Demographics
An Investing Megatrend: How Demographics and Social Changes are Shaping the Future
For millennia, people have found support and community through defining factors, ranging from age and race to income and education levels.
However, these characteristics are not static—and drastic demographic changes are starting to create powerful ripple effects in the 21st-century economy.
The Impact of Demographics and Social Changes
Today’s infographic from BlackRock delves into the significant impact that demographics and human rights movements have on global markets. Of the five megatrends explored in this series, demographics are predicted to have the farthest-reaching impact.

What are Demographics?
Demographics are the characteristics of populations that change over time. These include:
- Age
- Gender
- Race
- Birth and death rates
- Education levels
- Income levels
- Average family size
As a result, major demographic trends offer both unique challenges and opportunities for businesses, societies, and investors.
The Biggest Shifts
What are the biggest shifts in demographics that the world faces today?
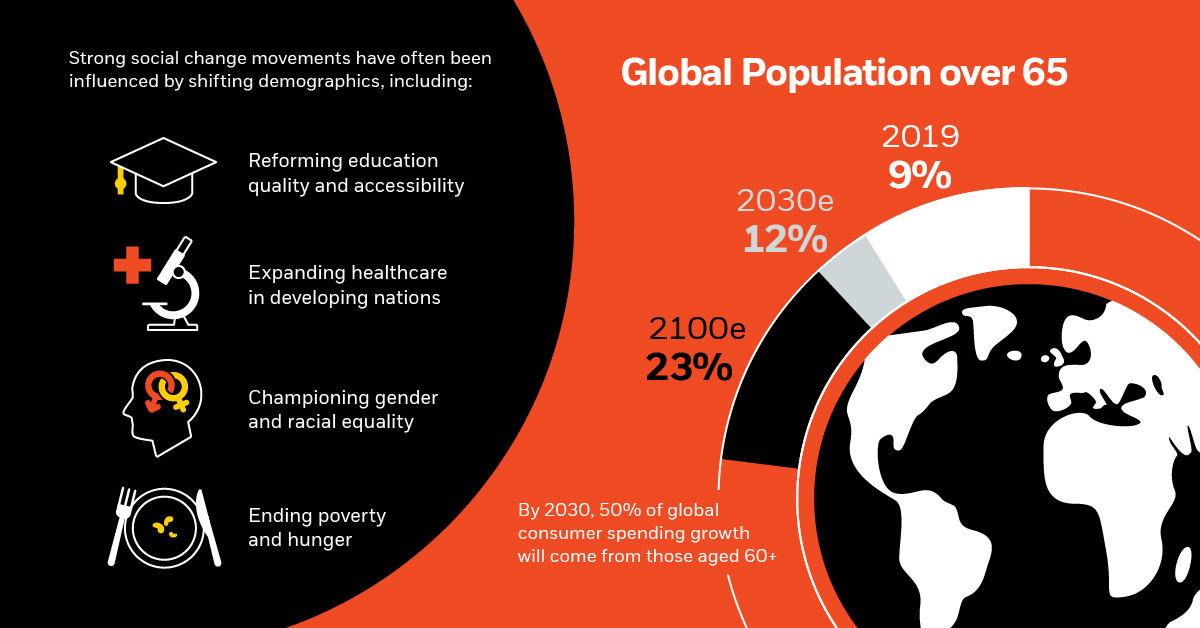
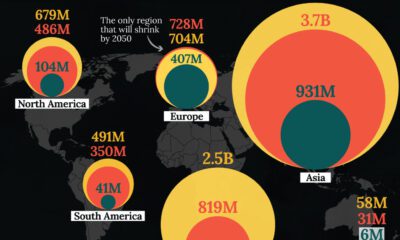
1. Aging Population
The global population is aging rapidly─as fertility rates decline worldwide, those in the 65 years and older age bracket are steadily increasing in numbers.
2. Future Workforce
As the population continues to age, fewer people are available to sustain the working population. For the first time in recorded history, the number of people in developed nations between 20 to 64 years old is expected to shrink in 2020.
3. Immigration Increase
Immigration has been steadily increasing since the turn of the 21st century. Primary migration factors range from the serious (political turmoil) to the hopeful (better job offers).
In particular, areas such as Asia and Europe see much higher movement than others, causing a strain on resources in those regions.
4. Consumer Spending
A steadily aging population is slowly shifting the purchasing power to older households. In Japan, for example, half of all current household spending comes from people over 60, compared with 13% of spending from people under 40.
How Does Social Change Play a Part?
Demographics are the characteristics of people that change over time, whereas social change is the evolution of people’s behaviours or cultural norms over time.
Strong social change movements have often been influenced by demographic changes, including:
- Ending poverty and hunger
- Expanding healthcare in developing nations
- Reforming education quality and accessibility
- Championing gender and racial equality
Examples of major human rights movements include creating stronger environmental policies and securing women’s right to vote.
Opportunities for Investors
These changes pose some exciting opportunities for investors, both now and in the near future.
Healthcare
Global healthcare spending is predicted to grow from US$7.7 trillion in 2017 to over US$10 trillion in 2022. To meet the demands of age-related illnesses, companies will need solutions that offer quality care at much lower costs—for patients and an overburdened healthcare system.
Changing Workforce
With a declining working population, adapting a workforce’s skill set may be the key to keeping economies afloat.
As automation becomes commonplace, workers will need to develop more advanced skills to stay competitive. Newer economies will need to ensure that automation supports a shrinking workforce, without restricting job and wage growth.
Education Reform
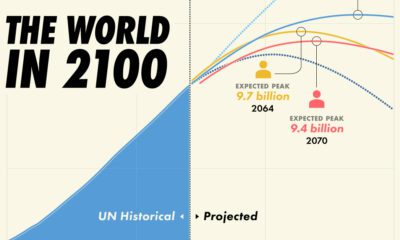
By 2100, over 50% of the world will be living in either India, China, or Africa.
Global policy leadership and sales of education goods and services will be shaped less by issues and needs in the U.S., and more by the issues and needs of Africa, South Asia, and China.
—Shannon May, CoFounder of Bridge International Academies
In the future, education and training in these growing regions will be based on skills relevant to the modern workforce and shifting global demographics.
Consumer Behaviour
Spending power will continue to migrate to older populations. Global consumer spending from those over 60 years is predicted to nearly double, from US$8 trillion in 2010 to a whopping US$15 trillion in 2020.
Investing Megatrends
Demographics and social changes are the undercurrents of many economic, cultural, and business decisions. They underpin all other megatrends and will significantly influence how the world evolves.
As demographics shift over time, we will see the priorities of economies shift as well─and these changes will continue to offer new opportunities for investors to make an impact for the future of a global society.
Demographics
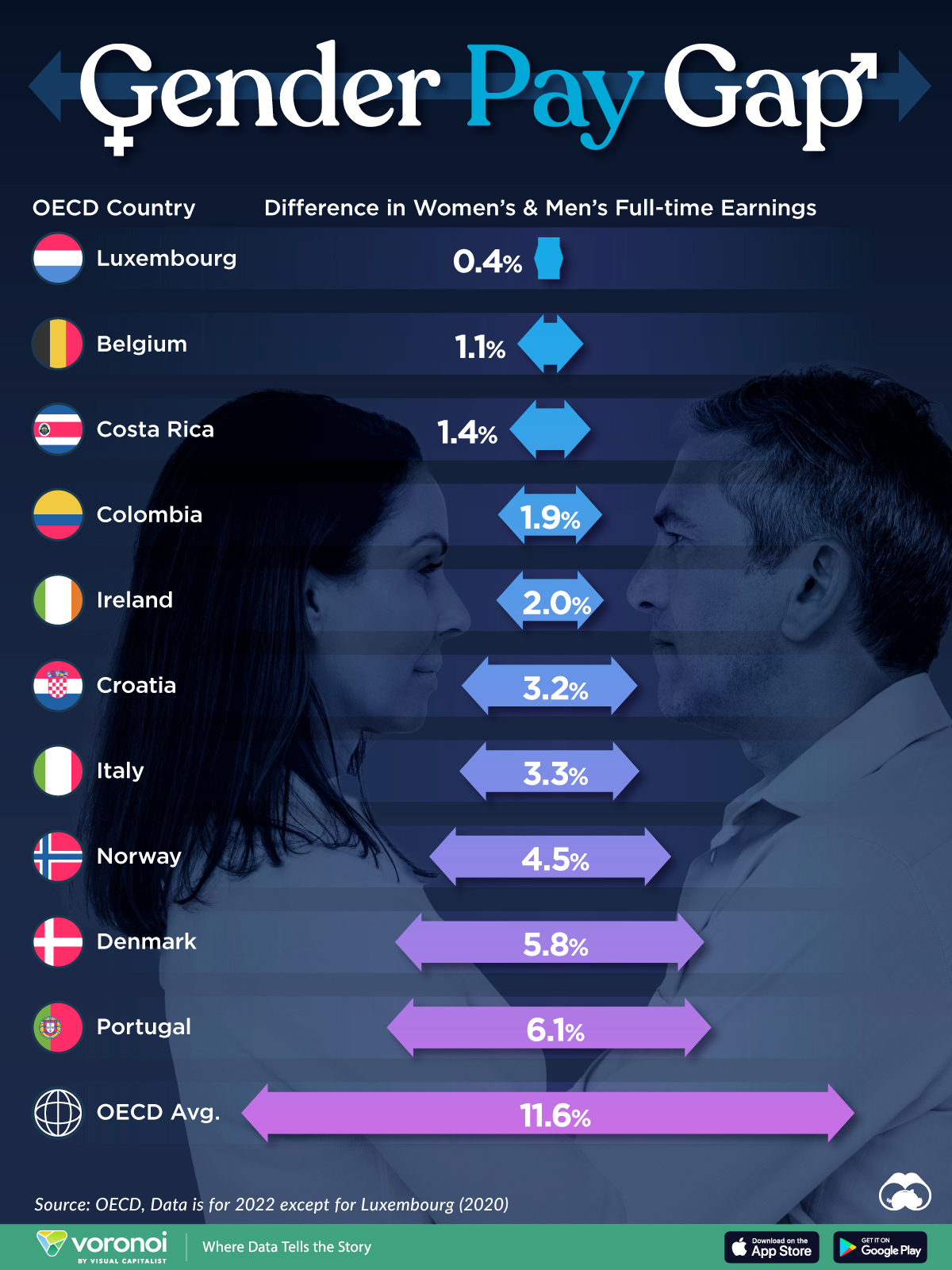
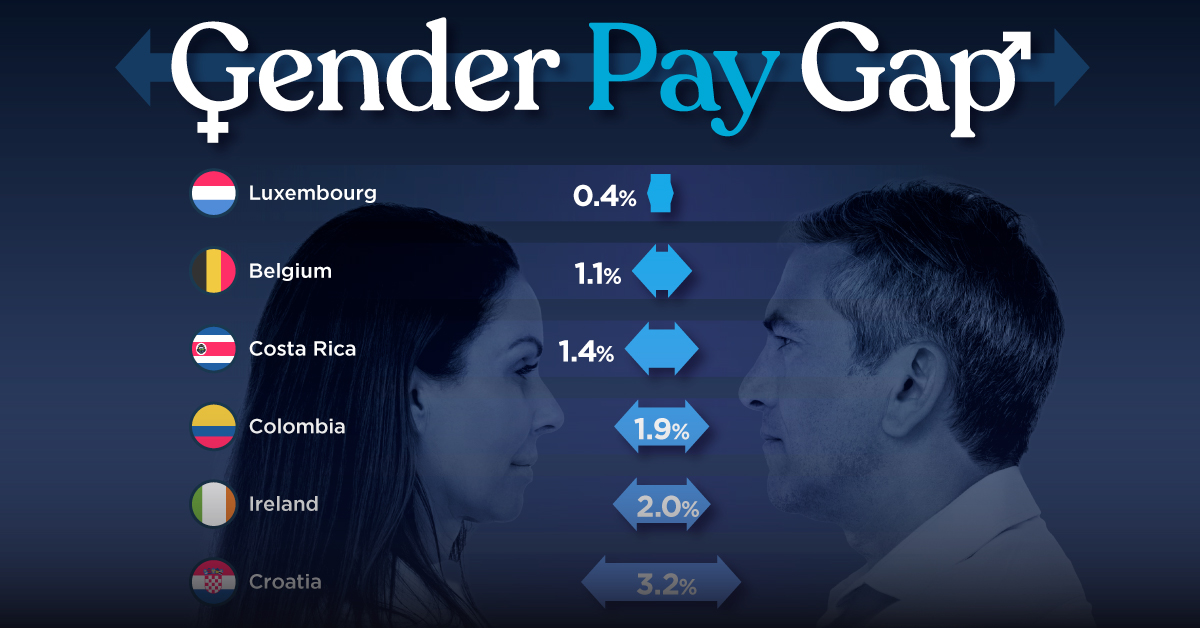
The Smallest Gender Wage Gaps in OECD Countries
Which OECD countries have the smallest gender wage gaps? We look at the 10 countries with gaps lower than the average.
The Smallest Gender Pay Gaps in OECD Countries
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on iOS or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
Among the 38 member countries in the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD), several have made significant strides in addressing income inequality between men and women.
In this graphic we’ve ranked the OECD countries with the 10 smallest gender pay gaps, using the latest data from the OECD for 2022.
The gender pay gap is calculated as the difference between median full-time earnings for men and women divided by the median full-time earnings of men.
Which Countries Have the Smallest Gender Pay Gaps?
Luxembourg’s gender pay gap is the lowest among OECD members at only 0.4%—well below the OECD average of 11.6%.
| Rank | Country | Percentage Difference in Men's & Women's Full-time Earnings |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 🇱🇺 Luxembourg | 0.4% |
| 2 | 🇧🇪 Belgium | 1.1% |
| 3 | 🇨🇷 Costa Rica | 1.4% |
| 4 | 🇨🇴 Colombia | 1.9% |
| 5 | 🇮🇪 Ireland | 2.0% |
| 6 | 🇭🇷 Croatia | 3.2% |
| 7 | 🇮🇹 Italy | 3.3% |
| 8 | 🇳🇴 Norway | 4.5% |
| 9 | 🇩🇰 Denmark | 5.8% |
| 10 | 🇵🇹 Portugal | 6.1% |
| OECD Average | 11.6% |
Notably, eight of the top 10 countries with the smallest gender pay gaps are located in Europe, as labor equality laws designed to target gender differences have begun to pay off.
The two other countries that made the list were Costa Rica (1.4%) and Colombia (1.9%), which came in third and fourth place, respectively.
How Did Luxembourg (Nearly) Eliminate its Gender Wage Gap?
Luxembourg’s virtually-non-existent gender wage gap in 2020 can be traced back to its diligent efforts to prioritize equal pay. Since 2016, firms that have not complied with the Labor Code’s equal pay laws have been subjected to penalizing fines ranging from €251 to €25,000.
Higher female education rates also contribute to the diminishing pay gap, with Luxembourg tied for first in the educational attainment rankings of the World Economic Forum’s Global Gender Gap Index Report for 2023.
See More Graphics about Demographics and Money
While these 10 countries are well below the OECD’s average gender pay gap of 11.6%, many OECD member countries including the U.S. are significantly above the average. To see the full list of the top 10 OECD countries with the largest gender pay gaps, check out this visualization.
-

 Real Estate2 weeks ago
Real Estate2 weeks agoVisualizing America’s Shortage of Affordable Homes
-

 Technology1 week ago
Technology1 week agoRanked: Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoWhich States Have the Highest Minimum Wage in America?
-

 Real Estate2 weeks ago
Real Estate2 weeks agoRanked: The Most Valuable Housing Markets in America
-

 Business2 weeks ago
Business2 weeks agoCharted: Big Four Market Share by S&P 500 Audits
-

 AI2 weeks ago
AI2 weeks agoThe Stock Performance of U.S. Chipmakers So Far in 2024
-

 Misc2 weeks ago
Misc2 weeks agoAlmost Every EV Stock is Down After Q1 2024
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoWhere Does One U.S. Tax Dollar Go?