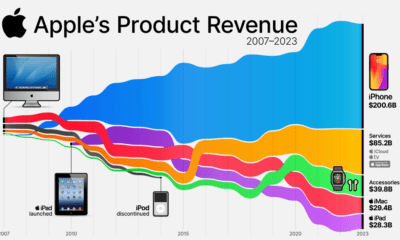
Technology
The Rising Speed of Technological Adoption
The Rising Speed of Technological Adoption
Technological progress is not the only thing rising at an exponential rate.
The rate at which newly commercialized technologies get adopted by consumers is also getting faster, too.
In the modern world, through increased connectivity, instant communication, and established infrastructure systems, new ideas and products can spread at speeds never seen before – and this enables a new product to get in the hands of consumers in the blink of an eye.
Visualizing Technological Adoption
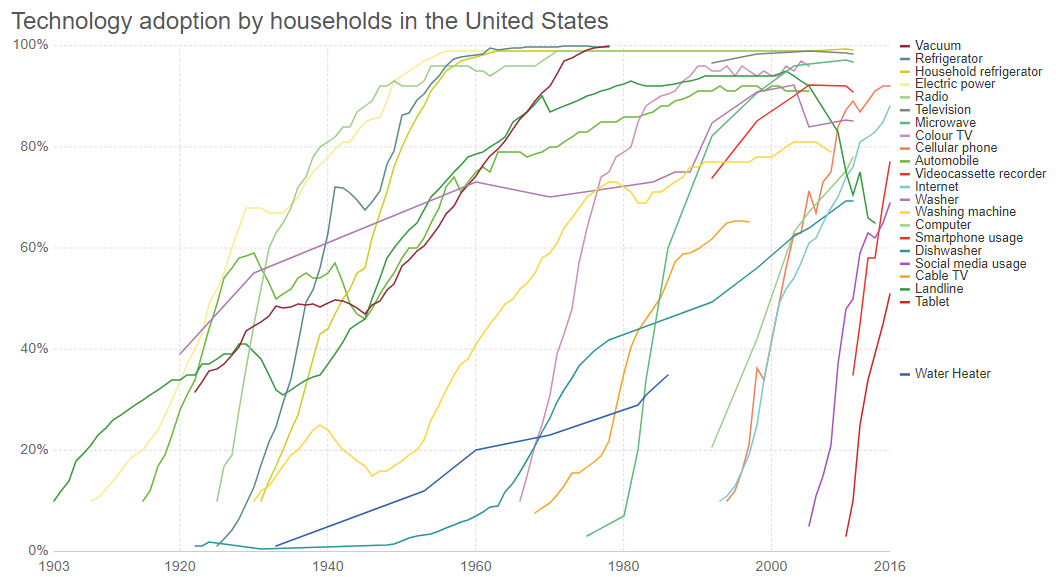
Today’s dynamic chart comes to us from Our World in Data, and it allows you to compare the adoption rates of new technologies over the period of more than a century.
In addition to the technologies you’ll find embedded on the initial chart above, you can also use the “Add technology” tab of the chart (bottom left) to list up to 40 tech data series on the chart in total. This allows you to gauge adoption rates for everything from color televisions to washing machines, while giving you an idea of the trajectory of many common technologies today.
A Blast From the Past
To get the full impact of the chart, it’s worth removing more modern technologies like smartphones, social media, tablets, cellular phones, and the internet from the list.
Here’s a look at adoption rates for the household appliances and products today that we would consider pretty essential, over a period of more than 120 years:
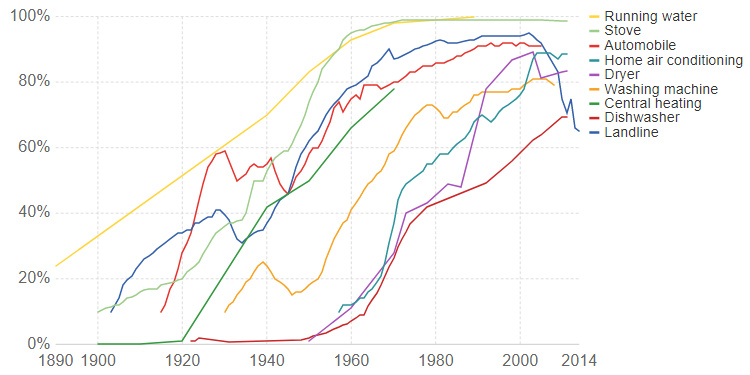
The telephone was invented in 1876, but it wasn’t until a century later that landlines reached a saturation point in households.
For this to happen, massive amounts of infrastructure had to be built and network effects also needed to accumulate to make the product worthwhile for consumers. Further, the telephone suffered from the “last-mile problem”, in which the logistics get tougher and more expensive as end-users get hooked up to a network.
As a result, it wasn’t until the 1960s that 80% of U.S. households had landlines in them.
New Adoption Speeds
Now, here’s a chart with many older technologies removed – keep in mind that the x axis has changed to a much shorter timespan (~65 years):
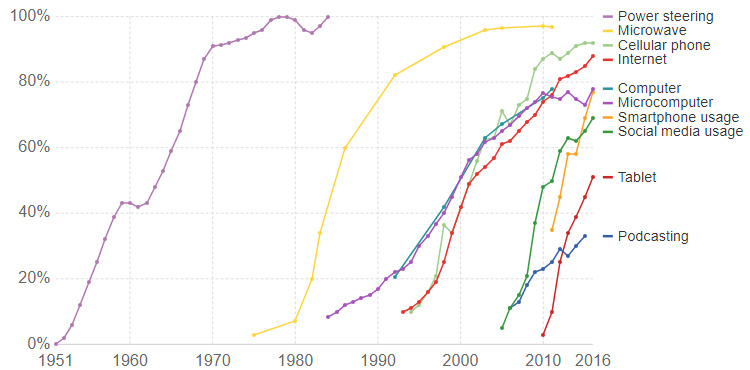
Microwaves, cell phones, smartphones, social media, tablets, and other inventions from the modern era all show fast-rising adoption rates. Standing out most on the chart is the tablet computer, which went from nearly 0% to 50% adoption in five years or so.
Why do newer technologies get adopted so quickly? It seems partly because modern tech needs less infrastructure in contrast with the water pipes, cable lines, electricity grids, and telephone wires that had to be installed throughout the 20th century.
However, it also says something else about today’s consumers – which is that they are connected, fast-acting, and not afraid to adopt the new technologies that can quickly impact their lives for the better.
Technology
Ranked: Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share
Nvidia is coming for Intel’s crown. Samsung is losing ground. AI is transforming the space. We break down revenue for semiconductor companies.
Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on Apple or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
Did you know that some computer chips are now retailing for the price of a new BMW?
As computers invade nearly every sphere of life, so too have the chips that power them, raising the revenues of the businesses dedicated to designing them.
But how did various chipmakers measure against each other last year?
We rank the biggest semiconductor companies by their percentage share of the industry’s revenues in 2023, using data from Omdia research.
Which Chip Company Made the Most Money in 2023?
Market leader and industry-defining veteran Intel still holds the crown for the most revenue in the sector, crossing $50 billion in 2023, or 10% of the broader industry’s topline.
All is not well at Intel, however, with the company’s stock price down over 20% year-to-date after it revealed billion-dollar losses in its foundry business.
| Rank | Company | 2023 Revenue | % of Industry Revenue |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Intel | $51B | 9.4% |
| 2 | NVIDIA | $49B | 9.0% |
| 3 | Samsung Electronics | $44B | 8.1% |
| 4 | Qualcomm | $31B | 5.7% |
| 5 | Broadcom | $28B | 5.2% |
| 6 | SK Hynix | $24B | 4.4% |
| 7 | AMD | $22B | 4.1% |
| 8 | Apple | $19B | 3.4% |
| 9 | Infineon Tech | $17B | 3.2% |
| 10 | STMicroelectronics | $17B | 3.2% |
| 11 | Texas Instruments | $17B | 3.1% |
| 12 | Micron Technology | $16B | 2.9% |
| 13 | MediaTek | $14B | 2.6% |
| 14 | NXP | $13B | 2.4% |
| 15 | Analog Devices | $12B | 2.2% |
| 16 | Renesas Electronics Corporation | $11B | 1.9% |
| 17 | Sony Semiconductor Solutions Corporation | $10B | 1.9% |
| 18 | Microchip Technology | $8B | 1.5% |
| 19 | Onsemi | $8B | 1.4% |
| 20 | KIOXIA Corporation | $7B | 1.3% |
| N/A | Others | $126B | 23.2% |
| N/A | Total | $545B | 100% |
Note: Figures are rounded. Totals and percentages may not sum to 100.
Meanwhile, Nvidia is very close to overtaking Intel, after declaring $49 billion of topline revenue for 2023. This is more than double its 2022 revenue ($21 billion), increasing its share of industry revenues to 9%.
Nvidia’s meteoric rise has gotten a huge thumbs-up from investors. It became a trillion dollar stock last year, and broke the single-day gain record for market capitalization this year.
Other chipmakers haven’t been as successful. Out of the top 20 semiconductor companies by revenue, 12 did not match their 2022 revenues, including big names like Intel, Samsung, and AMD.
The Many Different Types of Chipmakers
All of these companies may belong to the same industry, but they don’t focus on the same niche.
According to Investopedia, there are four major types of chips, depending on their functionality: microprocessors, memory chips, standard chips, and complex systems on a chip.
Nvidia’s core business was once GPUs for computers (graphics processing units), but in recent years this has drastically shifted towards microprocessors for analytics and AI.
These specialized chips seem to be where the majority of growth is occurring within the sector. For example, companies that are largely in the memory segment—Samsung, SK Hynix, and Micron Technology—saw peak revenues in the mid-2010s.
-

 Business2 weeks ago
Business2 weeks agoAmerica’s Top Companies by Revenue (1994 vs. 2023)
-

 Environment1 week ago
Environment1 week agoRanked: Top Countries by Total Forest Loss Since 2001
-

 Markets1 week ago
Markets1 week agoVisualizing America’s Shortage of Affordable Homes
-

 Maps2 weeks ago
Maps2 weeks agoMapped: Average Wages Across Europe
-

 Mining2 weeks ago
Mining2 weeks agoCharted: The Value Gap Between the Gold Price and Gold Miners
-

 Demographics2 weeks ago
Demographics2 weeks agoVisualizing the Size of the Global Senior Population
-

 Misc2 weeks ago
Misc2 weeks agoTesla Is Once Again the World’s Best-Selling EV Company
-

 Technology2 weeks ago
Technology2 weeks agoRanked: The Most Popular Smartphone Brands in the U.S.