Misc
Mercator Misconceptions: Clever Map Shows the True Size of Countries
This Clever Map Shows the True Size of Countries
Maps are hugely important tools in our everyday life, whether it’s guiding our journeys from point A to B, or shaping our big picture perceptions about geopolitics and the environment.
For many people, the Earth as they know it is heavily informed by the Mercator projection—a tool used for nautical navigation that eventually became the world’s most widely recognized map.
Mercator’s Rise to the Top
With any map projection style, the big challenge lies in depicting a spherical object as a 2D graphic. There are various trade-offs with any map style, and those trade-offs can vary depending on how the map is meant to be used.
In 1569, the great cartographer, Gerardus Mercator, created a revolutionary new map based on a cylindrical projection. The new map was well-suited to nautical navigation since every line on the sphere is a constant course, or loxodrome.
Geographic Inflation
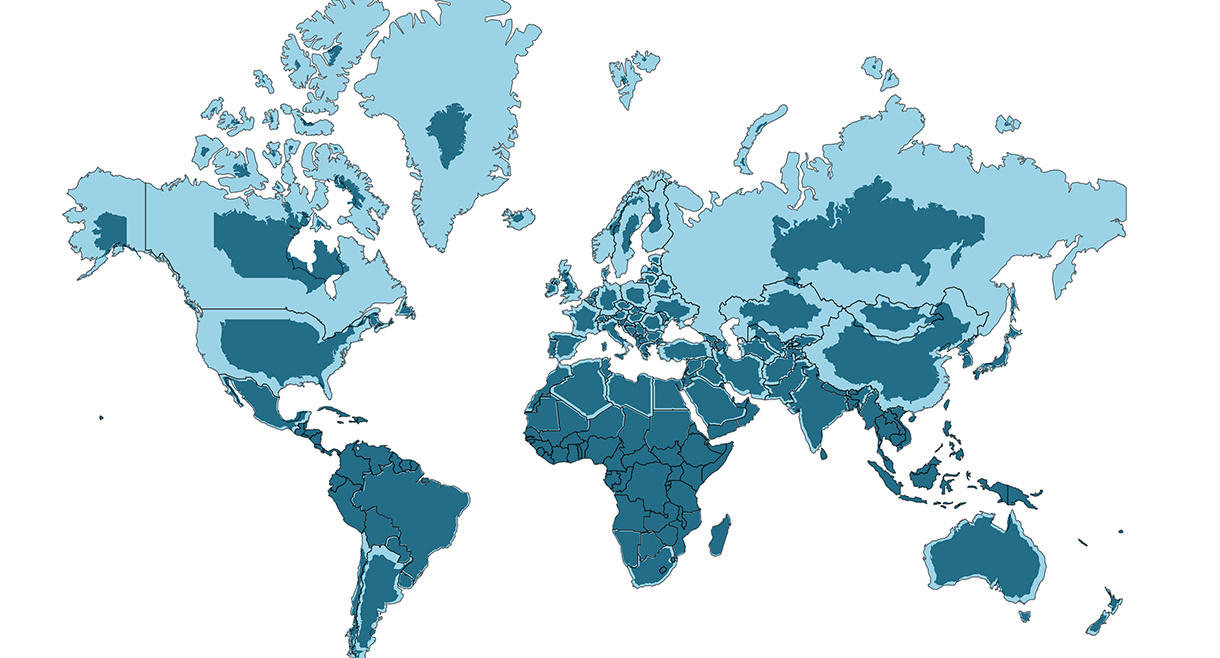
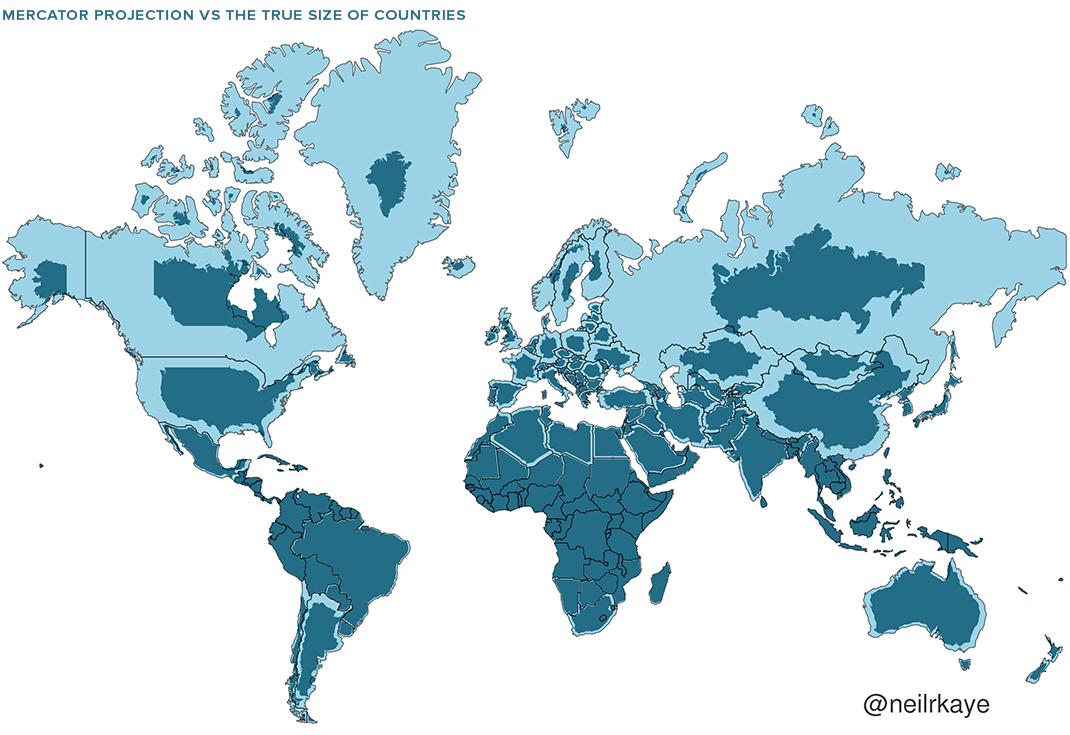
The vast majority of us aren’t using paper maps to chart our course across the ocean anymore, so critics of the Mercator projection argue that the continued use of this style of map gives users a warped sense of the true size of countries—particularly in the case of the African continent.
Mercator’s map inadvertently also pumps up the sizes of Europe and North America. Visually speaking, Canada and Russia appear to take up approximately 25% of the Earth’s surface, when in reality they occupy a mere 5%.
As the animated GIF below—created by Reddit user, neilrkaye – demonstrates, northern nations such as Canada and Russia have been artificially “pumped up” in the minds of many people around the world.
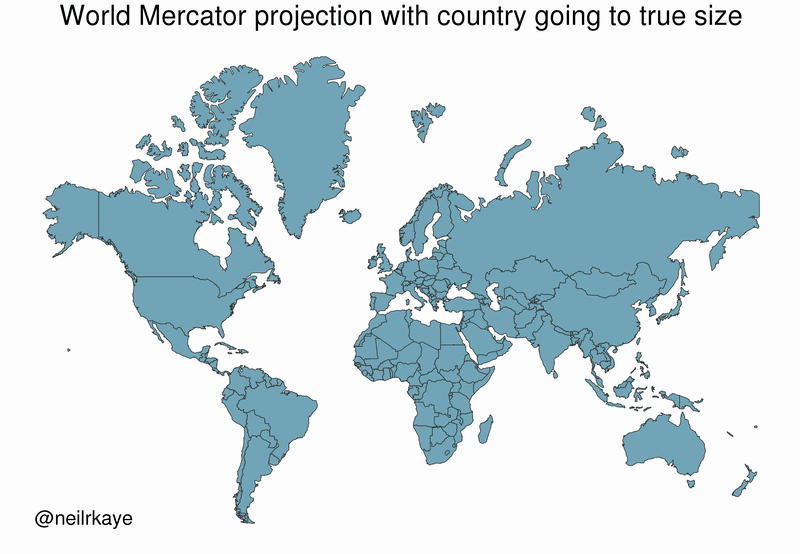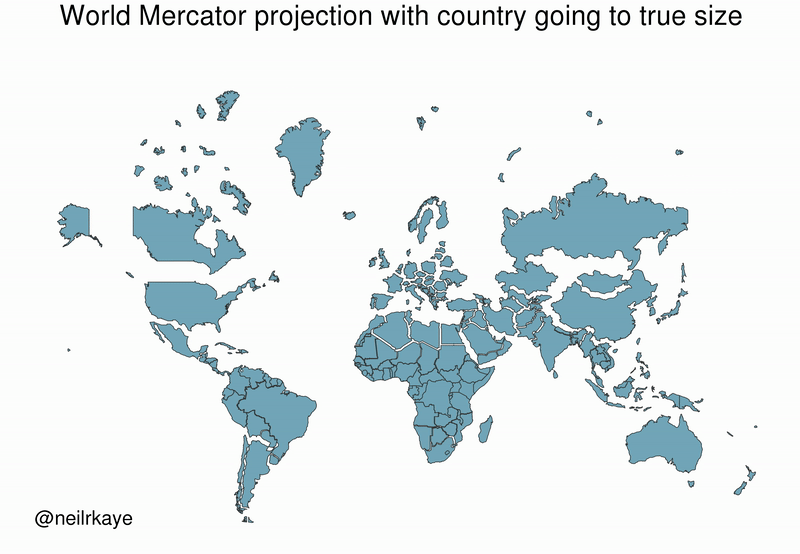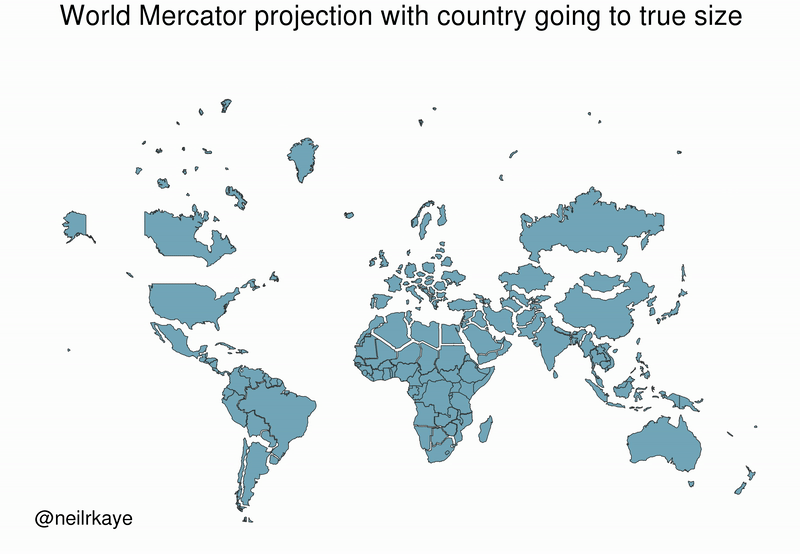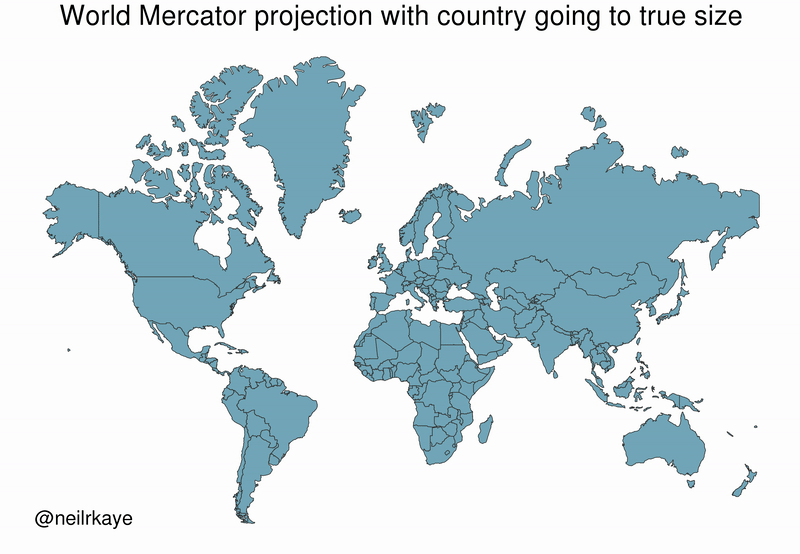
Greenland, which appears as a massive icy landmass in Mercator projection, shrinks way down. The continent of Africa takes a much more prominent position in this new, correctly-scaled map.
This visualization also highlights how distorted neighboring countries can look in Mercator projection. In the GIF above, Scandinavian countries no longer loom imposingly over their European neighbors, and Canada deflates to a size similar to the United States.
Despite inaccurate visual features—or perhaps because of them—the Mercator projection has achieved widespread adoption around the world. This includes in the classroom, where young minds are first learning about geography and forming opinions on the relationships between countries.
Getting Reacquainted with Globes
Google, whose map app is used by approximately 150 million people per month, took the bold step of using different projections for different purposes in 2018.
The Earth is depicted as a globe at further zoom levels, sidestepping map projection issues completely and displaying the world as it actually is: round. The result is a more accurate depiction of countries and landmasses.
With 3D Globe Mode on Google Maps desktop, Greenland's projection is no longer the size of Africa.
Just zoom all the way out at https://t.co/mIZTya01K3 😎🌍 pic.twitter.com/CIkkS7It8d
— Google Maps (@googlemaps) August 2, 2018
At closer zoom levels, users are typically using maps for things like navigation, which the Mercator projection was designed for. The exact angles of roads and borders are preserved in this projection.
In the Right Direction
In a more globally connected world, geographic literacy is more important than ever. As people become more accustomed to equal area maps and seeing the Earth in its spherical form, misconceptions about the size of continents may become a thing of the past.
This post was first published in 2018. We have since updated it, adding in new content for 2021.
Maps
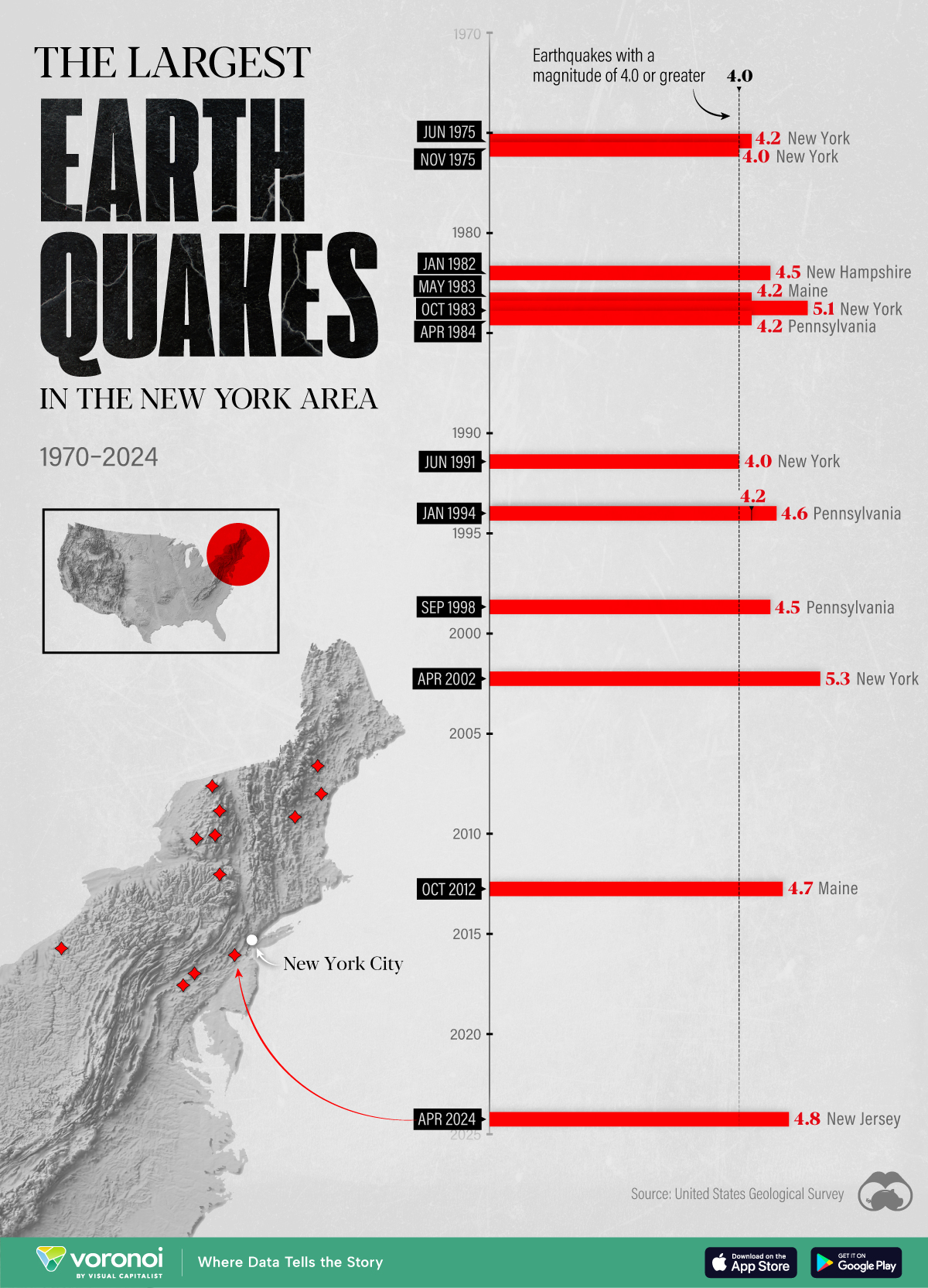
The Largest Earthquakes in the New York Area (1970-2024)
The earthquake that shook buildings across New York in April 2024 was the third-largest quake in the Northeast U.S. over the past 50 years.

The Largest Earthquakes in the New York Area
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on Apple or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
The 4.8 magnitude earthquake that shook buildings across New York on Friday, April 5th, 2024 was the third-largest quake in the U.S. Northeast area over the past 50 years.
In this map, we illustrate earthquakes with a magnitude of 4.0 or greater recorded in the Northeastern U.S. since 1970, according to the United States Geological Survey (USGS).
Shallow Quakes and Older Buildings
The earthquake that struck the U.S. Northeast in April 2024 was felt by millions of people from Washington, D.C., to north of Boston. It even caused a full ground stop at Newark Airport.
The quake, occurring just 5 km beneath the Earth’s surface, was considered shallow, which is what contributed to more intense shaking at the surface.
According to the USGS, rocks in the eastern U.S. are significantly older, denser, and harder than those on the western side, compressed by time. This makes them more efficient conduits for seismic energy. Additionally, buildings in the Northeast tend to be older and may not adhere to the latest earthquake codes.
Despite disrupting work and school life, the earthquake was considered minor, according to the Michigan Technological University magnitude scale:
| Magnitude | Earthquake Effects | Estimated Number Each Year |
|---|---|---|
| 2.5 or less | Usually not felt, but can be recorded by seismograph. | Millions |
| 2.5 to 5.4 | Often felt, but only causes minor damage. | 500,000 |
| 5.5 to 6.0 | Slight damage to buildings and other structures. | 350 |
| 6.1 to 6.9 | May cause a lot of damage in very populated areas. | 100 |
| 7.0 to 7.9 | Major earthquake. Serious damage. | 10-15 |
| 8.0 or greater | Great earthquake. Can totally destroy communities near the epicenter. | One every year or two |
The largest earthquake felt in the area over the past 50 years was a 5.3 magnitude quake that occurred in Au Sable Forks, New York, in 2002. It damaged houses and cracked roads in a remote corner of the Adirondack Mountains, but caused no injuries.
| Date | Magnitude | Location | State |
|---|---|---|---|
| April 20, 2002 | 5.3 | Au Sable Forks | New York |
| October 7, 1983 | 5.1 | Newcomb | New York |
| April 5, 2024 | 4.8 | Whitehouse Station | New Jersey |
| October 16, 2012 | 4.7 | Hollis Center | Maine |
| January 16, 1994 | 4.6 | Sinking Spring | Pennsylvania |
| January 19, 1982 | 4.5 | Sanbornton | New Hampshire |
| September 25, 1998 | 4.5 | Adamsville | Pennsylvania |
| June 9, 1975 | 4.2 | Altona | New York |
| May 29, 1983 | 4.2 | Peru | Maine |
| April 23, 1984 | 4.2 | Conestoga | Pennsylvania |
| January 16, 1994 | 4.2 | Sinking Spring | Pennsylvania |
| November 3, 1975 | 4 | Long Lake | New York |
| June 17, 1991 | 4 | Worcester | New York |
The largest earthquake in U.S. history, however, was the 1964 Good Friday quake in Alaska, measuring 9.2 magnitude and killing 131 people.
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoVisualizing the Growth of $100, by Asset Class (1970-2023)
-

 Money1 week ago
Money1 week agoWhere Does One U.S. Tax Dollar Go?
-

 Green2 weeks ago
Green2 weeks agoRanked: Top Countries by Total Forest Loss Since 2001
-

 Real Estate2 weeks ago
Real Estate2 weeks agoVisualizing America’s Shortage of Affordable Homes
-

 Maps2 weeks ago
Maps2 weeks agoMapped: Average Wages Across Europe
-

 Mining2 weeks ago
Mining2 weeks agoCharted: The Value Gap Between the Gold Price and Gold Miners
-

 Demographics2 weeks ago
Demographics2 weeks agoVisualizing the Size of the Global Senior Population
-

 Automotive2 weeks ago
Automotive2 weeks agoTesla Is Once Again the World’s Best-Selling EV Company