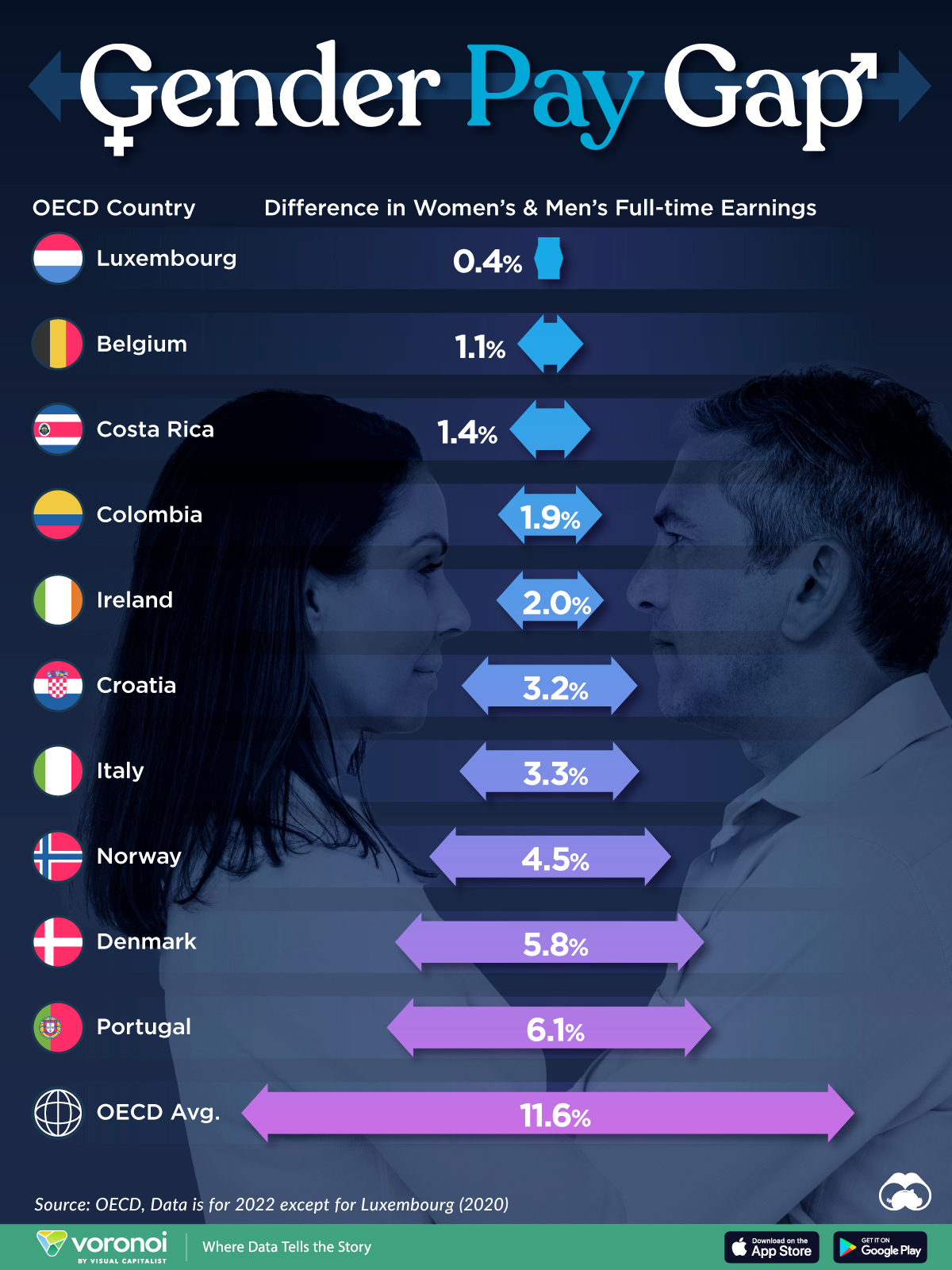
The Smallest Gender Pay Gaps in OECD Countries
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on iOS or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
Among the 38 member countries in the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD), several have made significant strides in addressing income inequality between men and women.
In this graphic we’ve ranked the OECD countries with the 10 smallest gender pay gaps, using the latest data from the OECD for 2022.
The gender pay gap is calculated as the difference between median full-time earnings for men and women divided by the median full-time earnings of men.
Which Countries Have the Smallest Gender Pay Gaps?
Luxembourg’s gender pay gap is the lowest among OECD members at only 0.4%—well below the OECD average of 11.6%.
| Rank | Country | Percentage Difference in Men's & Women's Full-time Earnings |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 🇱🇺 Luxembourg | 0.4% |
| 2 | 🇧🇪 Belgium | 1.1% |
| 3 | 🇨🇷 Costa Rica | 1.4% |
| 4 | 🇨🇴 Colombia | 1.9% |
| 5 | 🇮🇪 Ireland | 2.0% |
| 6 | 🇭🇷 Croatia | 3.2% |
| 7 | 🇮🇹 Italy | 3.3% |
| 8 | 🇳🇴 Norway | 4.5% |
| 9 | 🇩🇰 Denmark | 5.8% |
| 10 | 🇵🇹 Portugal | 6.1% |
| OECD Average | 11.6% |
Notably, eight of the top 10 countries with the smallest gender pay gaps are located in Europe, as labor equality laws designed to target gender differences have begun to pay off.
The two other countries that made the list were Costa Rica (1.4%) and Colombia (1.9%), which came in third and fourth place, respectively.
How Did Luxembourg (Nearly) Eliminate its Gender Wage Gap?
Luxembourg’s virtually-non-existent gender wage gap in 2020 can be traced back to its diligent efforts to prioritize equal pay. Since 2016, firms that have not complied with the Labor Code’s equal pay laws have been subjected to penalizing fines ranging from €251 to €25,000.
Higher female education rates also contribute to the diminishing pay gap, with Luxembourg tied for first in the educational attainment rankings of the World Economic Forum’s Global Gender Gap Index Report for 2023.
See More Graphics about Demographics and Money
While these 10 countries are well below the OECD’s average gender pay gap of 11.6%, many OECD member countries including the U.S. are significantly above the average. To see the full list of the top 10 OECD countries with the largest gender pay gaps, check out this visualization.
-

 Business2 weeks ago
Business2 weeks agoAmerica’s Top Companies by Revenue (1994 vs. 2023)
-

 Environment1 week ago
Environment1 week agoRanked: Top Countries by Total Forest Loss Since 2001
-

 Markets1 week ago
Markets1 week agoVisualizing America’s Shortage of Affordable Homes
-

 Maps2 weeks ago
Maps2 weeks agoMapped: Average Wages Across Europe
-

 Mining2 weeks ago
Mining2 weeks agoCharted: The Value Gap Between the Gold Price and Gold Miners
-

 Demographics2 weeks ago
Demographics2 weeks agoVisualizing the Size of the Global Senior Population
-

 Misc2 weeks ago
Misc2 weeks agoTesla Is Once Again the World’s Best-Selling EV Company
-

 Technology2 weeks ago
Technology2 weeks agoRanked: The Most Popular Smartphone Brands in the U.S.