Misc
Mercator Misconceptions: Clever Map Shows the True Size of Countries
This Clever Map Shows the True Size of Countries
Maps are hugely important tools in our everyday life, whether it’s guiding our journeys from point A to B, or shaping our big picture perceptions about geopolitics and the environment.
For many people, the Earth as they know it is heavily informed by the Mercator projection—a tool used for nautical navigation that eventually became the world’s most widely recognized map.
Mercator’s Rise to the Top
With any map projection style, the big challenge lies in depicting a spherical object as a 2D graphic. There are various trade-offs with any map style, and those trade-offs can vary depending on how the map is meant to be used.
In 1569, the great cartographer, Gerardus Mercator, created a revolutionary new map based on a cylindrical projection. The new map was well-suited to nautical navigation since every line on the sphere is a constant course, or loxodrome.
Geographic Inflation
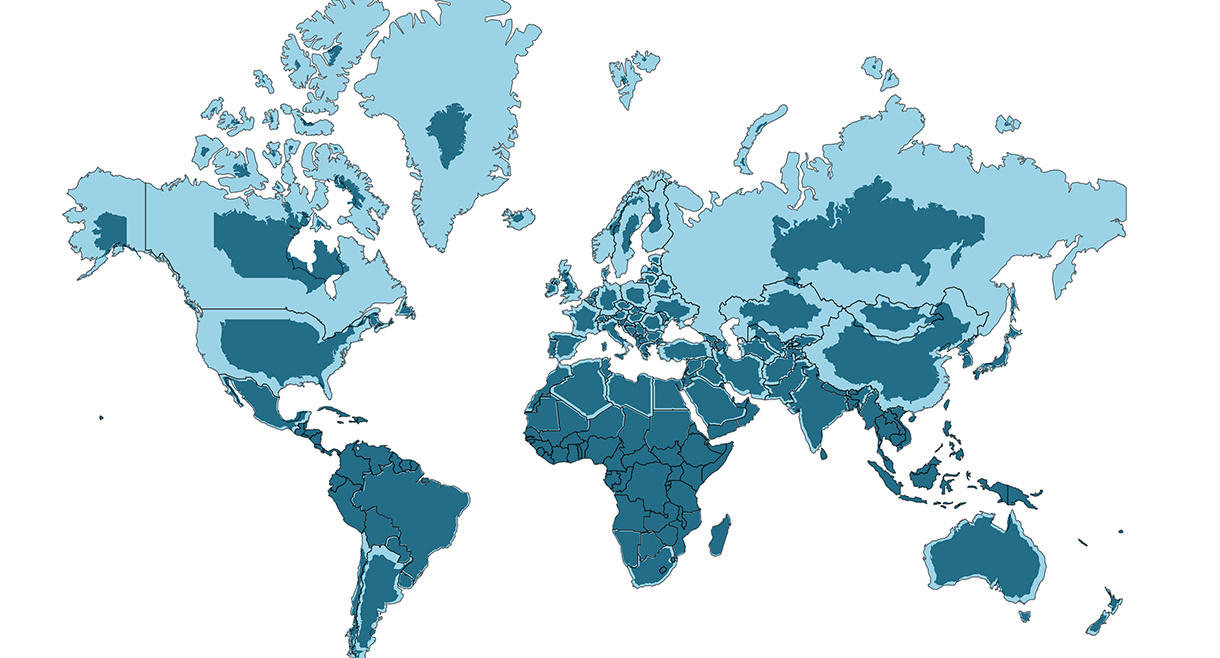
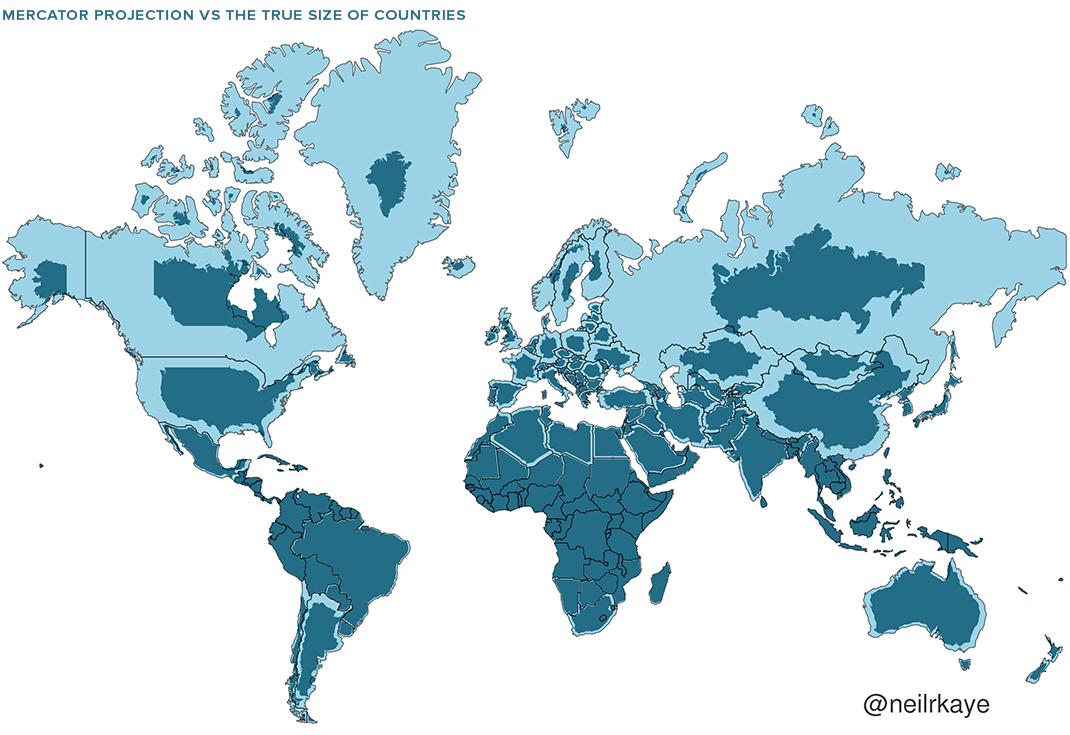
The vast majority of us aren’t using paper maps to chart our course across the ocean anymore, so critics of the Mercator projection argue that the continued use of this style of map gives users a warped sense of the true size of countries—particularly in the case of the African continent.
Mercator’s map inadvertently also pumps up the sizes of Europe and North America. Visually speaking, Canada and Russia appear to take up approximately 25% of the Earth’s surface, when in reality they occupy a mere 5%.
As the animated GIF below—created by Reddit user, neilrkaye – demonstrates, northern nations such as Canada and Russia have been artificially “pumped up” in the minds of many people around the world.
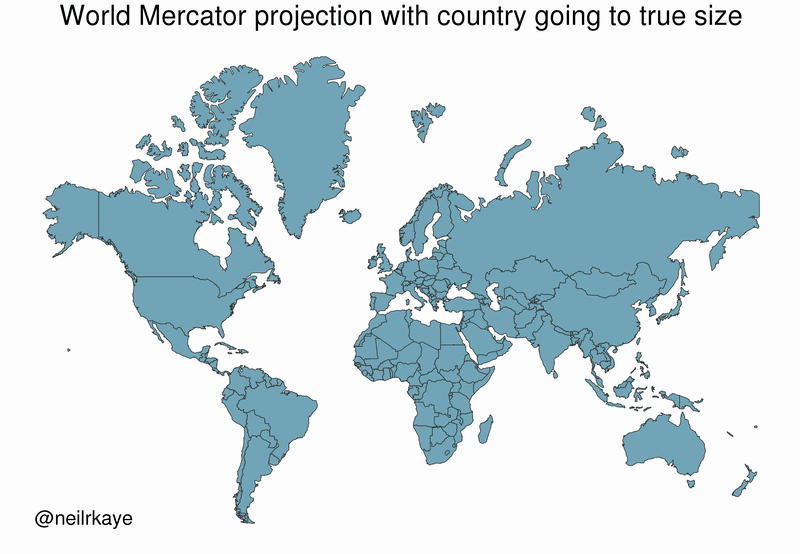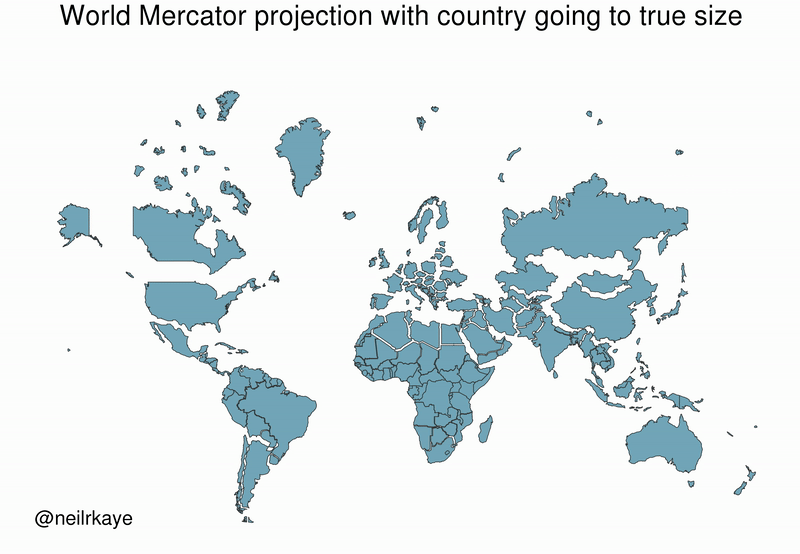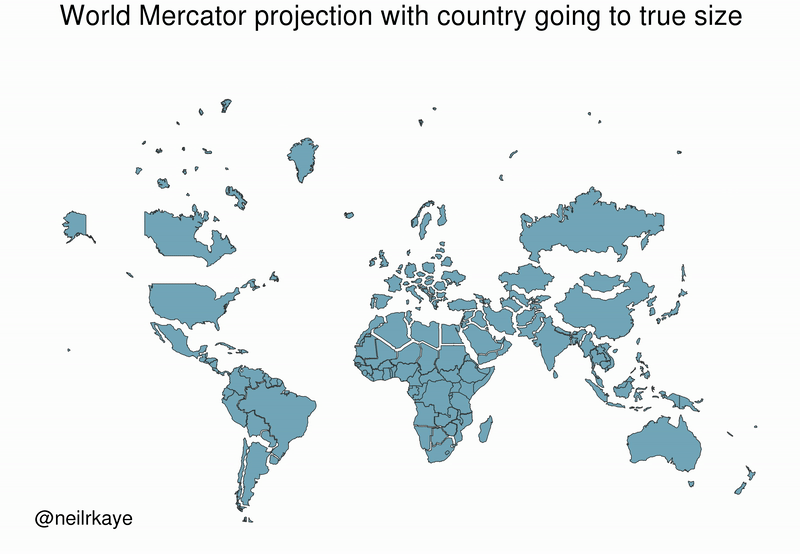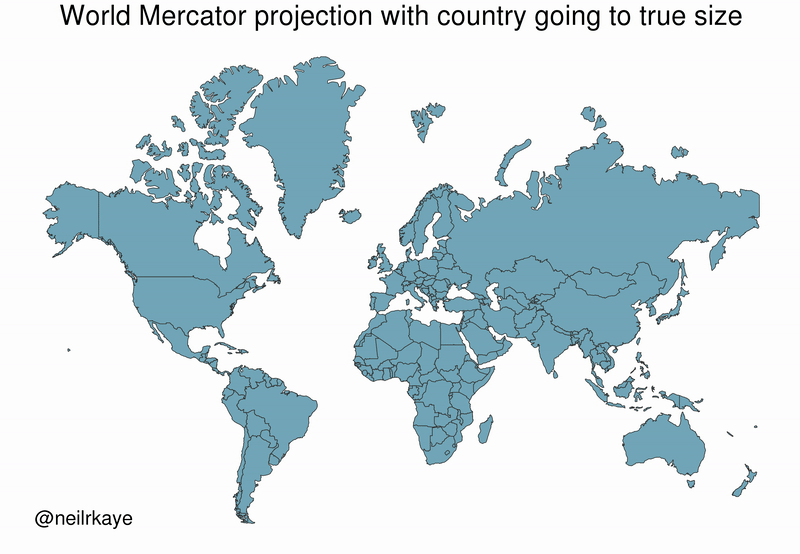
Greenland, which appears as a massive icy landmass in Mercator projection, shrinks way down. The continent of Africa takes a much more prominent position in this new, correctly-scaled map.
This visualization also highlights how distorted neighboring countries can look in Mercator projection. In the GIF above, Scandinavian countries no longer loom imposingly over their European neighbors, and Canada deflates to a size similar to the United States.
Despite inaccurate visual features—or perhaps because of them—the Mercator projection has achieved widespread adoption around the world. This includes in the classroom, where young minds are first learning about geography and forming opinions on the relationships between countries.
Getting Reacquainted with Globes
Google, whose map app is used by approximately 150 million people per month, took the bold step of using different projections for different purposes in 2018.
The Earth is depicted as a globe at further zoom levels, sidestepping map projection issues completely and displaying the world as it actually is: round. The result is a more accurate depiction of countries and landmasses.
With 3D Globe Mode on Google Maps desktop, Greenland's projection is no longer the size of Africa.
Just zoom all the way out at https://t.co/mIZTya01K3 😎🌍 pic.twitter.com/CIkkS7It8d
— Google Maps (@googlemaps) August 2, 2018
At closer zoom levels, users are typically using maps for things like navigation, which the Mercator projection was designed for. The exact angles of roads and borders are preserved in this projection.
In the Right Direction
In a more globally connected world, geographic literacy is more important than ever. As people become more accustomed to equal area maps and seeing the Earth in its spherical form, misconceptions about the size of continents may become a thing of the past.
This post was first published in 2018. We have since updated it, adding in new content for 2021.
Misc
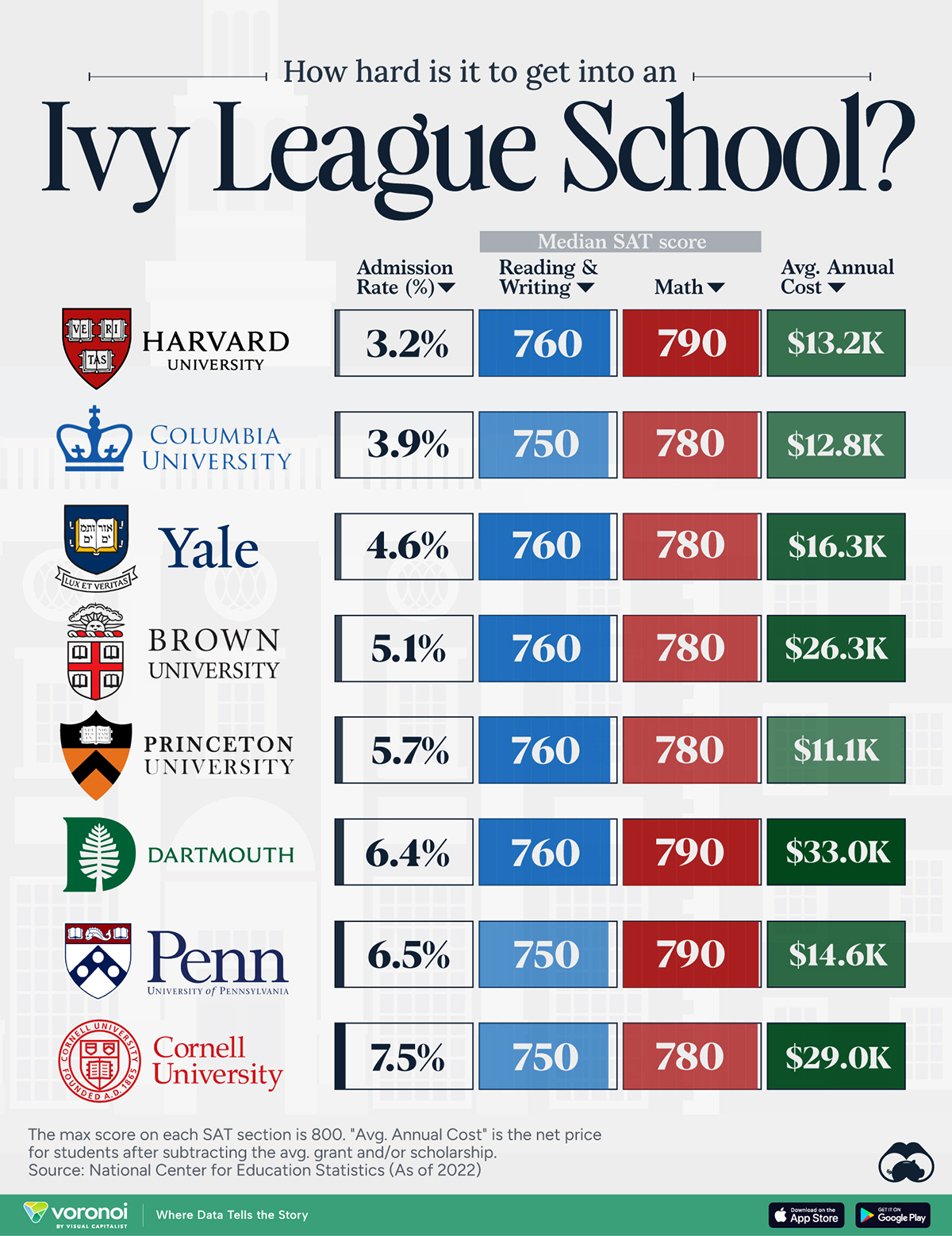
How Hard Is It to Get Into an Ivy League School?
We detail the admission rates and average annual cost for Ivy League schools, as well as the median SAT scores required to be accepted.
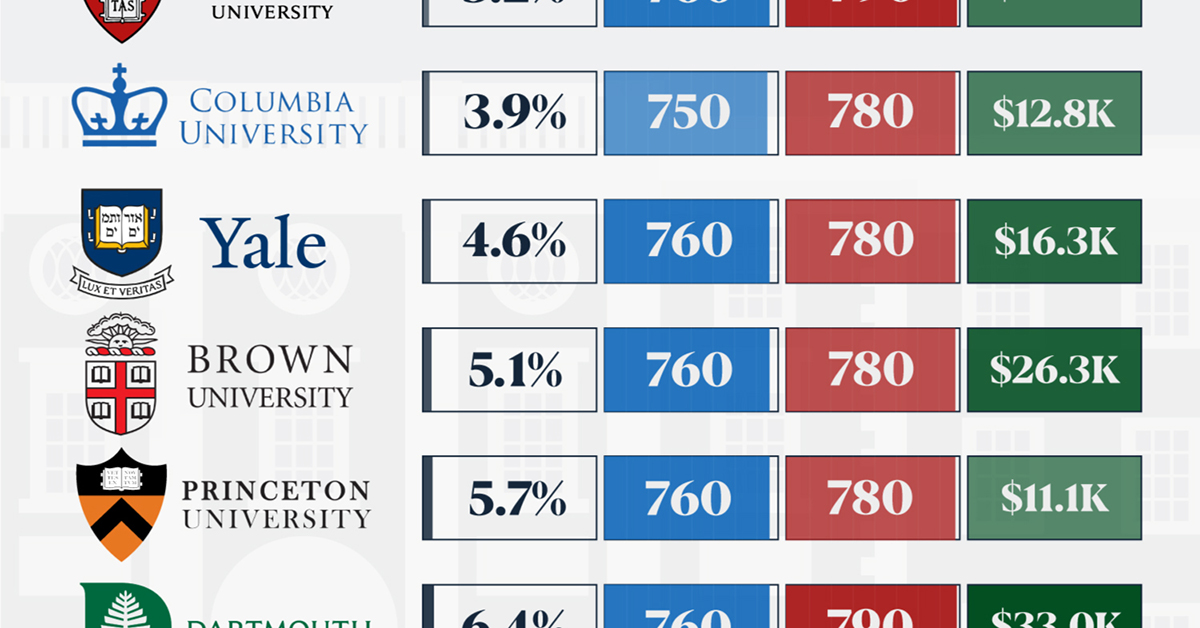
How Hard Is It to Get Into an Ivy League School?
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on iOS or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
Ivy League institutions are renowned worldwide for their academic excellence and long-standing traditions. But how hard is it to get into one of the top universities in the U.S.?
In this graphic, we detail the admission rates and average annual cost for Ivy League schools, as well as the median SAT scores required to be accepted. The data comes from the National Center for Education Statistics and was compiled by 24/7 Wall St.
Note that “average annual cost” represents the net price a student pays after subtracting the average value of grants and/or scholarships received.
Harvard is the Most Selective
The SAT is a standardized test commonly used for college admissions in the United States. It’s taken by high school juniors and seniors to assess their readiness for college-level academic work.
When comparing SAT scores, Harvard and Dartmouth are among the most challenging universities to gain admission to. The median SAT scores for their students are 760 for reading and writing and 790 for math. Still, Harvard has half the admission rate (3.2%) compared to Dartmouth (6.4%).
| School | Admission rate (%) | SAT Score: Reading & Writing | SAT Score: Math | Avg Annual Cost* |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Harvard University | 3.2 | 760 | 790 | $13,259 |
| Columbia University | 3.9 | 750 | 780 | $12,836 |
| Yale University | 4.6 | 760 | 780 | $16,341 |
| Brown University | 5.1 | 760 | 780 | $26,308 |
| Princeton University | 5.7 | 760 | 780 | $11,080 |
| Dartmouth College | 6.4 | 760 | 790 | $33,023 |
| University of Pennsylvania | 6.5 | 750 | 790 | $14,851 |
| Cornell University | 7.5 | 750 | 780 | $29,011 |
*Costs after receiving federal financial aid.
Additionally, Dartmouth has the highest average annual cost at $33,000. Princeton has the lowest at $11,100.
While student debt has surged in the United States in recent years, hitting $1.73 trillion in 2023, the worth of obtaining a degree from any of the schools listed surpasses mere academics. This is evidenced by the substantial incomes earned by former students.
Harvard grads, for example, have the highest average starting salary in the country, at $91,700.
-

 Mining2 weeks ago
Mining2 weeks agoCharted: The Value Gap Between the Gold Price and Gold Miners
-

 Real Estate1 week ago
Real Estate1 week agoRanked: The Most Valuable Housing Markets in America
-

 Business1 week ago
Business1 week agoCharted: Big Four Market Share by S&P 500 Audits
-

 AI1 week ago
AI1 week agoThe Stock Performance of U.S. Chipmakers So Far in 2024
-

 Misc1 week ago
Misc1 week agoAlmost Every EV Stock is Down After Q1 2024
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoWhere Does One U.S. Tax Dollar Go?
-

 Green2 weeks ago
Green2 weeks agoRanked: Top Countries by Total Forest Loss Since 2001
-

 Real Estate2 weeks ago
Real Estate2 weeks agoVisualizing America’s Shortage of Affordable Homes