Technology
How Tech is Changing the Modern Credit Landscape
From the beginnings of General Motors Acceptance Corporation to the introduction of the Diner’s Club charge card, the history of credit has been filled with game-changing innovations.
Today, new innovations in tech are continuing to shape the consumer credit industry – and with U.S. consumer debt sitting at $13 trillion, these changes could play a role in impacting how consumers access credit both today and in the future.
The Modern Credit Landscape
Today’s infographic comes to us from Equifax, and it gives a snapshot of modern credit as well as a perspective on how new technologies such as trended and alternative data are changing the landscape.
It’s the second part of our ongoing three-part series on credit:







Credit scores play a massive component of consumer life, and they are used to gauge creditworthiness for big purchases ranging from homes to launching a business.
Interestingly, how this scoring works is not at all static – and new technology is being applied to increase accuracy as well as open credit up to more consumers throughout society.
Traditional Credit Scoring
The modern numeric credit score emerged in 1989, and it uses logistic regression to make informed decisions on a consumer’s creditworthiness.
The scoring model is made up of five distinct categories:
| Category | Percentage | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Payment History | 35% | Are scheduled payments made on time? |
| Debt Burden | 30% | Includes multiple factors such as number of accounts with balances, amounts owed, and debt-to-limit ratio. |
| Length of Credit History | 15% | Average age of accounts and age of oldest account. |
| Types of Credit Used | 10% | What type of credit is used? (i.e. revolving, installments, etc.) |
| New Credit Requests | 10% | Hard new credit inquiries can hurt scores. |
But this model does have its limitations. For example, traditional credit scores give a snapshot of credit rather than showing how the “big picture” of a person’s credit is changing. Further, current scores can also can be inhibited by a lack of data, resulting in an inaccurate representation of a person’s credit.
Tech to the Rescue
On a global basis, the data universe is doubling every two years – and this abundant new resource is revolutionizing consumer credit.
Trended Data
Instead of looking at a snapshot of a credit score, it’s possible to analyze the direction, velocity, tipping points, and magnitude of changes in a consumer’s credit history to get a bigger, more accurate picture. This is called trended data, and it can offer up to 20% improvement in predictive performance.
Alternative Data
Credit history is important, but there are increasingly other sources of data that can provide a view of a consumer’s creditworthiness. Alternative data taps into information on property ownership, wealth, how customers pay everyday bills, and other data sources to provide a more well-rounded picture.
Other Tech
Technology has given consumers unprecedented access to their credit data – and in the meantime, new science behind neural networks is being implemented to give even more sophisticated scoring capabilities.
Technology
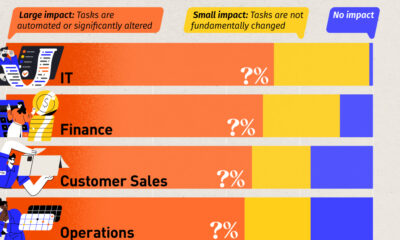
Ranked: Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share
Nvidia is coming for Intel’s crown. Samsung is losing ground. AI is transforming the space. We break down revenue for semiconductor companies.
Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on Apple or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
Did you know that some computer chips are now retailing for the price of a new BMW?
As computers invade nearly every sphere of life, so too have the chips that power them, raising the revenues of the businesses dedicated to designing them.
But how did various chipmakers measure against each other last year?
We rank the biggest semiconductor companies by their percentage share of the industry’s revenues in 2023, using data from Omdia research.
Which Chip Company Made the Most Money in 2023?
Market leader and industry-defining veteran Intel still holds the crown for the most revenue in the sector, crossing $50 billion in 2023, or 10% of the broader industry’s topline.
All is not well at Intel, however, with the company’s stock price down over 20% year-to-date after it revealed billion-dollar losses in its foundry business.
| Rank | Company | 2023 Revenue | % of Industry Revenue |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Intel | $51B | 9.4% |
| 2 | NVIDIA | $49B | 9.0% |
| 3 | Samsung Electronics | $44B | 8.1% |
| 4 | Qualcomm | $31B | 5.7% |
| 5 | Broadcom | $28B | 5.2% |
| 6 | SK Hynix | $24B | 4.4% |
| 7 | AMD | $22B | 4.1% |
| 8 | Apple | $19B | 3.4% |
| 9 | Infineon Tech | $17B | 3.2% |
| 10 | STMicroelectronics | $17B | 3.2% |
| 11 | Texas Instruments | $17B | 3.1% |
| 12 | Micron Technology | $16B | 2.9% |
| 13 | MediaTek | $14B | 2.6% |
| 14 | NXP | $13B | 2.4% |
| 15 | Analog Devices | $12B | 2.2% |
| 16 | Renesas Electronics Corporation | $11B | 1.9% |
| 17 | Sony Semiconductor Solutions Corporation | $10B | 1.9% |
| 18 | Microchip Technology | $8B | 1.5% |
| 19 | Onsemi | $8B | 1.4% |
| 20 | KIOXIA Corporation | $7B | 1.3% |
| N/A | Others | $126B | 23.2% |
| N/A | Total | $545B | 100% |
Note: Figures are rounded. Totals and percentages may not sum to 100.
Meanwhile, Nvidia is very close to overtaking Intel, after declaring $49 billion of topline revenue for 2023. This is more than double its 2022 revenue ($21 billion), increasing its share of industry revenues to 9%.
Nvidia’s meteoric rise has gotten a huge thumbs-up from investors. It became a trillion dollar stock last year, and broke the single-day gain record for market capitalization this year.
Other chipmakers haven’t been as successful. Out of the top 20 semiconductor companies by revenue, 12 did not match their 2022 revenues, including big names like Intel, Samsung, and AMD.
The Many Different Types of Chipmakers
All of these companies may belong to the same industry, but they don’t focus on the same niche.
According to Investopedia, there are four major types of chips, depending on their functionality: microprocessors, memory chips, standard chips, and complex systems on a chip.
Nvidia’s core business was once GPUs for computers (graphics processing units), but in recent years this has drastically shifted towards microprocessors for analytics and AI.
These specialized chips seem to be where the majority of growth is occurring within the sector. For example, companies that are largely in the memory segment—Samsung, SK Hynix, and Micron Technology—saw peak revenues in the mid-2010s.
-

 Real Estate2 weeks ago
Real Estate2 weeks agoVisualizing America’s Shortage of Affordable Homes
-

 Technology1 week ago
Technology1 week agoRanked: Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoWhich States Have the Highest Minimum Wage in America?
-

 Real Estate2 weeks ago
Real Estate2 weeks agoRanked: The Most Valuable Housing Markets in America
-

 Business2 weeks ago
Business2 weeks agoCharted: Big Four Market Share by S&P 500 Audits
-

 AI2 weeks ago
AI2 weeks agoThe Stock Performance of U.S. Chipmakers So Far in 2024
-

 Misc2 weeks ago
Misc2 weeks agoAlmost Every EV Stock is Down After Q1 2024
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoWhere Does One U.S. Tax Dollar Go?