Markets
$20 Trillion of U.S. Debt Visualized Using Stacks of $100 Bills
For most people, our experiences in everyday life are with using lower numbers like one, two, or ten. We not only comprehend what it means to buy five apples, but we can also visualize exactly what that might look like. In other words, these are numbers that fall within a range that is very intuitive for most humans.
Extrapolate that a little higher and we can still comprehend the numbers, but we start to lose that intuition.
Are there 1,500 or 2,000 people at a music venue? It’s hard to know for sure, but we do at least have a basic comprehension of the sizes of those numbers. Every day, we do math with numbers in the thousands – a paycheck, a credit card bill, or paying rent.
Millions, billions, trillions
This is where things start to get dodgy. Once numbers get beyond the millions, we don’t really have any intuition, tactile familiarity, or comprehension of what they mean.
For example:
- One million seconds = 12 days
- One billion seconds = 32 years
- One trillion seconds = 32,000 years
Going back in time a trillion seconds would place you well before written history, the building of the pyramids, and 10,000 years before the first cave wall paintings in France.
Our monkey brains don’t really know what to do with these giant abstractions, and so it helps to think about them in different ways, especially visually.
The Visual Interpretation
Looking at visual representations of these numbers will help to put them in perspective.
Below is a series of fantastic 3d graphics produced by Demonocracy.info that help to do this for the $20 trillion in U.S. Federal Government debt. It starts with a $100 bill, and goes from there. Enjoy!
1. Here is a single $100 bill.

2. Here is $10,000, or 100 of those same bills in a stack.

3. $1 million, or equal to 92 years of work for the average human on Earth.
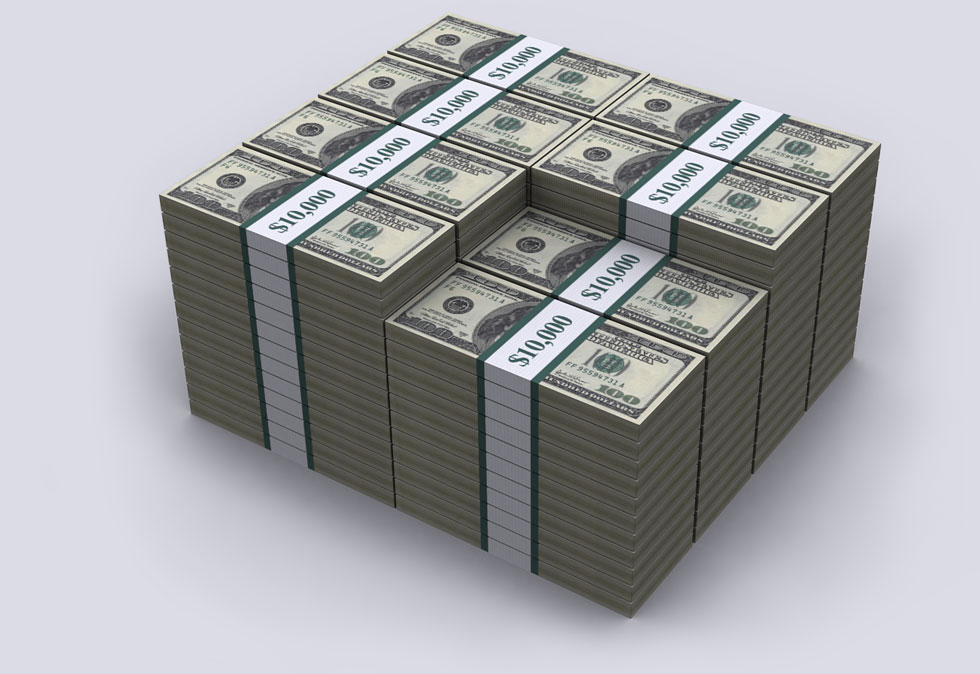

4. $100 million on a pallet. The couch is worth a cool $46.7 million, too.
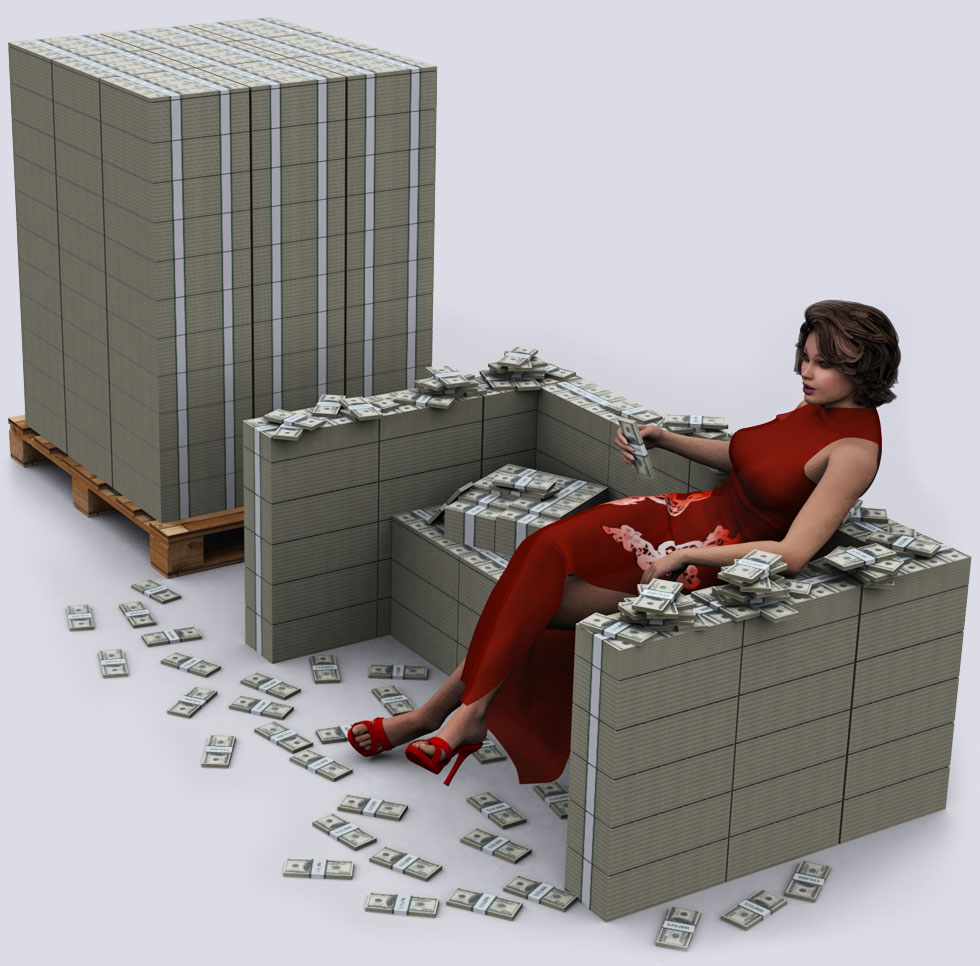

5. $1 Billion – getting bigger…
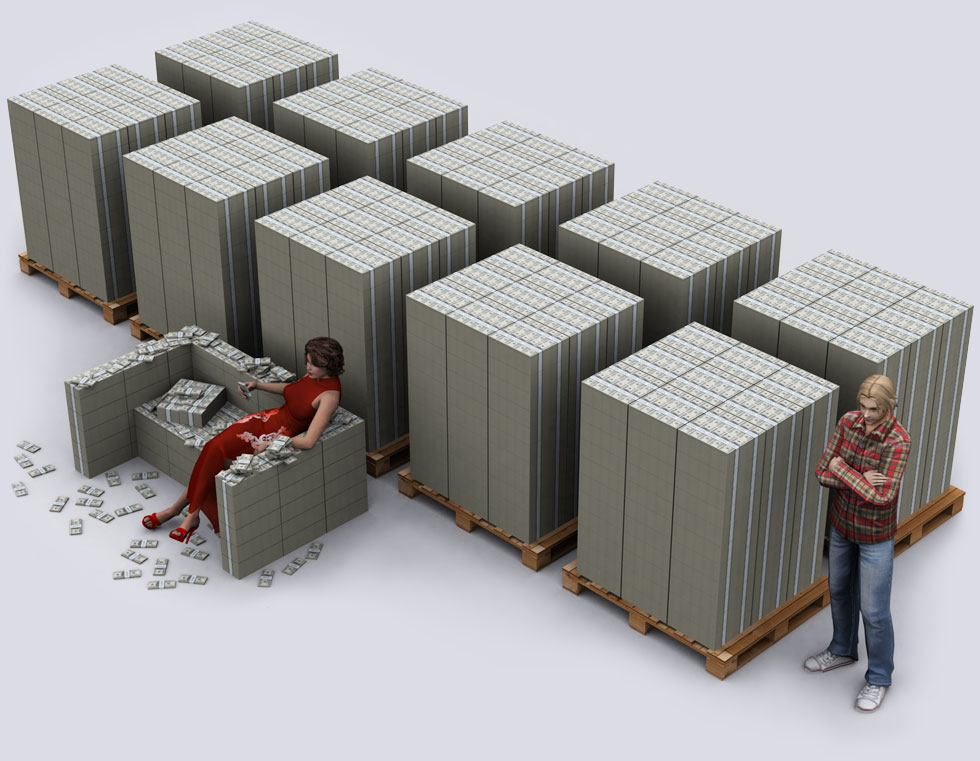

6. $1 trillion, looking at it from a front angle.

7. Here’s a better view of the $1 trillion with the White House.
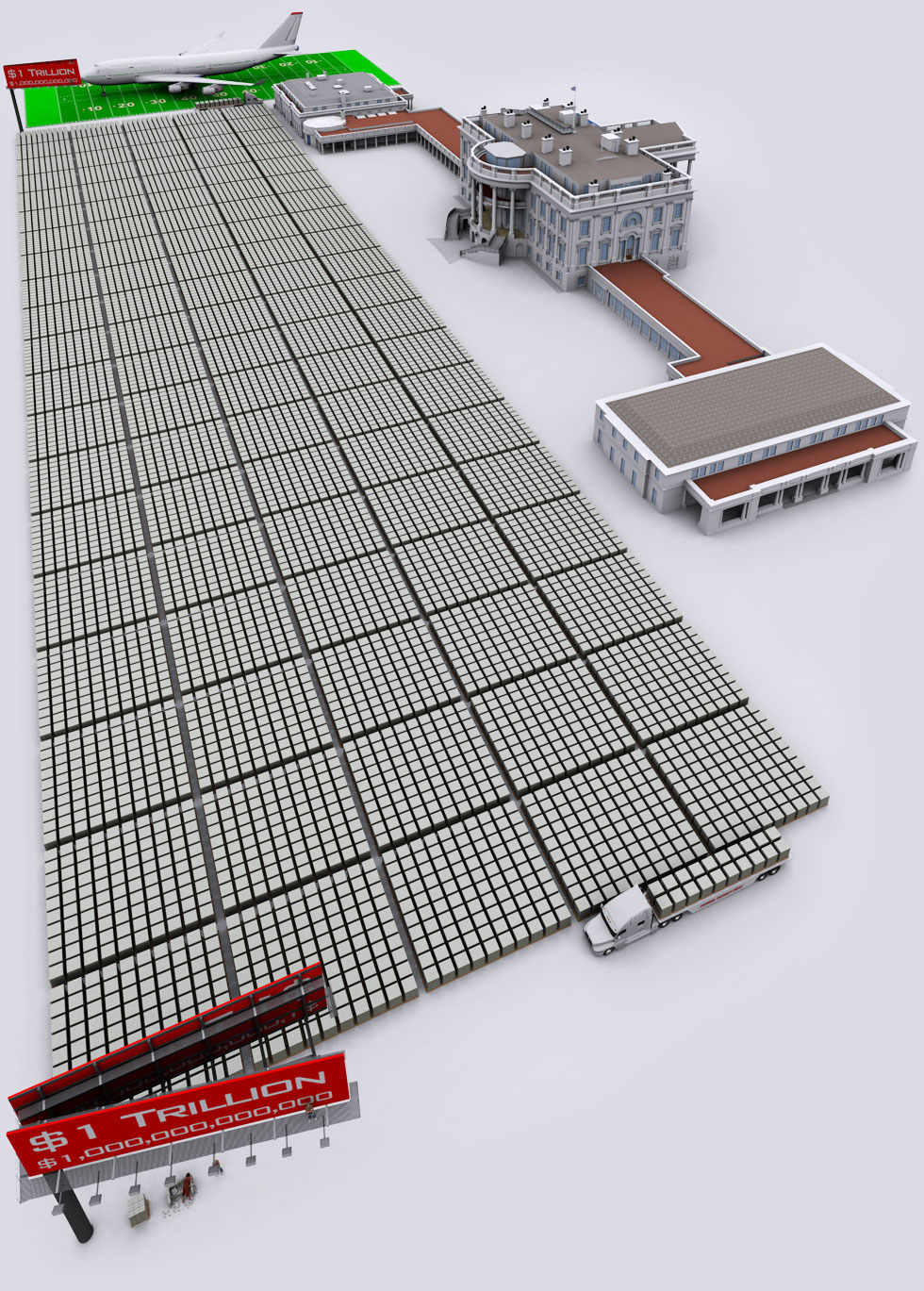
8. Finally, here’s $20+ trillion of U.S. government debt.

For more on putting the U.S. debt in perspective, here’s a video showing Trump’s $20 trillion problem, as well as visualizing the debt from a more 2d perspective.
Markets
U.S. Debt Interest Payments Reach $1 Trillion
U.S. debt interest payments have surged past the $1 trillion dollar mark, amid high interest rates and an ever-expanding debt burden.

U.S. Debt Interest Payments Reach $1 Trillion
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on iOS or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
The cost of paying for America’s national debt crossed the $1 trillion dollar mark in 2023, driven by high interest rates and a record $34 trillion mountain of debt.
Over the last decade, U.S. debt interest payments have more than doubled amid vast government spending during the pandemic crisis. As debt payments continue to soar, the Congressional Budget Office (CBO) reported that debt servicing costs surpassed defense spending for the first time ever this year.
This graphic shows the sharp rise in U.S. debt payments, based on data from the Federal Reserve.
A $1 Trillion Interest Bill, and Growing
Below, we show how U.S. debt interest payments have risen at a faster pace than at another time in modern history:
| Date | Interest Payments | U.S. National Debt |
|---|---|---|
| 2023 | $1.0T | $34.0T |
| 2022 | $830B | $31.4T |
| 2021 | $612B | $29.6T |
| 2020 | $518B | $27.7T |
| 2019 | $564B | $23.2T |
| 2018 | $571B | $22.0T |
| 2017 | $493B | $20.5T |
| 2016 | $460B | $20.0T |
| 2015 | $435B | $18.9T |
| 2014 | $442B | $18.1T |
| 2013 | $425B | $17.2T |
| 2012 | $417B | $16.4T |
| 2011 | $433B | $15.2T |
| 2010 | $400B | $14.0T |
| 2009 | $354B | $12.3T |
| 2008 | $380B | $10.7T |
| 2007 | $414B | $9.2T |
| 2006 | $387B | $8.7T |
| 2005 | $355B | $8.2T |
| 2004 | $318B | $7.6T |
| 2003 | $294B | $7.0T |
| 2002 | $298B | $6.4T |
| 2001 | $318B | $5.9T |
| 2000 | $353B | $5.7T |
| 1999 | $353B | $5.8T |
| 1998 | $360B | $5.6T |
| 1997 | $368B | $5.5T |
| 1996 | $362B | $5.3T |
| 1995 | $357B | $5.0T |
| 1994 | $334B | $4.8T |
| 1993 | $311B | $4.5T |
| 1992 | $306B | $4.2T |
| 1991 | $308B | $3.8T |
| 1990 | $298B | $3.4T |
| 1989 | $275B | $3.0T |
| 1988 | $254B | $2.7T |
| 1987 | $240B | $2.4T |
| 1986 | $225B | $2.2T |
| 1985 | $219B | $1.9T |
| 1984 | $205B | $1.7T |
| 1983 | $176B | $1.4T |
| 1982 | $157B | $1.2T |
| 1981 | $142B | $1.0T |
| 1980 | $113B | $930.2B |
| 1979 | $96B | $845.1B |
| 1978 | $84B | $789.2B |
| 1977 | $69B | $718.9B |
| 1976 | $61B | $653.5B |
| 1975 | $55B | $576.6B |
| 1974 | $50B | $492.7B |
| 1973 | $45B | $469.1B |
| 1972 | $39B | $448.5B |
| 1971 | $36B | $424.1B |
| 1970 | $35B | $389.2B |
| 1969 | $30B | $368.2B |
| 1968 | $25B | $358.0B |
| 1967 | $23B | $344.7B |
| 1966 | $21B | $329.3B |
Interest payments represent seasonally adjusted annual rate at the end of Q4.
At current rates, the U.S. national debt is growing by a remarkable $1 trillion about every 100 days, equal to roughly $3.6 trillion per year.
As the national debt has ballooned, debt payments even exceeded Medicaid outlays in 2023—one of the government’s largest expenditures. On average, the U.S. spent more than $2 billion per day on interest costs last year. Going further, the U.S. government is projected to spend a historic $12.4 trillion on interest payments over the next decade, averaging about $37,100 per American.
Exacerbating matters is that the U.S. is running a steep deficit, which stood at $1.1 trillion for the first six months of fiscal 2024. This has accelerated due to the 43% increase in debt servicing costs along with a $31 billion dollar increase in defense spending from a year earlier. Additionally, a $30 billion increase in funding for the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation in light of the regional banking crisis last year was a major contributor to the deficit increase.
Overall, the CBO forecasts that roughly 75% of the federal deficit’s increase will be due to interest costs by 2034.
-

 Real Estate2 weeks ago
Real Estate2 weeks agoVisualizing America’s Shortage of Affordable Homes
-

 Technology1 week ago
Technology1 week agoRanked: Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share
-

 Money1 week ago
Money1 week agoWhich States Have the Highest Minimum Wage in America?
-

 Real Estate1 week ago
Real Estate1 week agoRanked: The Most Valuable Housing Markets in America
-

 Business1 week ago
Business1 week agoCharted: Big Four Market Share by S&P 500 Audits
-

 AI2 weeks ago
AI2 weeks agoThe Stock Performance of U.S. Chipmakers So Far in 2024
-

 Misc2 weeks ago
Misc2 weeks agoAlmost Every EV Stock is Down After Q1 2024
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoWhere Does One U.S. Tax Dollar Go?















